Male Reproductive Issues - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 50
Title:
Male Reproductive Issues
Description:
Title: Male Reproductive Issues Author: sharris Last modified by: Richard Freeman Created Date: 7/19/2003 12:51:06 AM Document presentation format – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:630
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Male Reproductive Issues
1
Male Reproductive Issues
- RICHARD E. FREEMAN MD MPH
- 2013
- LOCK HAVEN UNIVERSITY
2
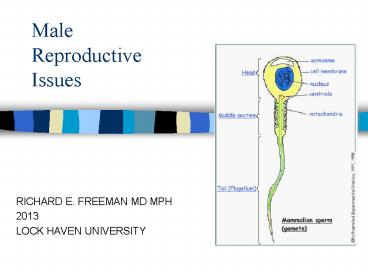
SPERMATOGENESIS
3
SPERMATOGENESIS
4
INFERTILITY
- DEFINITION Inability to conceive a child
- WHO
- A couple may be considered infertile if, after
two years of regular sexual intercourse, without
contraception, the woman has not become pregnant
(and there is no other reason, such as
breastfeeding or postpartum amenorrhea) - USA
- a woman under 35 has not conceived after 12
months of contraceptive-free intercourse - a woman over 35 has not conceived after 6 months
of contraceptive-free intercourse. - Primary infertility is infertility in a couple
who have never had a child. - Secondary infertility is failure to conceive
following a previous pregnancy.
5
- GENERAL
- 10 couples are affected by infertility
- 40 are from male factors!
- 30 of the 40 male factorscause is unknown
6
History
- DETAILED SEXUAL HISTORY
- DETAILED PREGNANCY HISTORY
7
Medical History
- Childhood illnesses
- post pubertal mumps orchitis and testicular
trauma or torsion - Cancer chemotherapy/radiation
- destroys germinal epithelium-dose dependent
- Diabetic neuropathy
- may result in either retrograde ejaculation or
impotence - DES exposure
- epididymal cysts or cryptochordism
- Precocious puberty
- adrenal-genital syndrome
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Delayed puberty
- Klinefelter's syndrome or idiopathic hypogonadism
8
History
- Hernia repair
- Cystic fibrosis (CBAVD)
- Mumps
- Thyroid disease
- Prolactinoma
9
History - Drugs
- Influence Reproductive cycle and male hormone
- anabolic steroids, cimetidine, and spironolactone
- Sperm Motility
- sulfasalazine and nitrofurantoin
- Decrease count and hormone interference
- Illicit drugs and alcohol (Liver failure)
- Seizure meds FSH
10
SOCIAL HISTORY
- Occupational and environmental toxins,
- Excessive heat-iron foundry worker
- Radiation- x-ray tech
- Illicit drug use
11
Physical Exam
- Look for HYPOGONADISM!
- poorly developed secondary sexual characteristics
- eunuchoidal skeletal proportions
- Arm span longer than height
- Crown to pubisPubis to floor ratio lt1
- sparse male hair distribution
- infantile genitalia
- muscle mass development
12
Physical Exam
- Hypogonadism may be associated with
- anosmia- inability to smell
- color blindness,
- cerebellar ataxia, hair lip, and cleft palate.
(Kallmann syndrome-isolated gonadotropin FSH/LH
deficiency with anosmia) - Thyroid
- Liver
- Neuro
- GU prostate exam
13
LABS
- FSH, LH
- DHT
- TSH
- ACTH
- GH
- Post coital
- DFI
- Anti sperm antibodies
- SPA (semen penetration assay)
14
Special Tests
- Vasography
- Testicular biopsy
- Ultrasound color flow
15
Sperm Count
- Fresh sample (to lab within 30 mins.) most sperm
in initial ejaculate - Male should be abstinent for 48 to 72 hours
- sperm concentration gt 20 million per ml
- total count gt 60 million/SAMPLE
- ejaculate volume gt 1.5 ml
- total motile count gt 30 million
- viable sperm gt 50
- normal shapes (morphology) gt 60
16
Sperm Terms
- Normal ejaculate
- Sperm concentration gt20 million/ml
- lt50 spermatozoa with forward progression
- lt30 spermatozoa with normal morphology
- No spermatozoa in the ejaculate
- No ejaculate
- Normozoospermia
- Normal ejaculate
- Asthenozoospermia
- Iatrogenic/abstinence
- Varioceles, cilia anomalies, Anti-spm Ab
- Teratozoospermia
- Azoospermia
- Aspermia
17
18
MALE INFERTILITYCLASSIFICATION
- PRE-TESTICULAR
- TESTICULAR
- POST-TESTICULAR
19
(No Transcript)
20
(No Transcript)
21
PRE-TESTICULAR CAUSES OF INFERTILITYsecondary
testicular failure
- Hypothalamic disease
- HYPOGONADROTROPIC HYPOGONADISM
- Isolated gonadotropin deficiency (Kallmann's
syndrome) - Isolated LH deficiency
- ("Fertile eunuch")
- Isolated FSH deficiency
- Congenital hypogonadrotropic syndromes
22
PRE-TESTICULAR CAUSES OF INFERTILITY secondary
testicular failure
- Pituitary disease
- Pituitary insufficiency
- (tumors, infiltrative processes, operation,
radiation) - Hemochromatosis
- EXOGENOUS HORMONES
- Estrogen excess
- Androgen excess
- Glucocorticoid excess
- Hyperprolactinemia
- Hyper and hypothyroidism
23
ENDOCRINE CAUSES
- EXOGENOUS HORMONES
- Estrogen excess
- Inhibits GnRH
- also direct effects on spermatogenesis
- Low FSH/LH/Testosterone
- ETIOLOGY
- Hepatic disease
- estrogen secreting tumor
- OBESITY
- Androgen excess
- Direct feedback inhibition on the hypothalmus
- Low intratesticular testosterone (necessary for
spermatogenesis - Endogenous-congenital adrenal hyperplasia,
tumors - Exogenous anabolic steroids
- Glucocorticoid excess
- Hyper and hypothyroidism
24
Hyperprolactinemia
- ETIOLOGY
- medications, stress, pituitary adenoma
- S/S
- erectile dysfunction
- low testosterone
- decreased libido
- Dx Screening-- low yield
- Prolactin level? MRI sella tursica
- TX
- Surgical excession of pituitary tumor (adenoma)
- Cabergoline(Dostinex)
- dopamine 2 receptor agonist
25
TESTICULAR CAUSES GENETICSPrimary Testicular
failure
- Y Chromosomal abnormalities (Klinefelter's
syndrome, XX disorder (sex reversal syndrome),
XYY syndrome) - Noonan's syndrome (male Turner's syndrome)
- Myotonic dystrophy
- Bilateral anorchia (vanishing testes syndrome)
- Sertoli-cell-only syndrome (germinal cell aplasia)
26
TESTICULAR CAUSESPrimary Testicular failure
- VARICOCELE
- Gonadotoxins (drugs, radiation)
- Orchitis
- Trauma
- Systemic disease
- (renal failure, hepatic disease, sickle cell
disease) - Defective androgen synthesis or action
- Cryptorchidism
- IDIOPATHIC-Majority
27
VARICOCELE
- Most common Attributable cause of Primary and
secondary infertility in males- 40 - Left sided
- -right angled insertion of L testicular vein into
the L renal vein- less valves - Theories
- Temperature elevation
- Reflux of toxic renal and adrenal metabolites
- Gonadotoxin metabolite clearance impairment
- Treatment LIGATION
- improves sperm count and semen quality
- INDICATIONS
- Palpable varicocele on exam
- known infertility
- Female partner has normal fertility
- Male- abnormal semen parameters
- - discomfort
- ADOLESCENT MALE Testicular hypotrophy (20
discrepancy in size)
28
POST-TESTICULAR CAUSES OF INFERTILITY SPERM
TRANSPORT
- Disorders of sperm transport
- Congenital disorders-
- Congenital Bilateral absence of the Vas deferens
(CBAVD) - - Cystic Fibrosis- CF transmembrane conductance
regulator test - Acquired disorders
- Functional disorders
29
POST-TESTICULAR CAUSES OF INFERTILITYSPERM
MOTILITY
- Disorders of sperm motility or function
- Congenital defects of the sperm tail
- Primary Ciliary Dyskinesia (PCD) effects other
organs with cilia - Maturation defects
- Globozoospermia
- round-headed sperm syndrome
- No acrosin-no penetration of zona pellucida
- Fibrous Sheath Dysplasia-
- stump tail syndrome
- short coiled immotile tails (genetic counseling
suggested) - Immunologic disorders-
- Infection
30
SPERM DNA FRAGMENTATION
- If greater than 30 have a DNA fragmentation
index (DFI) - Reduced fertility potential
- Reduction in term pregnancies
- Doubling in miscarriages
- Normal (morphology and motility) sperm may have
DNA fragmentation!
31
Causes of DFI
- Agegt46
- Pollution
- Smoking
- Febrile illness
- Drugs
- Radiation
- Chemicals
- Testicular cancer
- Varicocele
- Prolonged heat
- Hot tubs
- Truck drivers
- Cyclists
32
AZOOSPERMIA
Obstructive 40
TRUSTransrectal ultrasound
33
INFERTILITY Treatment
- Find the cause!!!!
- PESA/MESA
- microsurgical epididymal sperm aspiration
- TESE
- testicular sperm extraction
- IVF-
- invitro fertilization
- AIDS
- artificial insemination by donor
- TUREJD
- -Transurethral resection of the ejaculatory ducts
.shtml
34
INFERTILITY MEDICATIONS
- Gonadotropin-Releasing hormone agonists
- Gonadotropins- LH FSH
- Anti-estrogens
- - Clomiphene, Tamoxifen
- Aromatase inhibitors
- Testolactone /Anastrozole
- aromatase converts testosterone to estradiol
- Antioxidants
- -L-carnitine, Kallikrein, Thyroid
35
(No Transcript)
36
Male Menopause
37
(No Transcript)
38
Male Menopause - Andropause
- Occurs between 45-60 and is a gradual decline
over the years - 1/10 will experience hot flashes
- Also called
- Hypogonadism
- Male climacteric
- Viropause
- ADAM (androgen decline in aging males)
39
Andropause
- By age 80, testosterone levels are around
pre-pubertal levels!
40
Physical Symptoms
- Taking longer to recover from injuries and
illness. - Less endurance for physical activity.
- Feeling fat and gaining weight.
- Difficulty reading small print.
- Loss or thinning of hair.
- Sleep disturbances and fatigue.
- "Sore body syndrome" - stiffness.
- Excessive sweating.
- Cold hands and feet.
- Itching.
41
Psychological Symptoms
- Irritability.
- Indecisiveness.
- Anxiety and fear.
- Depression.
- Loss of self-confidence and joy.
- Loss of purpose and direction in life.
- Feeling lonely, unattractive and unloved.
- Forgetfulness and difficulty concentrating.
42
Sexual Symptoms
- Reduced interest in sex.
- Increased anxiety and fear about losing sexual
potency. - Increased fantasies about having sex with a new
and younger partner. - More relationship problems and fights over sex,
love and intimacy. - Loss of erection during sexual activity
(impotence).
43
Sexual Symptoms contd
- There is less of an urge to ejaculate.
- The force of ejaculation is not as strong as it
once was. The amount of the ejaculate is less and
one may have fewer sperm. - The testicles shrink and the scrotal sack droops.
The sack does not bunch up as much during
arousal.
44
Low T2 in men may cause
- Angina
- Atherosclerosis
- High blood cholesterol
- High blood triglycerides
- High blood pressure.
- High body mass index (obesity).
- Osteoporosis
45
Labs
- DHEA SulfateDihydrotesterone(DHT)EstradiolLHIG
F-1Testosterone, Total Free Total
Testosterone Free Testosterone
Free
- Thyroid Panel Free T3 Free
T4 TSH - PSA
46
Treatment
- Viagra, Levitra, Cialis
- Testosterone replacement therapy - TRT
- Side Effects
- Increase cholesterol
- Increase blood pressure
- Growth of body hair
- Male-pattern baldness
- Acne
- Fluid retention
- aggression
47
TRT Contd
- Monthly injections
- Patch - scrotum
- Implants q 4 mos
48
(No Transcript)
49
- QUESTIONS ?????
- SOURCE
- Wein Campbell-Walsh Urology 10th ed
- Chapter 21 Male infertility
- 2011 Saunders
- Can be accessed on MD Consult
50
(No Transcript)