Coagulation - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 35
Title:
Coagulation
Description:
... of Air Pollution, Seinfeld, J. H., John Wiley & Sons, 1986 ... Phillips, W. F., Phys. Fluids, 18, 1975, p1089-1093. Q: How about the transition regime? ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:204
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Coagulation
1
Coagulation
Reading Chap 12
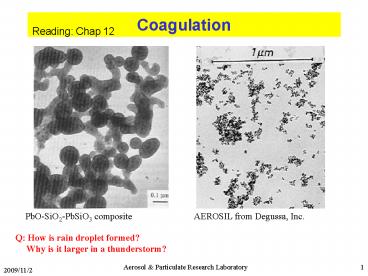
PbO-SiO2-PbSiO3 composite
AEROSIL from Degussa, Inc.
Q How is rain droplet formed? Why is it
larger in a thunderstorm?
2
- Definition The process whereby aerosol particles
collide with one another due to a relative motion
between them and adhere to from larger particles - Thermal Coagulation due to Brownian motion
- Kinematic Coagulation due to external forces
Q What are the possible external forces?
Q Any difference if solid or liquid particles
coagulate?
Agglomeration/Aggregation (if particles do not
merge) Coalescence (sintering)
Q Do solid particles stay agglomerated?
Q What are the effects of coagulation on aerosol?
3
Collision Frequency Function(Population Balance)
Collision Frequency
ni number concentration of size i particle
Q What factors affect the frequency?
- Rate of formation of size k particle
Rate of removal of size k particle
Net rate of size k particle
4
Continuous Distribution Function
Collision rate
Formation in range du
Loss in range du
Net rate of formation of particles of size u
5
Brownian Coagulation
Ref Chap 10 in Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics
of Air Pollution, Seinfeld, J. H., John Wiley
Sons, 1986
Ficks second law of diffusion (for spherical
coordinate)
Initial conditions?
Boundary conditions?
Solution
erf(x) erfc(x) 1
6
The rate (/s) at which particles arrive at the
surface (dpidpj)/2
Steady state solution
Diffusion coefficient for the relative motion
? Collision frequency function
7
Continuum regime
b1,2
Free molecular regime
dp1
Q Any trend? Whats the physics behind it?
8
Q How about the transition regime?
9
Limiting Conditions
Pratsinis, J. Colloid Int. Sci., 124(2), 416-,
1988.
Equal sizes
Very Different Sizes
Continuum Regime
Continuum Regime
Free Molecular Regime
Free Molecular Regime
10
Nearly Monodisperse System
- Collision frequency function
Coagulation equation
Q What is the 1st term? 2nd term?
Summing over all values of k
Integrating once
Q Initial condition?
11
Q Estimate the time for a mono-disperse aerosol
of 0.8 mm to fall to 10 of its original value if
the initial concentration is 108 /cm3. T 20
oC. How about for 3 mm?
Q How do you know if coagulation is the main
mechanism in your experimental system?
12
Q How does N change wrt time? n1? n2?
For k1
Coagulation Characteristic Time
General form
Q How long does it take for N 1012 /cc to
reduce to its half conc.? N 106?
Q How to slow down coagulation?
13
Q How do we estimate the importance of
coagulation compared to other mechanisms in the
system ?
Q If I have the final concentration and particle
size, can I determine the original PSD if
coagulation is the major mechanism?
14
Coagulation of a Log-Normally Distributed Aerosol
Log-normal size distribution function
kth moment of a log-normal size distribution
Net rate of formation by coagulation
15
(Free Molecular regime)
Relax the difficult form of b
Lee et al., (1984), J. Aerosol Sci., 3, 53-62.
16
Properties of log-normal function
(a)
(b)
17
Q How does N change wrt time? Q Whats the
impact of s0 on N?
Q How does sg change wrt time?
18
Mean value of coagulation coefficient for a
log-normally distributed aerosol
19
Asymptotic Behavior
- The size distribution of a coagulating aerosol
approaches a log-normal function with a FIXED ?g
Combining Eqs. (a) and (b)
After a long time,
Replacing Mk
Q What does it mean if sg 2? What about
sg 1?
20
Similarity Solution/Self-Preserving PSD
Ref Friedlander, Smoke, Dust and Haze, Oxford,
2000.
- Asymptotic forms can be reached after a long time
and are independent of the initial size
distribution - Assumption the fraction of the particles in a
given size range is a function only of particle
volume normalized by the averaged particle volume
(mean particle volume)
(dimensionless particle volume)
21
Similarity Solution (Continuum Regime)
Continuous distribution function
Similarity form
Change in the total number concentration with time
22
The result
Q Is the distribution time dependent?
a 0.9046 b 1.248
23
(No Transcript)
24
Comparison with Experimental Results
25
Similarity Solution (Free Molecular Regime)
a 6.67
26
Comparison of the asymptotic PSD
Q Does a log-normally distributed aerosol reach
self-preserving?
27
Collision in a Uniform, Laminar Shear Flow
- Particle in a uniform, laminar shear flow collide
because of their relative motion
Flow of particles into the shaded portion
28
Equation of coagulation by laminar shear
For nearly mono-disperse aerosols
Q How does it compare to Brownian
coagulation?
29
Summary
30
(No Transcript)
31
(No Transcript)
32
Integrate Eq.(1) by d? from 0 to 8
Assign
33
Equate (3) and (5)
34
Substitute Eq.(6) into Eq.(1)
Substitute Eq.(6) into Eq.(2)
35
Equate (7) and (8)