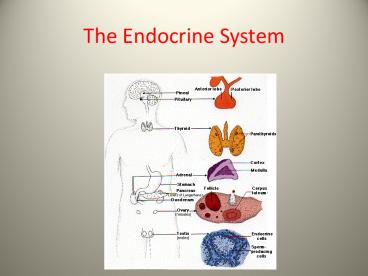
The Endocrine System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title:
The Endocrine System
Description:
Endocrine system controls most of the processes occurring in the body ... WHY are patients who suffer gigantism taller than those who suffer acromegaly? ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:91
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Endocrine System
1
The Endocrine System
2
Endocrine system characteristics
- Endocrine system is mostly controlled by the
nervous system - Endocrine system controls most of the processes
occurring in the body - Divided into cranial extracranial endocrine
glands - Cranial hypothalamus, pituitary pineal glands
- Extracranial thyroid, parathyroid, thymus,
pancreas, adrenals, gonads, GI tract placenta
3
Cranial endocrine glands
- Hypothalamus
- Many nuclei within this region to control
various aspects of homeostasis - Exhibits control over pituitary gland
- Blood supply / blood flow pattern is important
for control - portal system capillaries in hypothalamus
drain into portal venules (veins) that connect
to capillaries in the pituitary gland
(capillary-vein-capillary) - Hypothalamic neurons will release releasing
hormones or inhibiting hormones into these
capillaries/portal veins to eventually target the
pituitary gland
4
(No Transcript)
5
Pituitary gland - Hypophysis
- Known as the conductor or master gland but is
itself under control of the hypothalamus - Inferior region of the brain, nestled within the
sella turnica of the spenoid bone - 2 regions (visibly different)
- Adenohypophysis (anterior lobe)
- Most of the hormones are produced here
- Neurohypophysis (posterior lobe)
- More neural area, 2 hormones
6
Pituitary gland (hypophysis)
- Anterior lobe (adenohypophysis)
- Derived from ectodermal glandular tissue
- Linked to hypothalamus via the infundibulum
which has the hypophysial portal vascular system
(vascular communication) - Body anterior pituitary proper secretes 5
different hormones, prolactin (PL), growth
hormone (GH), thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH),
adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), Follicle
stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone
(LH) - Posterior lobe (neurohypophysis)
- Derived from nervous tissue
- extension of the brain
- Releases 2 hormones (which are synthesized in the
brain but stored in the posterior pituitary),
oxytocin and vasopressin (or antiduiretic hormone
(ADH)) - Intermediate lobe
- Thin, sandwiched between the 2 above layers
- secretes a minor hormone (melanin-stimulating
hormoneMSH)
7
(No Transcript)
8
Pineal gland
- roof of the 3rd ventricle)
- Larger in children than adults
- Secretes melatonin involved in circadian rhythm
9
Extracranial endocrine glandsThyroid gland
- Thyroid gland
- Below larynx, bi-lobed lateral to the trachea
- Largest endocrine gland
- Bloodflow via external carotid subclavian
arteries - Simple cuboidal epithelia (heavily reliant on
iodine) - Follicular cells secrete thyroxine (T4),
Tri-iodo-thyronine (T3) , parafollicular cell or
C cells secrete calcitonin
10
Parathyroid glands
- Posterior to the thyroid gland (para around)
- 4 distinct glandular formations
- Secretes parathyroid hormone ( parathormone
PTH)
11
Pancreas
- Has BOTH endocrine exocrine functions
- Endocrine Endocrine cells grouped into the
Islets (Islets of Langerhans). - 3 types of cells
- Alpha cells secrete glucagon
- Beta cells secrete insulin
- Delta cells secrete somatostatin
12
Minor gastrointestinal endocrine glands
- GI tract (gastrointestinal tract)
- Numerous endocrine cells distributed throughout
GI tract (often single cells) - Additional endocrine glands
- Salivary glands
- Brunners glands (duodenum)
13
Adrenal glands
- Located on the top of the kidneys
- Composed of 2 major parts
- Adrenal cortex 3 layers
- Zona glomerulosa secretes mineralocorticoids
- Zona fasciculata secretes glucocorticoids
- Zona reticularis secretes sex hormones
- Adrenal medulla is an extension of the
sympathetic autonomic nervous system (specialized
2nd motor neurons which secrete adrenaline)
14
Gonads
- Testicles Contains the seminiferous tubules
where sperm is made. In between the tubules, the
Leydig cells secretes testosterone - Ovaries The developing follicle secretes
estrogen and progesterone
15
Placenta
- Transfers waste from fetus to mother and
nutrients from mother to fetus - Secretes estrogen progesterone
- Also secretes human chorionic gonadotrophin
(hCG)whats used to change color of pregnancy
test sticks
16
Pituitary pathophysiology
- Panhypopituitarism reduced pituitary activity or
total loss of pituitary function - Abnormal growth hormone
- Inadequate during childhood pituitary dwarfism
- Inadequate during adulthood Simmonds disease
- Premature aging
- Oversecretion during childhood gigantism
- Oversecretion during adulthood acromegaly
- Bones thicken, soft tissues grow inappropriately
17
Acromegaly
Gigantism
Occurs during adulthood
Begins during childhood
WHY are patients who suffer gigantism taller than
those who suffer acromegaly?
18
Thyroid parathyroid pathophysiology
- Hypothyroidism
- During childhood cretinism (cretins)
- During adulthood myxedema
- Goiter (abnormal thyroid growth)
- Endemic inadequate iodine intake
- Graves disease
19
Pancreatic pathophysiology
- Diabetes mellitus
- Type I diabetes insulin dependent due to
autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells
(loss of insulin production) - Type II diabetes insulin insensitive due to
reduced responsiveness to insulin (metabolic
obesity)
20
Adrenal pathophysiology
- Pheochromatocytomas chromaffin cell tumor
- Excessive norepinephrine secretion resembles
ANS overstimulation - Addisons disease decreased mineralcorticoid
glucocorticoid secretion - Constant hypoglycemia, electrolyte imbalances
- Cushings syndrome increased glucocorticoid
secretion (Zona fasciculata) - Altered metabolism and physical changes
indicative of edema
21
Pediatric Cushings syndrome