Land surface memory - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Land surface memory
Description:
Improve weather & climate prediction with more accurate land initial conditions. Improve land surface model via data validation& model intercomparisons ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:89
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Land surface memory
1
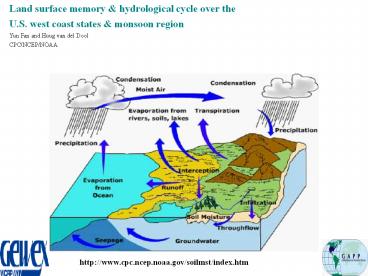
Land surface memory hydrological cycle over
the U.S. west coast states monsoon region Yun
Fan and Huug van del Dool CPC/NCEP/NOAA
http//www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/soilmst/index.htm
2
Outline
- Motivation
- Noah Land Surface Model Data
- Results
- Land surface hydrological cycle
- Land memory studies
- Summary
3
- Motivation
- Improve soil moisture data for CPCs drought
flood monitoring tools - Improve weather climate prediction with more
accurate land initial conditions - Improve land surface model via data validation
model intercomparisons - Provide a long time series of realistic land
surface data for land surface hydrological cycle,
land memory predictablity studies - Coupled atmosphere-land-ocean modeling
- Develop new tools to use land surface data for
climate monitoring prediction
4
Motivation Background
CPC Leaky Bucket Model (Huang et al 1996)
Where W(t) is soil water
content, P(t) precipitation, E(t)
evaportranspiration,
R(t) net streamflow divergence,
G(t) net groundwater loss. The balance
of the above equation is defined as
the budget (should equal dw/dt). Forcing Data
-CPC daily temperature updates
-CPC daily precipitation
updates (Higgins Shi)
-Monthly precipitation and temperature
from NCDC Data Coverage -73 years
(1931-yesterday) on 344 US climate divisions
- Current CPC soil moisture monitor climate
prediction activities - Drought flood monitoring
- Empirical forecast tools (Constructed Analog)
- GFS forecast climate prediction
5
Motivation Background (cont)
6
Motivation Background (cont)
http//www.cpc.ncep.noaa.gov/soilmst/index.htm
7
Noah Land Surface Model
Noah LSM Characteristics
- Flexible soil layers
- user specified number and thickness (2-N).
- Default is four soil layers (10, 30, 60, 100 cm
thick) - Soil hydraulics and parameters follow Cosby et
al. - Canopy resistance follows Jarvis et al.
- Satellite-based annual cycle of vegetation
greenness globally - 5-year monthly climatology (NESDIS AVHRR
- NDVI-based)
- Flexible vegetation and soil classes and their
parameters - easily modified via namelist I/O. Default 12
SiB veg classes and 9 - Zobler soil classes (i.e. ISLCP-I)
- Freeze/thaw soil physics follows Koren et al.
- Snowpack density and water-equivalent content
modeled - Patchy/fractional snow cover treated as function
of snowdepth veg type - Plug-compatible drop-in coding structure
- link via one subroutine call and one argument
list no common blocks
8
(No Transcript)
9
(No Transcript)
10
Data validation
11
Data validation
12
Land Surface Water Budget Soil Moisture
Evolution
P(t) - E(t) - R(t) G(t)
13
Land Surface Water Budget Over Coterminous USA
P(t) - E(t) - R(t) G(t)
14
Table.1 US monthly values of all components of
land surface hydrology (mm/mon)
Mon W P
E RG P-E-R-G 1 581.2
(294.2) 52.0 5.5 31.8
14.6 2 592.5 (304.0) 49.8
10.3 33.3 6.2 3
600.0 (308.8) 62.9 24.5
39.1 -0.7 4 595.6 (302.0)
59.4 42.8 30.2 -13.7
5 582.8 (289.8) 70.9 64.8
21.2 -15.1 6 564.6
(276.8) 66.2 75.7 14.2
-23.8 7 538.4 (260.1)
64.8 77.8 10.4 -23.5
8 520.1 (250.0) 62.2 67.6
9.0 -14.3 9 514.3
(248.3) 61.4 49.3 8.8
3.3 10 520.2 (253.3) 51.7
31.9 9.1 10.8 11
539.8 (266.8) 58.0 14.0
13.5 30.5 12 565.8 (282.6)
58.5 4.5 27.3 26.8
Year 559.0 (278.1) 59.8
39.1 20.7 0.0 averaged over
125W-75W, 30N-48N
15
Land Surface Water Budget Over western coast
states
P(t) - E(t) - R(t) G(t)
16
Table.2 US west coast states monthly values of
all components of land surface hydrology (mm/mon)
Mon W P
E RG
P-E-R-G 1 595.1 (305.7)
99.0 -1.4 60.1
39.7 2 622.4 (324.4)
79.6 1.3 63.7
15.2 3 636.2 (330.5)
74.5 15.9 70.3
-10.4 4 624.9 (317.4)
47.1 33.3 44.7
-31.6 5 595.2 (293.5)
36.1 53.4 21.5
-39.6 6 554.7 (266.0)
26.3 63.1 8.5
-45.6 7 504.6 (233.1)
13.5 61.9 2.5
-51.0 8 463.4 (207.4)
18.6 43.8 1.3
-26.5 9 450.0 (201.4)
26.3 26.6 1.4
-1.5 10 460.2 (211.8)
44.7 14.6 3.9
25.7 11 507.0 (247.2)
93.3 3.7 19.4
72.3 12 563.8 (284.5)
97.2 -3.0 46.6
53.5 Year 548.1 (268.6)
54.7 26.1 28.7
-0.1 averaged over 125W-115W,
32N-49N
17
Land Surface Water Budget Over US Monsoon Region
P(t) - E(t) - R(t) G(t)
18
Table.3 US monsoon region monthly values of all
components of land surface hydrology (mm/mon)
Mon W P
E RG P-E-R-G 1
407.6 (206.5) 19.7
11.1 1.1 7.6 2
414.3 (212.0) 18.6
13.9 1.6 3.2 3
415.1 (211.1) 20.8
21.7 2.1 -3.0 4
404.7 (199.7) 12.2
25.7 1.2 -14.6 5
389.6 (185.3) 15.3
29.6 0.8 -15.2 6
375.9 (172.8) 17.8
28.7 0.7 -11.5 7
372.9 (171.0) 49.3
40.8 1.6 6.9 8
380.8 (179.5) 55.4
47.4 2.0 6.0 9
383.3 (182.0) 38.3
35.1 1.4 1.910
384.6 (183.0) 24.7 22.5
0.8 1.311 388.3
(186.5) 19.5 12.8
0.7 6.012 397.7 (195.6)
24.2 9.4 0.9
13.9 Year 392.9 (190.4)
26.3 24.9 1.2
0.2 averaged over 115W-103W, 31N-37N
19
Standard Deviation of Land Surface Water Budget
components Soil Moisture from 1960-1998
20
Land Surface Memory for the Coterminous USA
21
Land Surface Memory for US
22
Land Surface Memory for West Coast States
23
Land Surface Memory for US Monsoon Region
24
Soil moisture correlation the west coast states
vs all US areas
25
Soil moisture correlation the US monsoon region
vs all US areas
26
Evaporation correlation the US monsoon region vs
all US areas
27
Soil moisture lag precip surface temperature
correlation the west coast states vs all US areas
28
Soil moisture lag precip surface temperature
correlation the US monsoon region vs all US areas
29
Summary
- In general, on a continental scale, the maximum
of soil moisture (W) is in winter and the minimum
is in summer, with some regional exceptions. - For the precipitation (P), the west coast states
have a strong seasonal cycle, with maximum in
winter and minimum in summer. In US monsoon
region P Florida it peaks in summer, while in
some area precipitation does not vary too much
over the course of the annual cycle. - Evaporation (E) shows a pronounced seasonal
cycle maximum in warm season and minimum in cold
season, while the runoff (surface
runoffsubsurface runoff) (R) is opposite, with
maximum in cold season and minimum in warm season
(exception mountain areas wait till spring
melt). - Land surface hydrological cycle most part of the
states - land surface water is recharged during
the cold season and discharged during the warm
season, with some exceptions the northern part
states, snow melt plays an important role for
land surface water recharge in the spring. In the
US monsoon area discharged in the spring
recharges in the summer. - Evolution of land surface memory depends on time
space. - Impact of land surface memory
- The west coast states has more large scale
structure - US monsoon region seems more localized







![[PDF]❤️DOWNLOAD⚡️ Consuming Ocean Island: Stories of People and Phosphate from Banaba (Tracking PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/10039615.th0.jpg?_=20240527039)






















