Unit 1: Honors Precalculus - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Unit 1: Honors Precalculus
Description:
Unit 1: Honors Precalculus Lesson 1: Standard 1.1 and 1.2 (1-1, 1-2) Lesson 2: Standard 1.3 (1-3, 1-4) Lesson 3: Standard 1.3 and 1.4 (1-5, 1-7) – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:310
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Unit 1: Honors Precalculus
1
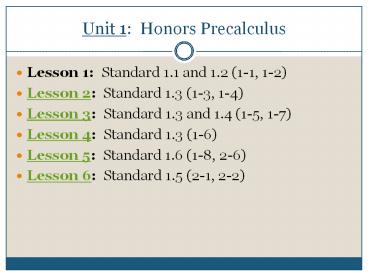
Unit 1 Honors Precalculus
- Lesson 1 Standard 1.1 and 1.2 (1-1, 1-2)
- Lesson 2 Standard 1.3 (1-3, 1-4)
- Lesson 3 Standard 1.3 and 1.4 (1-5, 1-7)
- Lesson 4 Standard 1.3 (1-6)
- Lesson 5 Standard 1.6 (1-8, 2-6)
- Lesson 6 Standard 1.5 (2-1, 2-2)
2
Welcome to Precalculus! Mrs. Bunting
Room C109
- Get an index card and your handouts.
- Pick up a textbook (Rust with spiral on front)
- Find your seat on the seating chart and take
your seat. Fill out your index card. - Please begin to work on reviewing the material
in Section 1-1 of your book. - Use your textbook and tablemates to help
yourself review this material. - You will need to TAKE NOTES on the material.
- Complete p 10 17 37 odd, 41-47 all
3
Standard 1.1 distinguish between relations and
functions, identify domain and range, and
evaluate functions (Section 1-1)p 10 17 37
odd, 41-47 all
- By the time you and your group finish you will
answer - What is a relation?
- What is contained in the domain of a relation?
In the range? - What is a function and how is it different from
a relation? - What is the vertical line test and what is it
used for? - What does function notation look like?
- How are functions evaluated for specific values?
4
What is Honors Precalculus?
- You will be introduced to
- Higher level algebra skills!
- Common and Natural Logarithms!
- Limits!
- Arithmetic, Geometric and Infinite Series!
- Polynomial, Rational and Exponential Functions!
- Lots of Trigonometry!
- Rectangular and Polar Coordinates!
- not necessarily in that order
5
What Can I Expect?
- We will cover at least a section a day.
- We will complete a unit pretty much weekly.
- Each quarter will have several portfolio
projects. - You can expect to have Precalculus work to do
every single night.
6
Grading to Standards
- In a nutshell
- 1. You need to master EVERY standard to pass.
- 2. Any standard which you do not pass must be
reassessed. - To Do Well
- 1. Complete your homework.
It is your
ticket to reassess. - 2. Reassess promptly while things are fresh.
7
Extra Help
- Tutorial right here in C109!
Everyday but Tuesday
(Library Duty) - Got Math?
- 3C in C211 Ms Kielkucki
- 3D in C106 Ms Ciliano
- 4C in C104 Mr. Lisella
- 4C in C100 Ms Rohrer
- 4D in C100 Ms Bunting
8
Unit 1 Get in Line
- In this unit we will complete
- Standard 1.1 distinguish between relations and
functions, identify domain and range, and
evaluate functions (1-1) - Standard 1.2 perform operations (add, subtract,
multiply, divide, compose) on functions (1-2) - Standard 1.3 analyze graphs and make
predictions based on linear functions (1-3,
1-4, 1-5, 1-6) - Standard 1.4 graph and interpret piecewise
functions (1-7) - Standard 1.5 solve systems of equations (2-1,
2-2) - Standard 1.6 solve systems of linear
inequalities (1-8, 2-6)
9
Standard 1.1 (continued) Using the Vertical
Line Test and Stating The Domain From A Graph
(1-1)
10
(No Transcript)
11
Standard 1.1 Finding the Domain of a Function
in Equation Form (1-1)
- To find out what the independent (x) values for a
function will be involves finding out what they
cannot be. - There are TWO Bozo No-Nos
- No values which cause zeros in denominators
- No values which cause a negative under a square
root (or any even root)
12
Find the values for x which are not in the domain
of the function, then state the domain in proper
set notation.
13
Find the values for x which are not in the domain
of the function, then state the domain in proper
set notation.
14
Find the values for x which are not in the domain
of the function, then state the domain in proper
set notation.
15
Find the values for x which are not in the domain
of the function, then state the domain in proper
set notation.
16
Standard 1.2 perform operations (add,
subtract, multiply, divide, compose) on functions
(1-2)
- When we finish this lesson you will be able to
- Perform basic math operations with functions
- Create, use and check composite functions
17
Given
- Add the functions
- Written
- It means
18
Given
- Subtract the functions
- Written
- It means
19
Given
- Multiply the functions
- Written
- It means
20
Given
- Multiply the functions
- Written
- It means
21
You try it
- Given
22
Composite Functions
- Careful with notation, this is not
multiplication. - It means you actually put one function into the
other. - The second one is going into the first.
23
Example
24
Example
25
To Check
26
Homework
- For Tomorrow
- HW 1.1 p 10 17 47 odd, 48-50 all
- HW 1.2 p 17 11 23 odd, 31
- By Monday
- Cover book
- Get your binder or notebook setup
- Get parental form turned in
27
Warm-Up
- P 25 41
- Have your homework out to be checked!
28
Homework
29
Standard 1.3 analyze graphs and make
predictions based on linear functions (1-3,1-4)
- At the end of this lesson you will be able to
- Identify and properly use the three forms of
linear equations - Find x- and y-intercepts
- Define, identify and use the formula for slope
- Identify the two special cases of slope
30
Linear Functions
- What does a linear equation look like?
- Are all the equations of lines also functions?
- How many of the forms do you remember?
31
Standard Form
32
Standard Form
- Where A, B and C are numbers like this.
- In this form you can tell what about the line?
- Nothing.
33
Slope-Intercept Form
- Where m is
- And b is
- In this form you can
- Tell exactly what the line looks like
- Graph the line
34
Point-Slope Form
- Used to develop the linear equation if you know
the slope, m, and one point on the graph, (x1,
y1). - Find the standard form of the equation of the
line which has a slope of -1 and passes through
the point (-4, 5).
35
What if you only have two points on the graph?
- Find the standard form of the equation which
passes through the points (6,5) and (4,-5). - Find slope.
- Use slope and one of the points to find equation
of the line.
36
Graph a couple
37
The Two Special Cases of Slope
38
Finding the Zero of a Linear Function
- Zero is another name for the x-intercept. You
will also hear it called a root. - The y-intercept is called b but not much else.
39
Finding x- and y-intercepts
40
Homework
- HW1 1.3 P24 13 33 every other odd
- HW2 1.3 P30 11 27 every other odd
41
Warm-up
42
Homework
43
Standard 1.3 analyze graphs and make
predictions based on linear functions (1-5)
- By the end of this lesson we will be able to
answer - How can parallel and perpendicular lines be
identified from their equations? - How can the properties of lines be used to
identify geometric figures? - How can the coefficient for an equation be found
so that it will be parallel or perpendicular to a
specific line?
44
Parallel and Perpendicular Lines
- Parallel lines have the same slope
- Perpendicular lines have slopes which are
negative reciprocals of each other. - Find the equation of the line parallel to the
equation above and passing through (2,-2) - Find the equation of the line perpendicular to
the equation above and passing through (-4,1)
45
Special Case
- Lines which have the same slope and the same
y-intercept are called coinciding.
46
Slope and Distance
- Consider the polygon with vertices at (0,0),
(1,3), (3,-1) and (4,2). - Is it a parallelogram?
- Is it a rectangle?
47
Are these lines parallel, coinciding
perpendicular or none of these?
neither
parallel
coinciding
perpendicular
48
Solving for an unknown coefficient
49
Solving for an unknown coefficient
50
Standard 1-4 graph and interpret piecewise
functions (1-7)
- In this lesson we will
- Identify piecewise functions including greatest
integer, step and absolute value. - Graph piecewise functions.
51
Piecewise Functions
- Different equations are used for different
intervals of the domain. - The graphs do not have to connect.
52
Graphing Piecewise Functions
53
Another
54
Step Functions
- Are piecewise functions whose graphs look like a
set of steps. - One example of a step function is the greatest
integer function.
55
An example of a step function fee schedule
- The cost of mailing a letter is 0.37 for the
first ounce and 0.23 for each additional ounce
or portion thereof.
56
The Absolute Value Function
57
Make sure you find the turning point
58
Make sure you find the turning point
59
Homework
- HW3 1.3 p36 13-31 odd
- HW 1.4 p49 11-33 odd
60
Warm-up Feel free to get a piece of graph paper
from the bin by the windows.
- Graph the functions
61
Homework
62
Standard 1.3 analyze graphs and make predictions
based on linear functions (1-6)
- In this section we will
- Draw and analyze scatter plots.
- Draw a best-fit line and write a prediction
equation. - Solve problems using prediction equation models.
63
Collecting and Using Data
- Real life data seldom forms nice straight lines
or smooth curves. - For graphs which approximate a line, a best-fit
line (also called a regression line) can be drawn
and a prediction equation can be determined.
64
Scatter Plots p 38
- Basically, data is the graph of a relation.
- If the graph shows a linear trend you can create
a prediction equation. - Accuracy of predictions depends on how closely
the data approximates a line.
65
Correlation p 40
- This refers to how closely a set of data actually
approximate a line. - If the data is very scattered, that is a weak
correlation. - If the data is very close to being on a line then
it has a strong correlation. - Our example had moderate correlation.
66
More About Correlation p 40
- Correlation is measured using a correlation
coefficient (r). - r lt ½ means weak, ½ lt r lt ¾ is moderate, ¾ lt r lt
1 is strong. - One means complete correlation.
- NOTICE r is positive for positive slopes and
negative for negative slopes.
67
The Prediction Equation
- Graph your data.
- Draw a best-fit line.
- Chose two points, on the line.
- Find their slope.
- Use the slope and one of the points to find the
prediction line.
68
Regression Lines on the Calculator
- Go to STAT, choose EDIT, and enter the x-values
in L1 and the y-values in L2. - Go to STAT PLOT (2nd, Y), press ENTER on 1Plot
1, and turn Plot1 On. - Go to WINDOW, and adjust your Xmin, Xmax, Ymin,
and Ymax to fit your data. - Go to GRAPH to see your points plotted.
- Go to STAT, choose CALC, arrow down to highlight
the appropriate regression model, and press
ENTER. Press L1 (2nd, 1), the comma (above the
7), L2 (2nd, 2), the comma again, then VARS,
choose Y-VARS, choose Function, choose Y1, and
press ENTER. - Go to Y to see that your equation has been
transferred to the Y screen. - Go to GRAPH to see your line.
- To enter an x-value and find the corresponding
y-value, go to CALC (2nd, TRACE) and choose
1value. Enter the x-value, and the y-value will
be provided. - To enter a y-value and find the corresponding
x-value, go to Y and next to Y2 graph the line
ya, where a is the y-value in which you are
interested. Then go to CALC (2nd, TRACE) and
choose 5intersect. Press ENTER three times, and
the point of intersection will be provided. - NOTE You may need to change your viewing window
to accomplish steps 8 and 9.
69
Nowdo it yourselves.
- Use the data your group was given.
- Paste the chart with your data and plot your
points on the large sheet of graph paper. - Draw a best-fit line.
- Choose two points on your line and determine your
prediction equation. Show all work on the graph
paper. Label it Hand Calculated Equation - Finally, use the graphing calculators to find the
regression equation. Record it on the graph
paper and label it Calculator Generated
Equation. - Make sure that you allow enough room on the paper
to answer your questions.
70
Homework
- HW5 1.3 p42 7 and 9
71
Warm-up.
- Grab a couple pieces of graph paper for the
lesson.
Feel free to hole punch it - For heavens sake! Finish those projects!
72
Homework
73
Standard 1.6 Graph and solve using linear
inequalities (1-8)
- In this section we will
- Graph linear inequalities
- Graph more complex inequalities
74
Inequality Graphs
- Any line will cut the coordinate plane into two
halves. - Any point on the line will cause the statement to
be true.
75
Inequality Graphs
- Any point above the line causes...
- Any point below the line causes...
76
Lets try this one
77
How about this?
78
Or this?
79
Okay Partners, wrangle these
- You will need graph paper.
- p 55
- Partner 1 graphs 12, Partner 2 graphs 10
- Switch papers and check each other.
- Partner 1 graphs 14, Partner 2 graphs 18
- Switch papers and check each other.
80
Answers
81
(No Transcript)
82
Standard 1.6 Solve systems of linear
inequalities (2-6)
- At the end of this section you should be able to
- Find the solution for a system of inequalities
using a graph - Graph a polygonal convex set
- Find the vertices for a polygonal convex set
- Find the minimum and maximum values for a
polygonal convex set
83
How can the solution for a system of inequalities
be determined using a graph?
84
What is a polygonal convex set?
- A polygonal convex set is the solution for a
system of inequalities. - The solution is contained within the polygon
formed by the boundaries of the inequalities.
85
First graph the inequalities and determine the
polygonal convex set.
86
How do I find the vertices for a polygonal convex
set?
87
How can I find the minimum and maximum values for
a polygonal convex set?
88
Try this one
(3,-11)
89
Word Problem!!! P111 26
90
One more!
- The Cruiser Bicycle Company makes two styles of
bicycles the Xenon, which sells for 200, and
the Yaris, which sells for 600. Each bicycle has
the same frame and tires, but the assembly and
painting time required for the Xenon is only 1
hour, while it is 3 hours for the Yaris. There
are 300 frames and 360 hours of labor available
for production. How many bicycles of each model
should be produced to maximize revenue, and how
much money will be made?
91
Homework Grab graph paper!
- HW1 1.6 P55 9 21 every other odd and 23
- HW2 1.6 P110 9 21
- HW3 1.6 P117 15
- Look for a Unit 1 Test on Tuesday 2/15!!!
- Portfolio 1 due on Wednesday 2/16!!!
92
Warm-up
93
Homework
94
Standard 1.5 solve systems of equations (2-1,
2-2)
- In these sections we will
- Solve systems of equations involving two
variables algebraically. - Solve systems of equations involving three
variables algebraically. - You will need a ruler and a piece of graph paper.
95
What does the solution for a system of linear
equations represent?
96
How Can We Solve a System?
- Graphing
- Elimination
- Substitution
97
Solve the following systems by graphing
98
Terminology
- If lines intersect ONE solution
a.k.a. consistent and independent - If same line twice INFINITE solutions
a.k.a. consistent and dependent - If lines are parallel NO solution
a.k.a. inconsistent - What were your graphs?
99
Substitution and Elimination
100
Word Problem!
- p 71 10
101
Solving Systems in 3 Variables
- A system in 3 variables represents the
intersection of 3 planes. - Look at page 73.
- You need 3 equations to solve.
- You have to have the same number of equations as
you have variables. - Solve using substitution or elimination.
102
Lets try some
How should the solution be written?
103
(No Transcript)
104
(No Transcript)
105
(No Transcript)
106
NowYOU think.
- Write a system of 3 equations that fits each
description. - The system has a solution of x - 5, y 9 and z
11. - There is no solution to the system.
- The system has an infinite number of solutions.
107
Homework
- HW1 1.5 P 71 22 25 all
- HW2 1.5 P 76 9, 11 and 13
- UNIT 1 Test on Tuesday 2/15
- Portfolio 1 due Wednesday 2/16