PTCA - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 44
Title: PTCA
1
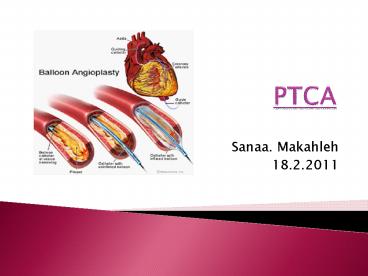
PTCA
- Sanaa. Makahleh
- 18.2.2011
2
Objectives
- What is Angiography ( PTCA).?
- How should I prepare?
- How is the procedure performed?
- What will I experience during and after the
procedure? - What are the benefits vs. risks?
3
What Is Coronary Angioplasty?
- Over time, a fatty substance called plaque can
build up in your arteries, causing them to harden
and narrow this condition is called
atherosclerosis. - Coronary angioplasty is a procedure used to open
blocked or narrowed coronary (heart) arteries. - The procedure improves blood flow to the heart
muscle.
4
Angioplasty is a common medical procedure. It may
be used to
- Improve symptoms of CHD, such as angina and
shortness of breath. (Angina is chest pain or
discomfort.) - Reduce damage to the heart muscle caused by heart
attack. A heart attack occurs if blood flow
through a coronary artery is completely blocked. - Reduce the risk of death in some patients.
5
Other Names for Coronary Angioplasty
- Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)
- Percutaneous intervention
- Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty
- Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty
- Balloon angioplasty
- Coronary artery angioplasty
6
(No Transcript)
7
How Is Coronary Angioplasty Done?
8
(No Transcript)
9
Blood vessel with arthrosclerosis treated with
balloon angioplasty Coronary stent
10
Preparation before the procedure
- Cardiologists do coronary angioplasties at
hospitals. - Doctor will take a medical history (including
the medicines you take), a physical exam, and
explain the procedure. - some routine tests, such as blood tests, an EKG
(electrocardiogram), and a CHEST X Ray. - Consent form
11
- If the patient smoke he should quit, as smoking
increases the risk of getting a wound infection
and slows recovery. - You should inform your physician of any
medications you are taking and if you have any
allergy, especially to contrast material/ dye - Also inform your doctor about recent illnesses
or other medical conditions.
12
- You may be asked to remove some or all of your
clothes and to wear a gown during the exam. - You may also be asked to remove jewelry,
dentures, eye glasses and any metal objects or
clothing that might interfere with the x-ray
images.
13
- Women should always inform their physician and
x-ray technologist if there is any possibility
that they are pregnant. - If an x-ray is necessary, precautions will be
taken to minimize radiation exposure to the baby.
14
- If you are breast feeding at the time of the
exam, you should ask your radiologist how to
proceed. - It may help to pump breast milk ahead of time
and keep it on hand for use after contrast
material has cleared from your body, about 24
hours after the test.
15
Once the angioplasty is scheduled, your doctor
will advise you
- When to begin fasting (not eating or drinking)
before the procedure. Often you have to stop
eating and drinking by midnight the night before
the procedure. - What medicines you should and shouldn't take on
the day of the angioplasty. - When to arrive at the hospital and where to go.
16
- Even though angioplasty takes only 1 to 2 hours,
you'll likely need to stay in the hospital
overnight or longer. - Your doctor may advise you not to drive for a
certain amount of time after the procedure, so
you may have to arrange for a ride home.
17
What To Expect During Coronary Angioplasty
- Coronary angioplasty is done in a special part of
the hospital called the cardiac catheterization
laboratory. The "cath lab" has special video
screens and x-ray machines. - In the cath lab, pt lie on a table. An
intravenous (IV) line will be placed in your arm
to give you fluids and medicines. The medicines
will relax you and prevent blood clots .
18
- To prepare for the procedure, the area where your
doctor will insert the catheter will be shaved
and then numbed ( local anesthesia). - During angioplasty, you'll be awake but sleepy
- ( conscious sedation).
19
- You will not feel the catheter in your artery,
but when the contrast material is injected, you
may have a feeling of warmth or a slight burning
sensation. - The most difficult part of the procedure may be
lying flat for several hours. During this time,
you should inform the nurse if you notice any
bleeding, swelling or pain at the site where the
catheter entered the skin.
20
- You may resume your normal diet immediately after
the exam. - You will be able to resume all other normal
activities 8 to 12 hours after the exam.
21
- Provide patient with proper information they need
about wearing of elastic stoking to prevent blood
clots forming due to immobility after the
procedure. - Patient can take over-the-counter painkillers
such as paracetamol. - Advice about how the pt can improve his diet and
lifestyle.
22
The Procedure
- The doctor will use a needle to make a small
hole in an artery in your arm or groin. - A thin, flexible guide wire will be inserted
into the artery through the small hole. - The needle is then removed, and a tube called a
sheath is placed over the guide wire and into the
artery.
23
- Video with animation
- Angioplasty
- stinting
24
What To Expect After Coronary Angioplasty
- After coronary angioplasty, pt will be moved to
a special care unit. - He stay there for a few hours or overnight.
- He must lie still for a few hours to allow the
blood vessel in your arm or groin (upper thigh)
to seal completely.
25
- Nurses will check pt heart rate and blood
pressure. - They also will check your arm or groin for
bleeding. - After a few hours, pt will be able to walk with
help. - The place where the catheter (Sheath) were
inserted may feel sore or tender for about a
week.
26
Going Home
- How much activity or exercise pt can do.
- When he should follow up with his doctor.
- What medicines you should take.
- What you should look for such as a signs of
infection around the area where the sheath was
inserted. - When he should call his doctor. For example, you
may need to call if you have shortness of breath
a fever or signs of infection, pain, or bleeding
.
27
- Your doctor will prescribe medicine to prevent
blood clots . - Taking your medicine as prescribed is very
important. - If you got a stent during angioplasty, the
medicine reduces the risk that blood clots will
form in the stent. - Blood clots in the stent can block blood flow and
cause a heart attack.
28
- Lifestyle changes may include
- Changing your diet.
- Quit smoking
- doing physical activity regularly.
- losing weight or maintaining a healthy weight.
- Reducing stress.
29
What Are the Risks of Coronary Angioplasty?
- Bleeding from the blood vessel where the
catheters were inserted. - Blood vessel damage from the catheters.
- An allergic reaction to the dye given during the
angioplasty. - An arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat).
- The need for emergency coronary bypass grafting .
30
- Damage to the kidneys caused by the dye used.
- (Acetylcysteine medication ) improve renal
function before the angioplasty - Heart attack .
- Stroke .
- Sometimes chest pain can occur during angioplasty
because the balloon briefly blocks blood supply
to the heart.
31
- The risk of complications is higher in
- People aged 75 and older.
- People who have kidney disease or diabetes .
- People who have poor pumping function in their
hearts. - People who have extensive heart disease and
blockages in their coronary (heart) arteries .
32
Sheath Removal Care Post Percutaneous
Transluminal Angioplasty (PTCA)
- Arterial sheaths will be removed by designated
- personnel, or a cardiologist.
- When
- No hematoma will develop at sheath site.
- Patient will maintain adequate perfusion to
affected extremity. - Discontinue heparin drip, as per doctor order.
33
- Verify that dressing supplies are available -
4x4 elastoplasts. - Have 0.9 NS IV infusion set up.
- Have Atropine available as per doctor order.
- Why ?
34
- Monitor HR, B/P and O2 saturation q 10 minutes x
30 minutes immediately after sheath removal. - Follow your hospital policy.
- Then monitor vital signs q 15 minutes x 1 hour,
then q 30 minutes x 1 hour, then q 1 hour x 2
hours. - Assess circulation, motion and sensation to both
feet. - Apply PRESSURE to site not less than 30 minute
and as per doctor order. ( FemoStop).
35
- FemoStop / Gold Compression Assist Device
- The FemoStop Gold Compression Assist Device
includes an integrated digital manometer and
transparent, inflatable dome that offer precise,
hands-free femoral artery or vein compression. - Compared to manual compression, FemoStop Gold
has been shown to help achieve homeostasis
quicker and more comfortably, while helping to
improve staff efficiency.
36
- Maintain bed rest while pressure is in place.
- No bending of groin is permitted. May turn side
to side for back care. - May resume diet, per doctor order.
- Obtain 12-lead EKG.
- Notify your doctor for
- a. Absent or diminished pulse in affected limb.
- b. Presence of a hematoma.
- c. Symptomatic bradycardia or other arrhythmia.
- d. Bleeding at insertion site.
- e. Recurrence of chest pain.
37
Sheath Removal Care Post Percutaneous
Transluminal Angioplasty (PTCA)
- PATIENT TEACHING
- Reinforce need for no bending of affected limb,
frequent vital signs and pulse checks, bed rest
per doctor order post sheath removal. - Instruct patient to report any numbness,
tingling or acute pain of affected limb, or
right/left lower quadrant abdominal pain.
38
- Reinforce the following to patient
- a. Signs and symptoms of bleeding or hematoma.
- b. Dont strain while you are on bed.
- c. Use a pillow as a splint for coughing.
- d. Dont strain to start urine stream.
- e. RN will monitor puncture site for redness,
swelling, hardness or abnormal drainage.
39
Side-effects of angioplasty
- These are the unwanted, but mostly temporary
effects of a successful treatment. - Chest pain while the balloon is being inflated in
the artery and some pain or bruising where the
catheter was inserted.
40
Complications of angioplasty
- The possible complications of any operation
include an unexpected reaction to the anesthetic,
excessive bleeding or developing a blood clot,
usually in the leg deep vein thrombosis. - Specific complications of angioplasty are rare
but can include the following
41
- The treated arteries gradually re-narrowing.
- If this happens the angioplasty may need to be
repeated. Stents may help to slow down the
narrowing. - Some people can have an allergic reaction to the
dye used in the angiogram. - Bleeding at the insertion site, retroperitoneal
bleeding or hematoma. - Arterial thrombosis and distal embolization.
42
- The angioplasty may need to be repeated straight
away or emergency coronary artery bypass graft
surgery may be needed to bypass the affected
veins. - The tip of the catheter can dislodge a clot of
blood or fatty plaque from the wall of a blood
vessel. It's possible for these to block an
artery leading to the heart or brain, causing a
heart attack or stroke.
43
In summary the complications are
- Serious complications needs emergency
interventions - Coronary spasm, restonosis, and thrombosis.
- Bleeding Hematoma at site of vascular
cannulation. - compromised blood flow to involved extremity.
- Contrast induced renal failure.
- Dysrhythmias
- Vasovagal response
44
- Reference
- Burns, S. Chulay, M. (2006). Essential of
Critical Care Nursing. American Association of
Critical Care Nurses. McGraw Hill