Typical Memory Layout - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Typical Memory Layout
Description:
Check your BSP documentation. To add off-board memory: void memAddToPool (pPool, ... System Memory Pool Used for dynamic memory allocation in programs: malloc( ). – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:120
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Typical Memory Layout
1
Typical Memory Layout
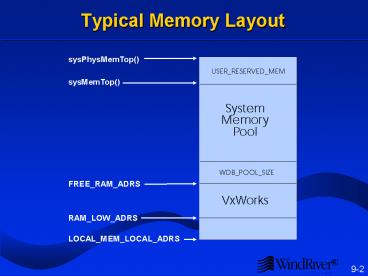
sysPhysMemTop() sysMemTop() FREE_RAM_ADRS
RAM_LOW_ADRS LOCAL_MEM_LOCAL_ADRS
2
Target Server Memory Pool
- A pool of memory on the target reserved for use
by the Tornado tools - Dynamic loading of object modules.
- Passing string arguments to tasks spawned on
target. - Creation of variables from WindSh.
- The target server manages the pool, keeping
overhead such as block lists on the host. - The initial size of the target server memory pool
is configured by WDB_POOL_SIZE. The default is
1/16 of sysMemTop( ) - FREE_RAM_ADRS. - Additional memory is silently allocated from the
system memory pool if needed.
3
System Memory Pool
- Used for dynamic memory allocation in programs
- malloc( ).
- Creating tasks (stack and TCB).
- VxWorks memory requests.
- Initialized at system start-up.
- Can modify USER_RESERVED_MEM to reserve memory
for application-specific use. - May need to modify sysPhysMemTop( ) (or just
LOCAL_MEM_SIZE) when adding memory to your board.
Check your BSP documentation. - To add off-board memory
- void memAddToPool (pPool, poolSize)
- pPool must be the local address of the memory.
4
Allocating/Releasing Memory
- To dynamically allocate memory
- void malloc (nBytes)
- Returns a pointer to the newly allocated memory
or NULL on error. - Uses first-fit algorithm.
- Free memory is stored in a linked list.
- Some (small) overhead for each malloc( ).
- To release allocated memory
- void free (ptr)
- Adjacent blocks are coalesced.
5
Debugging Options
- Default malloc( ) debugging If request too
large, log an error message. - Default free( ) debugging
- Check block for consistency.
- If corrupted suspend task, log error message.
- Can change default debugging options with
- void memOptionsSet (options)
- Options can be
- MEM_ALLOC_ERROR_LOG_FLAG
- - MEM_ALLOC_ERROR_SUSPEND_FLAG
- MEM_BLOCK_CHECK
- MEM_BLOCK_ERROR_LOG_FLAG
- MEM_BLOCK_ERROR_SUSPEND_FLAG
6
Examining Memory
- Use the Browser.
- Enter the memory partition ID in the Show box.
System Memory Pool Size Currently Allocated
Free Blocks Total
Allocated Free List
7
Additional System Memory Management Routines
- void calloc (nElems, size) Allocate zeroed
memory for an array. - void realloc (ptr, newSize) Resize an allocated
block. The block may be moved. - int memFindMax( ) Returns the size of the
largest free block in system memory.
8
Fine Tuning
- For fast, deterministic allocation of fixed size
buffers, use message queues instead of malloc( ).
9
Generic Partition Manager
- VxWorks provides low-level routines to create and
manipulate alternate memory pools. - High-level routines like malloc( ) and free( )
call these lower level routines, specifying the
system memory pool. - Application may use alternate memory partitions
to reduce fragmentation. - Application may use alternate memory partitions
to manage memory with different properties.
10
Creating a Memory Partition
- PART_ID memPartCreate (pPool, size)
- pPool Pointer to memory for this partition.
- size Size of memory partition in bytes.
- Returns a partition id (PART_ID), or NULL on
error. - The memory for this partition (pPool) may be
taken from - A separate memory board.
- A block allocated from the system memory
partition. - The top of the CPU boards RAM.
11
Managing Memory Partitions
- System partition management routines call
routines listed below, specifying the PART_ID as
memSysPartId. - Generic System Memory Pool
- memPartAlloc( ) malloc( )
- memPartFree( ) free( )
- memPartShow( ) memShow( )
- memPartAddToPool( ) memAddToPool( )
- memPartOptionsSet( ) memOptionsSet( )
- memPartRealloc( ) realloc( )
- memPartFindMax( ) memFindMax( )
12
Example Creating a Memory Partition
- -gtpartId memPartCreate(pMemory,100000)
- new symbol partId added to symbol table.
- partId 0x23ff318 value 37745448 0x23ff328
partId 0x10 - -gtptrmemPartAlloc(partId,200)
- new symbol ptr added to symbol table.
- ptr 0x23ff2ec value 37652632 0x23e8898
- -gtshow partId
- status bytes blocks ave block max block
- ------ ------ ------- --------- -----------
- current
- free 99776 1 99776 99776
- alloc 208 1 208 -
- cumulative
- alloc 208 1 208 -
13
Summary
- Standard C routines are used for dynamic memory
allocation. - To configure the system memory pool
- Modify sysPhysMemTop( ).
- Specify USER_RESERVED_MEM.
- Call memAddToPool( ).
- For fast, deterministic allocation of fixed size
buffers, use message queues instead of malloc( ). - Create separate memory partition for off-board
memory, or to help reduce fragmentation.