Cognitive Map to Course Introduction - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 9
Title:
Cognitive Map to Course Introduction
Description:
New learning And make Changes in my ... Immunology Physics Genes Emotions Pharmacology Education Behaviorism Began in ... Present School Environment models Survival ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:132
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Cognitive Map to Course Introduction
1
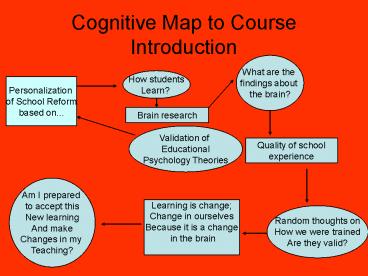
Cognitive Map to Course Introduction
What are the findings about the brain?
How students Learn?
Personalization of School Reform based on...
Brain research
Validation of Educational Psychology Theories
Quality of school experience
Am I prepared to accept this New learning And
make Changes in my Teaching?
Learning is change Change in ourselves Because
it is a change in the brain
Random thoughts on How we were trained Are they
valid?
2
Search Engine on Brain
- http//search.yahoo.com/search?phumanbrainandl
earning - http//search.yahoo.com/search?phumanbraindevel
pmentaudiovisual - http//search.yahoo.com/search?frfp-pull-web-tp
humanbraindevelopment
3
Rethinking the Brain
- Chapter 1
- I am not inattentive, you are just boring
- Thorn Hartmann
4
the brain is a rain forest jungle
- Quiet vs. teaming with life
- Internal clocks
- Ecosystems and brain regions are interdependent
- Law of the jungle and the brain is survival
- Jungle/brain has no teacher/training?simple rich,
evolving system with different pathways - Jungle has no memory except what it needs for
survival?brain survival economically, socially,
emotionally and physically - When does learning takes place?
5
- History
- Brain based learning began in 1980s
- By 1990s exploded
- Immunology
- Physics
- Genes
- Emotions
- Pharmacology
- Education
- Behaviorism
- Began in the 50s?Skinner Watson (earlier)
- Goal achieving the highest rank in test scores
- See the mind as tabula rasa
- At the expense of being creative, depressed
- oppositional, motivated and in control
6
Researching Research (adults)
- Resilient Factors (Seligman)
- Optimism
- Choice
- Control
- Social support
- Hardy Adults (Kobasa)
- Challenge
- Commitment
- Internal locus of control
- Seven Human Needs (Holocaust Survivors)
- Security
- Acceptance
- Belonging
- Self determination
- Structure
- Purpose
- Validation
- Greatest Human Needs (Glenn)
- Personal potency
- Control
- Relationships where feelings and ideas are
respected - Life has significance
7
Researching the Research (children)
- Coping Skills (Sapolsky)
- Physical Outlet
- Choice
- Control
- Predictability
- Social interaction
- Basic Needs (Glasser)
- Power
- Freedom
- Fun
- Belonging
- Love
- Resilient children (Werner)
- Internal locus of control
- Physical interaction with environment
- Assigned responsibility
- Age appropriate reading skills
- Variety of support
- Ten things every child needs (McCormick Tribune)
- Interaction/communication
- Touch
- Stable relationships/self esteem
- Safe environment
- Quality of child care
- Play/music/reading
8
- Present School Environment?models
- Survival of the fittest
- Determined behaviorists
- Brain based naturalist
- What is brain-based learning?
- An approach based on needs
- of learner
- In accordance with the way the brain
- is naturally designed to learn
- In biology the way things work depend
- on their physical structure, i.e. genetic
- inheritance depends on the structure of the
DNA and digestion depends on the structure of the
gut - Therefore the structure designed for human
learning is the brain
So we should create the conditions for this to
happen
9
A
A
A
A
A
A
Activation

















![Introduction to Biopsychology [PSB 4002] PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/6377876.th0.jpg?_=20150404023)











![CSCE 580 Artificial Intelligence Introduction and Ch.1 [P] PowerPoint PPT Presentation](https://s3.amazonaws.com/images.powershow.com/6301291.th0.jpg?_=20201003053)
