Bone Formation - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 22
Title:
Bone Formation
Description:
... Calcitonin Correction for Hypercalcemia Correction for Hypocalcemia Other Factors Affecting Bone Fractures and Their Repairs Fractures and Their Repair ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:247
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Bone Formation
1
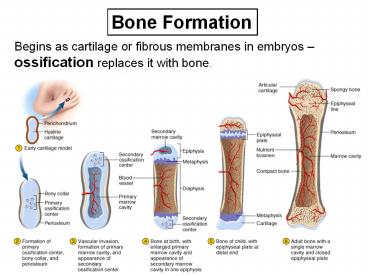
Bone Formation
Begins as cartilage or fibrous membranes in
embryos ossification replaces it with bone.
2
Fetal Skeleton at 12 Weeks
3
Bone Growth and Remodeling
- Bones increase in length
- epiphyseal plate
- epiphyseal line is left behind when cartilage
gone - Bones increase in width appositional growth
- osteoblasts lay down matrix in layers on outer
surface and osteoclasts dissolve bone on inner
surface - Bones remodeled throughout life
- architecture of bone determined by mechanical
stresses - action of osteoblasts and osteoclasts
- greater density and mass of bone in athletes or
manual worker is an adaptation to stress
4
Control of Growth Remodeling
- Growth hormone from pituitary gland and sex
hormones control long bone growth - PTH (parathyroid hormone) activates osteoclasts
to break down bone and release Ca2 ions to blood
if levels too low. - When Ca2 level is too high, deposits in bone
matrix where mechanical stress is high.
5
Dwarfism
- Achondroplastic
- long bones stop growing in childhood
- normal torso, short limbs
- spontaneous mutation during DNA replication
- failure of cartilage growth
- Pituitary
- lack of growth hormone
- normal proportions with short stature
6
Ion Imbalances
- Changes in calcium can be serious
hypocalcemia causes excitability of nervous
system if too low muscle spasms, tremors or
tetany laryngospasm and suffocation
hypercalcemia depresses nervous system muscle
weakness and sluggish reflexes, cardiac arrest
7
Hormonal Control of Calcium Balance
- Calcitriol, PTH and calcitonin maintain normal
blood calcium concentration.
8
Calcitriol (Activated Vitamin D)
9
Calcitonin
- Secreted by thyroid gland when calcium
concentration rises too high - Functions
- reduces osteoclast activity as much as 70
- increases the number and activity of osteoblasts
- Can be used to treat what condition???
10
Correction for Hypercalcemia
11
Correction for Hypocalcemia
Increased absorption from intestines
Calcitriol
12
Other Factors Affecting Bone
- Hormones, vitamins, and
- growth factors
- Growth rapid at puberty
- hormones stimulate osteogenic cells, chondrocytes
and matrix deposition in growth plate - girls grow faster than boys and reach full height
earlier (estrogen stronger effect) - males grow for a longer time and taller
- Growth stops (epiphyseal plate closes)
- teenage use of anabolic steroids premature
closure of growth plate and short adult stature
13
Fractures and Their Repairs
14
Fractures and Their Repair
- Stress fracture caused by trauma
- car accident, fall, athletics, etc
- Pathological fracture in bone weakened by disease
- bone cancer or osteoporosis
- Open (simple) vs closed (compound) fractures
- Reduction is realignment of broken bone ends
- Immobilization to allow healing.
15
Healing of Fractures
Bony Callus
Hematoma
Remodeling
Fibrocartilage Callus
3-4 months
6 weeks
16
Joints (Articulations)
- Classified two ways
- Function degree of movement
- Structure fibrous tissue, cartilage, or joint
cavities separate the bones
17
Structural Fibrous Cartilaginous Synovial
Functional Synarthroses Amphiarthroses Diarthroses
18
Synarthroses/ Fibrous joints
19
Amphiarthroses/ Cartilaginous Joints
20
Diarthrotic/Synovial Joints
Condyloid
21
Synovial Joint Structure
22
Quiz
1. _______________ is secreted by the
parathyroid gland when calcium blood levels are
low. It increases osteoclast population,
promotes calcium resorption by the kidneys,
promotes calcitriol synthesis in the kidneys. It
also inhibits collagen synthesis and bone
deposition by osteoblasts.
- ____________ is secreted by thyroid gland when
calcium concentration rises too high. - It reduces osteoclast activity as much as 70
and increases the number and activity of
osteoblasts.
3. ________ is made by the skin, liver, and
kidneys, and behaves as a hormone that raises
blood calcium concentration by -increases
intestinal absorption and absorption of calcium
from the skeleton -increasing osteoclasts -promoti
ng urinary reabsorption of calcium ions