The Respiratory System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
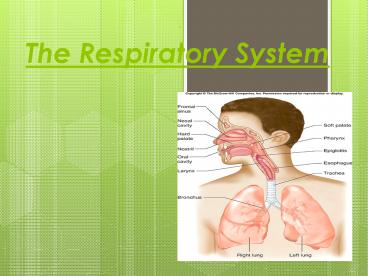
The Respiratory System
Description:
The Respiratory System Respiration Physiology The process by which oxygen is supplied to the cells and used. ... Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3) – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:154
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Respiratory System
1
The Respiratory System
2
Respiration Physiology
- The process by which oxygen is supplied to the
cells and used. - External-movement of gas between the atmosphere
and the lungs. - Internal-utilization of oxygen by the cells to
produce energy. - Gases and Gas Laws
- Respiration is dependent on the gas laws.
- Gases-moves from high pressure to lower pressure
or high concentration to lower.
3
- Pressure-an increase in pressure indicates a
decrease in volume - Volume- an increase in volume indicates a
decrease in pressure - Pressure and volume are inversely related
- P1V1P2V2
- As pressure increases in lungs, volume decreases
by air moving out. - As pressure decreases, volume increases by air
moving in.
4
INTERNAL RESPIRATION
EXTERNAL RESPIRATION
5
(No Transcript)
6
- Inspiration-air moves into the lungs.
- diaphragm relaxes/drops, pressure inside lungs
decreases, air moves in. - Expiration-air moves out of lungs.
- diaphragm contracts/raises, pressure inside lungs
increases, pushes air out.
7
Gas Exchange
- Alveoli-structure of gas exchange, 300 million in
a lung - Capillaries surround alveoli and carry blood to
and from lungs where gas exchange occurs. CO2 is
released and O2 is picked up.
8
Alveolus and capillary exchanging gases
9
(No Transcript)
10
Cell and capillary exchanging CO2
11
Capillary and cells exchanging O2
12
- Hemoglobin molecule in blood, binds four oxygen
molecules at Fe (iron) binding sites. Carries
oxygen through body and removes carbon dioxide. - Concentration gradients- driving force of gas
exchange. - O2 into alveoli from inhalation diffuses into
blood - CO2 from blood diffuses into alveoli
13
(No Transcript)
14
(No Transcript)
15
Carbon Dioxides Role
- CO2 is carried in three ways
- Dissolved in the blood plasma.
- Bound to hemoglobin (in red blood cell)
- As a bicarbonate ion in plasma
- CO2 H2O? H2CO3? H HCO3-
- Carbon water carbonic
hydrogen bicarbonate - Dioxide acid
ion ion -
(ACIDIC) - This is called a buffering system
- Controls the pH of the blood (how acidic it is)
based on amount of CO2 - Determines if rapid breathing is needed to
release CO2 and increase O2.