Matter - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 31
Title:
Matter
Description:
Chemistry I: Chapter 2 What is Chemistry? Textbook Definition: The science of matter and the changes it undergoes. Dictionary Definition: The science of the ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:109
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Matter
1
Matter
Chemistry I Chapter 2
2
What is Chemistry?
- Textbook Definition The science of matter and
the changes it undergoes. - Dictionary Definition The science of the
composition, structure, properties, and reactions
of matter, especially of atomic and molecular
systems.
3
Chemistry
- The central science Why?
- Because most of the phenomena that occur in the
world involve chemical changes
4
What is Matter?
- the material of the universe
- has mass and volume
- mass the amount of matter in an object
- volume the amount of space an object takes up
5
The Nature of Matter
Gold
Mercury
- Chemists are interested in the nature of matter
and how this is related to its atoms and
molecules.
6
Chemistry Matter
- We can explore the MACROSCOPIC world what we
can see - to understand the PARTICULATE (MICROSCOPIC)
worlds we cannot see. - We write SYMBOLS to describe these worlds.
7
A Chemists View of Water
Macroscopic
H2O (gas, liquid, solid)
Symbolic
Particulate
8
A Chemists View
Macroscopic
2 H2(g) O2 (g) --gt 2 H2O(g)
Particulate
Symbolic
9
The Macroscopic View
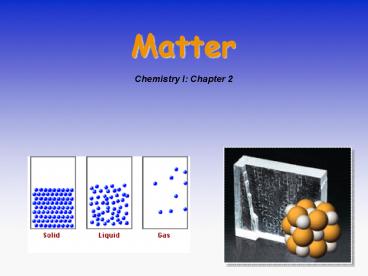
- The states of matter
- Solids
- Liquids
- Gases
- Plasma
10
Kinetic Nature of Matter
- Matter consists of atoms and molecules in
constant random motion.
11
STATES OF MATTER
- Solids have rigid shape, fixed volume. External
shape can reflect the atomic and molecular
arrangement. - Reasonably well understood.
- Liquids have no fixed shape and may not fill a
container completely. - Not well understood.
- Gases expand to fill their container.
- Good theoretical understanding.
12
OTHER STATES OF MATTER
- PLASMA an electrically charged gas Example
the sun or any other star
13
Gas Liquid Solid
low density high density high density
fills container completely does not expand to fill container - has definite volume rigidly retains its volume
assumes shape of container assumes shape of container retains own shape
14
The Particulate Nature of Matter
- All matter is made up of atoms
- Elements consist of atoms of the same type
- H, He, Cs, Ru, Fe, O
- Compounds are formed when atoms chemically bond
to one another in a specific way - CO, H2O, NaBr, C6H12O6
15
Properties of Matter
- Physical vs. Chemical Properties
- physical property - characteristic of a substance
that can be observed without changing the
substances identity - chemical property - characteristic of a substance
that can only be observed if the identity of the
substance is changed
16
Physical Properties
- What are some physical properties?
- color
- melting and boiling point
- odor
17
ChemicalProperties
- What are some chemical properties?
- Flammability
- Reactivity with water
- If it tarnishes
18
Physical vs. Chemical Properties
- physical
- chemical
- physical
- physical
- chemical
- Examples
- melting point
- flammable
- density
- magnetic
- tarnishes in air
19
Changes of Matter
- Physical vs. Chemical Changes
- physical change - change in one or more physical
properties, but does not affect the composition
of a substance - chemical change - change in the composition of a
substance, in which a substance becomes a new
substance (aka, a chemical reaction)
20
Physical Changes
- Some physical changes would be
- boiling of a liquid
- melting of a solid
- dissolving a solid in a liquid to give a
homogeneous mixture a SOLUTION.
21
Chemical Changes
- Some chemical changes would be
- Hydrogen and oxygen combining to form water
- Silver tarnishing
- Baking a cake
- Any chemical reaction!
22
Chemical Changes
- Burning hydrogen (H2) in oxygen (O2) gives H2O.
23
Sure Signs of a Chemical Change
- Heat
- Light
- Gas Produced (not from boiling!)
- Precipitate a solid formed by mixing two
liquids together
http//jchemed.chem.wisc.edu/JCESoft/CCA/CCA0/MOVI
ES/S1047.MOV
24
Physical vs. Chemical Changes
- Examples
- rusting iron
- dissolving in water
- burning a log
- melting ice
- grinding spices
- chemical
- physical
- chemical
- physical
- physical
25
Classifying Matter
- pure substances (elements and compounds) always
have the same composition - mixtures (heterogeneous and homogeneous)
composition varies made up of 2 or more pure
substances
26
How do you know what type of matter it is?
- Pure substances
- elements cannot be broken down into anything
smaller than the representative atoms - compounds can be chemically separated
(decomposed), using chemical reactions
27
How do you know what type of matter it is?
- Mixtures can be separated physically
- homogeneous same throughout no visibly
different parts uniform a solution - heterogeneous contains regions with different
properties visibly different areas doesnt mix
(not uniform)
28
Types of Mixtures
- Variable combination of 2 or more pure substances.
Heterogeneous visibly separate parts
Homogeneous Same throughout
29
Mixture Separation Techniques
- filtration - separation of solid from a liquid
using filter paper - only one for heterogeneous mixtures
- parts already have to be in different states for
filtration to work - distillation - depends on different boiling
points of the substances in a solution
30
Mixture Separation Techniques
- chromatography - separates parts of a solution
using their different levels of attraction for a
stationary substance - crystallization - boils off liquid to leave
crystallized (solidified) substance that had been
dissolved in the liquid
31
Matter Flowchart
yes
no
Can it be physically separated?
32
Matter Flowchart
yes
no
Can it be physically separated?