Mesosome PowerPoint PPT Presentations
All Time
Recommended
Normal flora is the mixture of microorganisms (bacteria and ... ???? ???? ?????? Osmatic barrier ????? ??? ????? ??????? ???????. 2. ??????????? Mesosomes: ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Isolate organelles to study their function. isolation is accomplished by ... mesosome. 17. Prokaryotic Cell. basic cell shapes. coccus - sphere. bacillus - rod ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: Slide 1 Author: 004fs480 Last modified by: freddie.steinkamp Created Date: 10/17/2003 2:00:12 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Cell, discovery of cell, features of cells,cell theory,types of cells, features of cell,shape of cell .
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: Evolution of Eukaryotic Cells Author: ROSS KONING Last modified by: ROSS KONING Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3) Other titles
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Bacteria Structure and Function Prokaryote & Eukaryote Evolution Cellular Evolution Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells. Prokaryote = without a nucleus. Eukaryote = with a nucleus ... reproduction is asexual or sexual. reproduction is always asexual ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
3 domain system
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Bacteria Structure and Function Prokaryote & Eukaryote Evolution Cellular Evolution Current evidence indicates that eukaryotes evolved from prokaryotes between 1 and ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
This power point presentation describes about Best natural ankle arthritis treatment to ease foot swelling effectively.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
the prokaryotes kingdom monera
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Cell Structure and Function Cell Theory Based upon work of Theodor Schwann, Matthais Schleiden and Rudolph Virchow. All organisms are composed of cells Cells are the ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Bacilli: rods , 0.5-1 m in ... however, in certain bacilli they are composed of ... Bacillus and Clostridium. Identification of Bacteria. Pathogenesis ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
2.3 Eukaryotic Cells 2.3.1 Draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell. 2.3.2 Annotate the diagram from 2.3.1 with ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Homeostasis metabolism
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Bacterial Cell Structure and Function Lecture Cell Morphology Staphylococcus Diplococcus Streptobacilli Spirillum Spriochetes Bacterial Cell Structure and Function ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: Author: skyjx Last modified by: wsw Created Date: 6/5/2000 12:03:43 PM Document presentation format: Company
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: 1- Author: crystal Last modified by: Ayman Created Date: 11/11/2006 4:54:30 AM Document presentation format
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
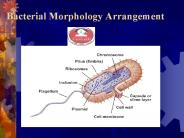
Bacterial Morphology Arrangement Robert Hooke (1635-1703) English Scientist First to use the microscope to observe cells Coined the term cell Anton van ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Chapter 4 Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells No Nucleus No Organelles Cell Wall of ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Cells Cytology Functions Of Life Metabolism chemical reactions necessary for life Response Homeostasis maintenance of internal stability (equilibrium) Growth ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Functional Anatomy of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Chapter 4 Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells Prokaryotic cells No Nucleus No Organelles Cell Wall of ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Archaeal cell walls Can be gram-positive or gram-negative Gram-positives often have a thick surface layer Gram-negatives often have a thin layer of protein or ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Objective To be able to describe the main features of bacterial cells and to understand the different nutritional and metabolic types. References
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: Lecture #12 Date _____ Author: Chris Hilvert Last modified by: klestinski Created Date: 11/17/2000 7:30:55 PM Document presentation format
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... Bacterial Cell Structures & Functions Size relationships among prokaryotes Bacterial Cell Structure Appendages - fdlagella, pili or fimbriae Surface layers ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Introduction to the Cell
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
rod shaped, Gram negative, lophotrichous. chemoheterotrophs. Pseudomonas ... Sulfolobus (hot springs of Yellowstone National Park) - oxidizes sulfur ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Eubacteria are
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: Bez nadpisu Author: Ji Schindler Last modified by: SCH Created Date: 9/1/2001 6:43:51 AM Document presentation format: P edv d n na obrazovce
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Biotechnologies and genetic engineering Genetic information is coded into DNA molecules as: A: genes B: codons ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
... Figure 4.13a Peptidoglycan in Gram-Positive Bacteria Figure 4.6 The Cell Wall Prevents osmotic lysis 4-7 Differentiate protoplast, spheroplast, and L form.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: PowerPoint Author: Last modified by: APPLE Created Date: 9/5/2002 8:15:01 AM Document presentation format: (4:3)
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: PowerPoint Author: Last modified by: PIN LING Created Date: 9/5/2002 8:15:01 AM Document presentation format:
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: PowerPoint Author: Last modified by: PIN LING Created Date: 9/5/2002 8:15:01 AM Document presentation format:
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Cell Envelope. Plasma membrane phospholipid bilayer with embedded and peripheral proteins ... Cell membrane has. hydrocarbons in place. of fatty acids ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
CHAPTER 4 The Organization of Cells Chapter 4: The Organization of Cells The Cell: The Basic Unit of Life Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Organelles that Process ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Characteristics of microbes Major groups of microorganisms Viruses Not cells; contain either RNA or DNA in envelope; can only multiply in living cells.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Movement across membrane for many substances is controlled ... Prevents osmotic lysis. In some cases recognized by host immune system. Target for antibiotics. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Prokaryotes Lack nuclei Typically lack or have very few internal membranes Cytoplasm contains ribosomes, storage granules that hold glycogen, lipid, or phosphate ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Cell Size, Shape and Arrangement. Cell Shape - others ... Protoplast. Includes: inclusion bodies and ribosomes. Prokaryotic Structure. Cytoplasmic Matrix ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Growth: cell enlargement, cell number. Evolution: long term adaptation ... All of these nutritional modes are found among prokaryotes! ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Ultrastructure of bacterial cell. Form and Function. Structure of a Prokaryotic Cell Bacterial Morphology and Ultrastructure Only two types of cells are produced by ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Contenen una petita quantitat d'ADN diferent de la del nucli i uns ... que cont l ADN i que transmet l ARN. ESTRUCTURA: ... de la circulaci molecular de ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: Slide 1 Author: Suslow Last modified by: Admin Created Date: 1/4/2005 12:33:20 AM Document presentation format: (4:3) Company: UC Davis
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Ch 4 Functional anatomy of Bacteria and other Microbes Or The differences between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic cells Proks and euks are similar in chemical composition ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Outline Cell Theory Cell Size Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Organelles Nucleus Endomembrane System Cytoskeleton Centrioles, Cilia, and Flagella Cell Theory A ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Biochemistry 'The chemistry of the living cell.' Biochemistry can be divided into two levels of study: ... Roots of modern biochemistry. China - 4th century BC ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Cells Topic 2 Chapters 4,5,9
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chapter 14 The Prokaryotic Chromosome: Genetic Analysis in Bacteria Outline of Chapter 14 General overview of bacteria Range of sizes Metabolic activity How to grow ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
The differences between Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic cells. Proks and euks are similar in ... Can present taxis. Negative. Positive. Monotrichous. Peritrichous ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cellular Structure * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Inclusion Bodies 6. gas vacuoles - storage of metabolic gases such ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
I love to live near the good restaurants and eat when I please. ... I can survive adverse conditions or I can ensure that those that follow me do. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
formed by injection of veins. formed by metamorphic segregation (chemical migration) ... irregular or cross-cutting 'granitic' bands or veins in a darker, ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Outline Cell Theory Cell Size Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells Organelles Nucleus Endomembrane System Cytoskeleton Centrioles, Cilia, and Flagella Cell Theory A ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view