Bonding Notes - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 27
Title:
Bonding Notes
Description:
Bonding Notes * An ion is an atom with a charge. Which atoms form cations and which form anions? H is not a metal ! NON-METALS form ANIONS (-) METALS form CATIONS ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:110
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Bonding Notes
1
Bonding Notes
2
An ion is an atom with a charge. Which atoms
form cations and which form anions?
H is not a metal !
NON-METALS form ANIONS (-)
METALS form CATIONS ()
3
- Ions form charges because
- of their number of
- valence electrons!!!
4
- Valence electrons are the electrons in the
highest occupied energy level (s p) of an
element
5
Quick Trick for Valence e-
- The group number tells the of valence e--Group
1 (1A) has one valence electron - -Group 2 (2A) has two valence electron
- Group 13 (3A) has three valence electrons
- Group 15 (5A) has five valence electrons
- Group 17 (7A) has seven valence electrons
- Group 18 (8A) has eight valence electrons (except
Helium which has two.
6
Na
Group number?
1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1
Electron configuration?
1A
Period?
Ne 3s1
3
Valence electrons
Cation or anion (loss or gain of e-)?
He 2s22p6
Why?
7
2
Ca
Group number?
Electron configuration?
Ar 4s2
2A
Valence electrons
Period?
4
Cation or anion (loss or gain of e-)?
Ne 3s23p6
Why?
8
2-
S
Group number?
Electron configuration?
Ne 3s2 3p4
6A
Valence electrons
Period?
3
Cation or anion (loss or gain of e-)?
Ne 3s23p6
Why?
9
Practice
- Page 9 charges of Ion Worksheet
10
- Octet Rule In forming compounds, atoms tend to
achieve the electron configuration of a noble
gas
11
Octet Rule
- Noble gas atoms are unreactive because their
electron configurations are especially stable. - This stability results from the fact that the
noble-gas atoms outer s and p orbitals are
completely filled by a total of eight electrons. - Other atoms can fill their outermost s and p
orbitals by sharing electrons through bonding. - Such bond formation follows the octet rule
Chemical compounds tend to form so that each
atom, by gaining, losing, or sharing electrons,
has an octet of electrons in its highest energy
level.
12
Lewis Electron Dots
- A visual representation of the valence electrons
of the atom. - The inner electrons and the nuclei are
represented by the elements symbol. - The dots representing the electrons are arranged
symmetrically around the symbol. - Chemical bonds are formed between atoms using the
unpaired valence electrons.
13
- We can represent the number of valence electrons
in a pictorial representation called - Electron Dot Diagrams
14
Now you practice!!
- Read the directions and complete the worksheet-
pg 19 --Valence e- and the Periodic table
worksheet
15
Atom/ ion Highest energy level Valance e- Lewis Dot structure / electron dot notation
O
C
F-
Ba
16
A chemical bond is a mutual electrical attraction
between the nuclei and valence electrons of
different atoms that binds the atoms together
- Ionic bonding
- Metal Nonmetal
- (Cation Anion)
- chemical bonds form electrical attraction.
- atoms GIVE UP electrons to other atoms.
- Form an Ionic Compound
- Covalent bonding
- Nonmetal Nonmetal
- SHARING of electrons between atoms.
- Form a Molecular Compound
- Trickycovalent bond but molecular compound!!
17
Ionic Compound
- Called Ionic bond Ionic Compound
- Made of metal and nonmetal (cation anion)
- Complete transfer of electrons
- Na Cl- NaCl
- electrically neutral salts -minerals in the
earths - Formula Unit (ExampleNaCl)
- a chemical formula of the smallest sample of an
ionic compound
18
(No Transcript)
19
Properties of ionic compounds
Crystalline solids (salts) Ions sit shoulder to
shoulder
High melting points (800ºC for NaCl- hard to
break bonds)
Conduct electricity in solution
High boiling points
Break easily (brittle)
Many dissolve easily in water - ions separate
20
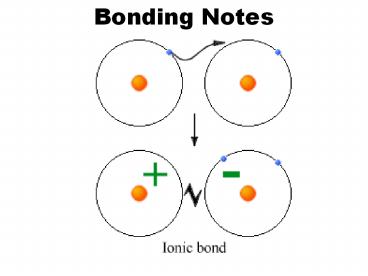
- Ionic Bond
- Electrons are transferred from one atom to
another.
21
(No Transcript)
22
Molecular Compounds/ Covalent Bonds
23
Molecular Compounds-Covalent Bonds
- e- are shared between nonmetal atoms
- Most atoms achieve complete octet
24
Properties of Molecular Compounds
- Non-metal Non-metal covalent bond
- 2 non-metals SHARE e- to become stable like noble
gases (think hold hands) - low melting boiling points (below 300ºC)
- solid, liquid, or gas at room temp.
- Molecular Formula
- carbon dioxide CO2 water H2O
- Molecules form shapes
25
Covalent Bonds
- Covalent bondingthe sharing of electrons between
two nonmetals. This creates a molecular compound
or molecule. - The goal is to attain eight valence
electronsstability - Do not forget that hydrogen is a nonmetal.
26
Multiple Covalent Bonds
- Single bondformed when one pair of electrons is
shared between two atoms. - Example H2
- Double bondinvolves two shared pairs of
electrons. - Example Ethene C2H4
- Triple bondinvolves three shared pairs of
electrons. - Example N2
27
Diatomic Molecules atoms that bond with
themselves
- NitrogenN2
- OxygenO2
- FluorineF2 (All the halogens)
- ChlorineCl2
- BromineB2
- IodineI2
- HydrogenH2
- Note These molecules start with the atomic
number seven form the shape of the number seven
on the PT. Dont forget hydrogen in the upper
left corner.
28
Practice Lewis Compounds
- Ionic Bonding activity- page 20 21
- Do page 20 together
29
Review Lewis Structures
- Shared pairsboth atoms can claim the electrons
to achieve the octet rule and become like noble
gas configurations - Unshared pairspairs of valence electrons that
are not shared between atomsalso called lone
pairs. - ExampleF2
30
Represent the following Compounds in as Lewis Dot
- 1. NaCl
- 2. K3P
- 3. CaO