Chapter 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions 2.1 Quadratic Functions - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title:
Chapter 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions 2.1 Quadratic Functions
Description:
Chapter 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions 2.1 Quadratic Functions Definition of a polynomial function Let n be a nonnegative integer so n={0,1,2,3 } – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:122
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Chapter 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions 2.1 Quadratic Functions
1
Chapter 2 Polynomial and Rational Functions 2.1
Quadratic Functions
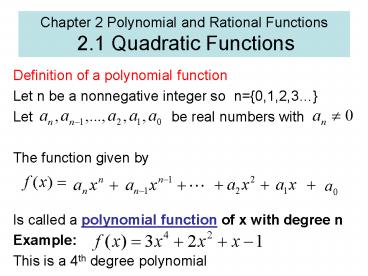
- Definition of a polynomial function
- Let n be a nonnegative integer so n0,1,2,3
- Let be real
numbers with - The function given by
- Is called a polynomial function of x with degree
n - Example
- This is a 4th degree polynomial
2
Polynomial Functions are classified by degree
- For example
- In Chapter 1
- Polynomial function
- , with
- Example
- This function has
- degree 0, is a
- horizontal line and is called
- a constant function.
3
Polynomial Functions are classified by degree
- In Chapter 1
- A Polynomial function
- ,
- is a line whose slope is m
- and y-intercept is (0,b)
- Example
- This function has a degree
- of 1,and is called a
- linear function.
4
Section 2.1 Quadratic Functions
- Definition of a quadratic function
- Let a, b, and c be real numbers with .
- The function given by f(x)
- Is called a quadratic function
- This is a special U shaped curve called a ?
5
Parabola !
- Parabolas are symmetric to a line called the axis
of symmetry. - The point where the axis intersects with the
parabola is the vertex.
6
The simplest type of quadratic is
- When sketching
- Use as a reference.
- (This is the simplest type of graph)
- agt1 the graph of yaf(x)
- is a vertical stretch of the
- graph yf(x)
- 0ltalt1 the graph of yaf(x)
- is a vertical shrink of the graph yf(x)
- Graph on your calculator
- , ,
7
Standard Form of a quadratic Function
The graph of f(x) is a parabola whose axis is the
vertical line xh and whose vertex is the point (
, ). -shifts the graph right or
left -shifts the graph up or
down For agt0 the parabola opens up alt0 the
parabola opens down
NOTE!
8
Example of a Quadratic in Standard Form
- Graph
- Where is the Vertex? ( , )
- Graph
- Where is the Vertex? ( , )
9
Identifying the vertex of a quadratic function
- One way to find the vertex is to put the
quadratic function in standard form by completing
the square. - Where is the vertex? ( , )
10
Identifying the vertex of a quadratic function
- Another way to find the vertex is to use
- the Vertex Formula
- If agt0, f has a minimum x
- If alt0, f has a maximum x
- a b c
- NOTE
the vertex is ( , ) - To use Vertex Formula-
- To use completing the square start
- with to get
11
Identifying the vertex of a quadratic
function(Example)
- Find the vertex of the parabola ( , )
- The direction the parabola opens?________
- By completing the square? By the Vertex Formula
12
Identifying the x-Intercepts of a quadratic
function
- The x-intercepts are found as follows
13
Identifying the x-Intercepts of a quadratic
function (continued)
- Standard form is
- Shape_______________
- Opens up or down?_____
- X-intercepts are
14
Identifying the x-Intercepts of a Quadratic
Function (Practice)
- Find the x-intercepts of
15
Writing the equation of a Parabola in Standard
Form
- Vertex is
- The parabola passes through point
- Remember the vertex is
- Because the parabola passed through we
have
16
Writing the equation of a Parabola in Standard
Form (Practice)
- Vertex is
- The parabola passes through point
- Find the Standard Form of the equation.
17
Homeworkp.95-96 1-8 all, 9-33x3
- p. 96 36-60x3