Science Notebook Layout DON - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Science Notebook Layout DON
Description:
Science Notebook Layout DON T COPY UNDERLINED TEXT Mrs. Aguirre s Webpage: http://www.quia.com/profiles/caguirre Density of Solids Introduction to Density – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:65
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Science Notebook Layout DON
1
Science Notebook Layout DONT COPY UNDERLINED
TEXTMrs. Aguirres Webpage http//www.quia.com/p
rofiles/caguirre
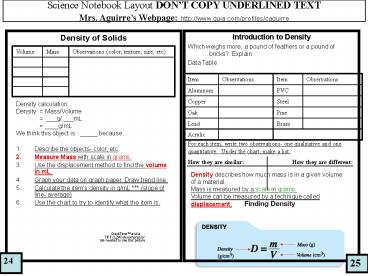
Density of Solids
Introduction to Density Which weighs more, a
pound of feathers or a pound of bricks?
Explain. Data Table
Volume Mass Observations (color, texture, size, etc)
Item Observations Item Observations
Aluminum PVC
Copper Steel
Oak Pine
Lead Brass
Acrylic
- Density calculation
- Density Mass/Volume
- ___g/ ___mL
- ____g/mL
- We think this object is _____ because
- Describe the objects- color, etc
- Measure Mass with scale in grams.
- Use the displacement method to find the volume in
mL. - Graph your data on graph paper. Draw trend line.
- Calculate the items density in g/mL. (slope
of line- average) - Use the chart to try to identify what the item is.
For each item, write two observations- one
qualitative and one quantitative. Under the
chart, make a list How they are similar
How they are different
Density describes how much mass is in a given
volume of a material. Mass is measured by a scale
in grams. Volume can be measured by a technique
called displacement.
24
25
2
Science Notebook Layout DONT COPY UNDERLINED
TEXTMrs. Aguirres Webpage http//www.quia.com/p
rofiles/caguirre
26
27
3
Science Notebook Layout DONT COPY UNDERLINED
TEXTMrs. Aguirres Webpage http//www.quia.com/p
rofiles/caguirre
Density Stations
26
27
4
Science Notebook Layout DONT COPY UNDERLINED
TEXTMrs. Aguirres Webpage http//www.quia.com/p
rofiles/caguirre
Page 28 Liquid Layers Reflection
Page 29 Liquid Layers
- Prentice Hall density column video
- Name 3 items denser than water. Explain why you
think they are denser. - What is the difference between mass and density?
- Why does she tilt the cylinder when she is
pouring the liquids? - Why do the liquids form layers?
- Why do the solids float between the layers?
- What do you think the four liquids are?
Yellow Red Blue Green - Correct order from top to bottom.
- Which is most dense? Why?
- Which is least dense? Why?
- What would happen if you turned the straw upside
down? Why? - 6. Calculate the density of each liquid (each
cylinder has 50 mL of liquid in it) - Blue
- Green
- Yellow Red
- Water, salt water, isopropanol, and glycerine.
- Each is colored a different color.
- Your goal is to layer them in your straw with
your partner. - Make a hypothesis of the order.
- Fill it in the blanks
- Test it out.
- Draw arrows to show the movement of the liquids
up or down. - Repeat until you get the order correct.
- Once you have the order correct, draw it NEATLY
on page 29- color it!! - Describe how you figured it out in a short
paragraph
Density mass / volume ____ g
/ 50 mL
28
29
5
Science Notebook Layout DONT COPY UNDERLINED
TEXTMrs. Aguirres Webpage http//www.quia.com/p
rofiles/caguirre
31
THE SODA CANS Why does the diet soda float and regular soda sink? Use mass, density, and volume in your answer. Draw a picture!! Eureka Video Notes THE SODA CANS Why does the diet soda float and regular soda sink? Use mass, density, and volume in your answer. Draw a picture!! Eureka Video Notes
Volume Density
In each box, you must have a labeled picture
(with vectors!!) and a description of what is
happening Link to YouTube copy of video we
watched http//www.youtube.com/watch?vhkT3ulsGWy
A
30
6
Science Notebook Layout DONT COPY UNDERLINED
TEXTMrs. Aguirres Webpage http//www.quia.com/p
rofiles/caguirre
Buoyancy Analysis
- 7. Does increasing the weight of the film can
affect the buoyant force? - Hypothesis When you add pennies to the can, the
buoyant force will ________ because _________. - Test it out
- Weight of heavier film can in air _____ N
- Weight of heavier film can under water _____N
- Buoyant force (subtract!!!) _____N
- Compare the buoyant forces (todays vs
yesterdays) - 8. How does the buoyant force compare to the
weight of the displaced water? - Collect displaced water from displacement tank
- Weigh it on the scale using NEWTONS!!!
32
33
7
Science Notebook Layout DONT COPY UNDERLINED
TEXTMrs. Aguirres Webpage http//www.quia.com/p
rofiles/caguirre
The Physics Of Ice Cream
Atoms (p 52) Atoms in solids (p 54)
Atoms in liquids (p 54) Atoms in gases (p 54)
For each box, draw a picture and write one main
idea.
34
35
8
Science Notebook Layout DONT COPY UNDERLINED
TEXTMrs. Aguirres Webpage http//www.quia.com/p
rofiles/caguirre
Dance of the Molecules
Solid Liquid Gas Solid Liquid Gas Solid Liquid Gas
Solids keep their shape because. Solids cant change their volume because Liquids change their shape because. Liquids cant change their volume because Gases change their shape because. Gases can change their volume because
Explain the motion of the molecules in each state
36
37
9
Science Notebook Layout DONT COPY UNDERLINED
TEXTMrs. Aguirres Webpage http//www.quia.com/p
rofiles/caguirre
Intermolecular Forces (Page 96)
What they do Properties of
The role of Thermal Energy Explaining Phases of Matter
In each box, include a picture to describe main
idea of reading and a 1-2 sentence summary of the
paragraph.
38
39
10
Science Notebook Layout DONT COPY UNDERLINED
TEXTMrs. Aguirres Webpage http//www.quia.com/p
rofiles/caguirre
41 Squ eeeee zing molecules
Problem How does the volume of matter change
if pressure is increased? Info we have Particle
theory of matter solid liquid
gas Hypothesis Look at your pictures
above What will happen to the volume of each as
books are piled on (give eg 100, 0, 50, ?
Give a reason for each. Gas (air) The volume
will be ____ because____ Liquid (water) The
volume will be ____ because____ Solid (ice)
The volume will be ____ because____
40 Data Analysis What percent of the volume of
each remains after pressure is increased? Gas
(air) Percent ----- x 100 Liquid (water)
----- x 100 Solid (ice) ----- x 100
Conclusion Gas 3 lines max EXPLAIN WHY THE
VOLUME CHANGED. Use reasons from your notes on
pages 35-36 Include how CLOSELY PACKED THE
MOLECULES MUST BE. Underline the word molecules
Liquid 3 blank lines Solid For each (solid,
liquid), EXPLAIN WHY THE VOLUME DIDNT CHANGE.
Use reasons from your notes on pages 35-36.
Include how CLOSELY PACKED THE MOLECULES MUST
BE. Underline the word molecules. Conclusion
The most surprising conclusion from this
experiment was Look at your hypothesis!
Pressure (Number of Books) Gas Volume (cm3) Liquid volume Solid Volume
0 One
1 notebook
2 line
3 For each
4 line
Picture Draw the syringe with and without
books. Include numbers to show volume with 0
books and volume with 4 books.
41
40
11
Science Notebook Layout DONT COPY UNDERLINED
TEXTMrs. Aguirres Webpage http//www.quia.com/p
rofiles/caguirre
Melting Ice Graph My melting point
was_______________
Magic Shell Lab
What is the freezing/ melting point of Magic
Shell? Background(answer) A)Define
Melting/freezing point B) What does temperature
tell us about the motion of molecules?
Freezing Freezing Melting Melting
Time (sec) Temp. (C) Time (sec) Temp. (C)
0 0
10 10
20 20
30 30
40 40
50 50
60 60
70 70
80 80
Magic Shell Discussion 1) Look at the
temperatures you recorded as you cooled the shell
topping. It will seem almost as if the mixture
stalled at a certain temperature. What is this
temperature? 2) Look at the temperatures you
recorded as you heated the shell topping. Is the
stalled temperature about the same as it was
when you cooled the mixture? 3. See next page
for graph of magic shell 3) Make a cooling curve
graph and a heating curve graph. Place time on
the x axis and temperature on the y axis. Label
the area of your cooling graph where freezing
occurred. Label the area of your heating graph
where melting occurred. 4. When you cooled and
then heated the shell topping, the temperature
stalled. What was happening at this
temperature? 5. What would magic shell topping be
like if the freezing/melting point was 20 C? 6.
What about if the freezing/melting point was 0 C?
Roles my role is___________
42
43
12
Magic Shell Graph
13
Science Notebook Layout DONT COPY UNDERLINED
TEXTMrs. Aguirres Webpage http//www.quia.com/p
rofiles/caguirre
Ice Cream- Page 45
Changes of State- use pages 96-101 in California
Physical Science book
Words to use Freezing Melting Vaporization Conden
sation Boiling Evaporation Sublimation
Predict how the temperature will change as your
ice cream freezes.
gas
Why does adding salt to ice make it colder?
liquid
Chlorine (Cl)
Sodium (Na)
Salt NaCl
A) Draw each state, B) Add arrows and labels for
each of the changes of state listed C) Include
pictures of the changes of state D) All should be
colored!!
The melting/ freezing point of water is _____
C. By adding salt to ice it ____________ the
melting/ freezing point to below 0C. Heat energy
is needed to change _____________ ice to
______________ water. This makes the
temperature low enough to _____________ the
liquid milk into ____________ ICE CREAM!!!!
solid
44
45
14
Science Notebook Layout DONT COPY UNDERLINED
TEXTMrs. Aguirres Webpage http//www.quia.com/p
rofiles/caguirre
Its Freezing Discussion
Ice only Line
Ice and salt Line
1. What happened after you added the salt to the
ice? Was the temperature above or below the ice
only? 2. What is the only factor that could have
caused the changes shown in question 1? What does
this tell you about the freezing point
temperature of salt water compared to fresh
water? Use page 260 to give explanation. 3. Heat
energy is needed to change phase from a solid to
a liquid. List the possible sources of the heat
needed for this phase change in your beaker. Use
page 260 to give explanation. 4. Explain how we
could use the information we found out about
temperature changes in salt water in this
experiment to make ice cream. 5. In the radiator
of your car you put a combination of antifreeze
and water to keep your car engine cool in the
summer and prevent the radiator from freezing in
the winter. Explain how you think this works in
terms of what you saw in the experiment you just
did. Use page 261 to give explanation.
46
47