Protocol Suites TCPIP - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 27
Title:
Protocol Suites TCPIP
Description:
... to obtain a physical address broadcasts an ARP request onto the TCP/IP network. ... the IP address in the request then replies with its physical hardware address. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:179
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Protocol Suites TCPIP
1
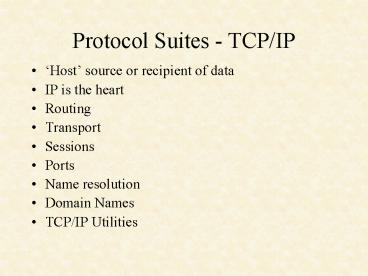
Protocol Suites - TCP/IP
- Host source or recipient of data
- IP is the heart
- Routing
- Transport
- Sessions
- Ports
- Name resolution
- Domain Names
- TCP/IP Utilities
2
IP Addresses
- IP address logical address
- 4 bytes, 32 bits
- 1st 4 bits of address determine address class
- 0000xxxx 1-126 Class A
- 1000xxxx 127-191 Class B
- 1100xxxx 192-223 Class C
- 1110xxxx 224-239 Class D
- 1111xxxx 239-255 Class E
3
Numbers
4
Subnet masking
- A bit in the subnet mask equal to 1 means the
corresponding bit in the IP address belongs to
either the net or subnet part of the IP address - Class A 255.0.0.0
- Class B 255.255.0.0
- Class C 255.255.255.0
- Possible hosts
- A 256256256-2 host ids (16.7 million)
- B 256256 -2 host ids (65,534)
- C 254 host ids
- Host Ids gt1
5
Special IP Addresses
- 127.0.0.1 loopback
6
Node settings
- IP Address
- Static
- Dynamic - DHCP
- Subnet Mask
- Default Gateway (address of a router)
7
(No Transcript)
8
Routing
- Examine each packet
- Determine destination network
- Static manually enter a route to next router in
internetwork - Dynamic learning protocols
- RIP router information protocol
- OSPF open shortest path first
- EGP exterior gateway
- BGP border gateway
9
Transport Layer
- TCP
- Transmission Control
- Connection oriented
- Interactive apps
- UDP
- User Datagram
- Connectionless
- Not time critical
10
Sessions Ports
- Sockets
- IP port
- Standardized for applications
- HTTP (80
- FTP(20,21)
- TFTP(69)
- SMTP(25)
- POP3(110)
- SNMP(161)
- Telnet(23)
- http//www.pcurtis.com/rem_pop.htm
11
Misc
- Proxy Servers
- Firewalls
- Routers as Firewalls
12
Name Resolution
- DNS (Domain name service)
- Names lt gt IP addresses
- Hierarchical name space
- TLDs
- .com .org .edu..
- Subdomains wwu.edu
- Computer names www.cbe.wwu.edu
- DNS Root Servers
- Hosts file
- WINS (Windows only!internet name service)
13
NetBIOS Apps WINS
- NetBIOS cannot use DNS
- WINS client registration
- Name IP address
- (both unique)
- Interrupted by router
- LMHOSTS local table of ipnetBIOS
- Uniqueness not guaranteed
14
Configuring IP
- Static
- DHCP
- IPCONFIG
- Winipcfg
15
TCP/IP Utilities
- Ping
- Traceroute or tracert
- Arp
- Netstat
- Nbtstat (NetBIOS names)
- Many more.
16
Ping
17
pinging
18
Tracert
19
Arp protocol
- Short for Address Resolution Protocol, a TCP/IP
protocol used to convert an IP address into a
physical address (called a DLC address), such as
an Ethernet address. A host wishing to obtain a
physical address broadcasts an ARP request onto
the TCP/IP network. The host on the network that
has the IP address in the request then replies
with its physical hardware address. - There is also Reverse ARP (RARP) which can be
used by a host to discover its IP address. In
this case, the host broadcasts its physical
address and a RARP server replies with the host's
IP address. - Webopedia.com
20
Arp functions
21
Arp
22
Netstat functions
23
Netstat r
24
Netstat n
25
Netstat a
26
Netstat -e
27
nbtstat functions http//www.zdnet.co.uk/news/spe
cials/2000/10/enterprise/techrepublic/2002/02/arti
cle002.html