Network Cabling - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title:
Network Cabling
Description:
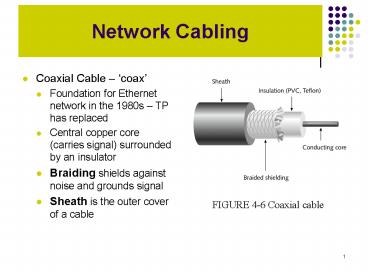
Network Cabling Coaxial Cable coax Foundation for Ethernet network in the 1980s TP has replaced Central copper core (carries signal) surrounded by an ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:374
Avg rating:5.0/5.0
Title: Network Cabling
1
Network Cabling
- Coaxial Cable coax
- Foundation for Ethernet network in the 1980s TP
has replaced - Central copper core (carries signal) surrounded
by an insulator - Braiding shields against noise and grounds signal
- Sheath is the outer cover of a cable
FIGURE 4-6 Coaxial cable
2
Network Cabling
- Coaxial Cable continued
- Has high resistance to interference from noise
- Can carry signal farther than TP before
amplification is needed, but not as good as fiber - More expensive than TP
- Generally supports a lower throughput
- Also requires that each end of its segments be
terminated with a resistor
3
Network Cabling
TABLE 4-1 Types of coaxial cable
4
Network Cabling
- Thicknet (10Base5)
- Thicknet
- Also called thickwire Ethernet
- Rigid coaxial cable used for original Ethernet
networks - IEEE designates Thicknet as 10Base5 Ethernet
- 10 10Mbps baseband max segment length 500
meters (1640 feet) - Rarely used on modern networks
- Difficult to manage
- Rigid
- 10 Mbps throughput restriction
5
Network Cabling
- Thicknet (10Base5)
- Throughput
- 10Mbps
- Cost
- gt thin, lt fiber
- Connector
- Noise immunity
- High resistance
- Size and scalability
- Max 100 nodes per segment
FIGURE 4-7 Thicknet cable transceiver with detail
of a vampire tap piercing the core
6
Network Cabling
- Thinnet (10Base2)
- Also known as thin Ethernet, was most popular
medium for Ethernet LANs in the 1980s - 10Mbps, baseband, 200 m
- Rarely used on modern networks
- Replaced by TP
- More flexible than thicknet
7
Network Cabling
- Thinnet (10Base2)
- Throughput-10Mbps
- Cost - lt thick / fiber, gt TP
- Size and scalability max 30 nodes per segment
- Connector BNC (British Naval Connector)
barrel/T - Noise Immunity better than TP, but not as good
as thicknet
FIGURE 4-8 Thinnet BNC connectors
8
Network Cabling
- BUS topology
- Small lans
- Doesnt scale well
- Not fault tolerant
- Hard to troubleshoot
- Signal Bounce
- Caused by improper termination
- Travels endlessly
FIGURE 4-9 Typical coaxial network using a bus
topology
9
Network Cabling
- Twisted-Pair (TP) Cable like telephone wiring
- Consists of color-coded pairs of insulated copper
wires twisted around each other and encased in
plastic coating - One wire in the pair carries the signal
information while the other is grounded and
absorbs interference - Twists help reduce effects of crosstalk,
interference caused by signals traveling on
nearby wire pairs infringing on another pairs
signals - Alien Crosstalk occurs when signals from adjacent
cables interfere with another cables
transmission - Occurs when cables are packed together in a
conduit
10
Network Cabling
- Twist Ratio
- Number of twists per meter or foot in a
twisted-pair cable - The more twists per inch, the more resistant the
pair will be to forms of noise
FIGURE 4-10 Twisted-pair cable
11
Network Cabling
- Differences in TP
- Twist ratio
- of wire pairs (1-4200)
- Grade of copper used
- Type of shielding and material used
- Early vs. modern networks
- Early had 2 wire pairs one to send and one to
receive - Modern have 4 pairs with gt 1 pair for both
sending and transmitting data simultaneously - Most common form of cabling used in todays
networks
12
Network Cabling
- Shielded Twisted-Pair (STP)
- Consists of twisted wire pairs that are not only
individually insulated, but also surrounded by a
shielding made of metallic substance (foil)
between pairs and jacket (sheath)
FIGURE 4-11 STP cable
13
Network Cabling
- Unshielded Twisted-Pair
- Consists of one or more insulated wire pairs
encased in a plastic sheath - Does not contain additional shielding
- Less expensive
- Less resistance to noise
FIGURE 4-12 UTP cable
14
Network Cabling
- Characteristics of TP
- 10BaseT 10Mbps, baseband, TP (IEEE)
- Relatively inexpensive
- Easy to install
- Can span a significant distance before needing a
repeater - Not as good as coax
- Most often implemented in a STAR configuration
- Can handle faster throughput (as compared to
coax) - More prone to physical damage than coax
15
Network Cabling
- TIA (Telecomm. Industry Assoc.) and EIA
(Electronic Industry Assoc.) finalized
specifications for TP into a standard dividing TP
into categories (CAT3, CAT5, etc.)
Figure 4-13 CAT5 UTP cable
16
Network Cabling
- Categories of TP wiring
17
Network Cabling
- STP and UTP
- Throughput
- 20Kbps 1Gbps (or more)
- Cost varies
- Features, STP
- Connector - RJ-45
- Noise immunity
- STP better
- Size and scalability
- Max segment length is 100m (328)
FIGURE 4-14 RJ-45 connector, used by both STP and
UTP