Sarcomere PowerPoint PPT Presentations
All Time
Recommended
Title: Muscle Physiology Author: Donna Drontle Last modified by: drontld Created Date: 9/14/2002 12:55:59 AM Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3)
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... affect the actin-myosin interaction, thereby causing contractile dysfunction. ... DCM Associated Mutations in Non-Contractile Proteins ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
The Muscular System Muscle Tissues Skeletal Muscle Tissue Smooth Muscle Tissue Cardiac Muscle Tissue Muscle Anatomy Sarcomere Sarcomere Sarcomere Actin and Myosin ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
The Muscular System Muscle Tissues Skeletal Muscle Tissue Smooth Muscle Tissue Cardiac Muscle Tissue Muscle Anatomy Sarcomere Sarcomere Sarcomere Actin and Myosin ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Physiology Review The SARCOMERE is the functional unit of the muscle. A sarcomere is found between two Z lines. Neural Stimulation Phase 1 of Muscle Physiology: The ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Fiber architecture Quantification of muscle structure Relationship to functional capacity Muscle as one big sarcomere Independent fibers/fascicles
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Perimysium: Around fascicles (bundles of muscle fibers) ... Sarcomere: contractile subunits. Z lines: separate sarcomeres. A (Dark) bands - length of myosin ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... Muscle fiber shortening occurs as myosin pulls on actin in a repetitive ratcheting fashion Thin filaments move toward the center of the sarcomere Activation ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Muscle Physiology Dynamics of Muscle Contraction MMHS Anatomy Thick and Thin Filaments A. Muscle movement (=contraction) occurs at the microscopic level of the sarcomere.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Skeletal muscle structure from the sarcomere molecular components to the ... Enlarged axon terminal =bouton. Somatic motor neuron axon. Muscle fiber (cell) ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Filaments and the Sarcomere ... They are arranged in compartments called sarcomeres, separated by Z discs. ... arranged so lacks sarcomeres. Sliding of thick ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Myofilament Substructure: Cross-Bridges. Myofilament Substructure: ... Cylindrical. Multinucleated. 5 to 100 m in diameter. Electron Micrograph of Sarcomere ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
... Impulses signal calcium to be released from adjacent terminal cisternae Are associated with paired terminal cisterns to form triads that circle each sarcomere; ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Skeletal Muscle Microscopic Anatomy Fig. 6.3, pg. 159 The myofibrils are chains of tiny contractile units called sarcomeres, which are aligned end to end
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Frank-Starling Law of the heart. 40 60 80 100 120 140 160. Percentage sarcomere length ... intrinsic (Starling's Law) extrinsic (principally autonomic) Stroke ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Contain contractile elements. SKELETAL MUSCLE. Microscopic Anatomy: ... Smallest contractile. unit of a muscle fiber. Myofibril consists of. linked sarcomeres ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Individual muscle fibers are wrapped and held together by connective tissue ... Contractile elements of skeletal muscle cells. Sarcomere. Functional Unit. See Diagram! ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
1. Bone marrow cells promote myocardial regeneration: ... Unknown molecular signal(s) Cardian myosin. a-Sarcomeric actin. Connexin 43. Csx/Nkx2.5. MEF2. GATA-4 ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
premyofibrils, nascent myofibrils and mature myofibrils. ... develop into mature sarcomeres. ... The earliest precursors of mature thin and thick filaments FORM ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Sarcomere- segment of myofibril from one Z line to the next, contractile unit of muscle. ... Contractile unit of muscle. A muscle cell. Thin connective tissue ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
The sliding filament mechanism, in ... Contractile 'cells' Locations of the 3 muscle types: ... 3) The sarcomere is the contractile unit of the muscle cell. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Gross Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle Muscle fiber Endomysium Fascicle Perimysium Epimysium Deep facia Connective Tissue Sheaths Endomysium Perimysium Epimysium Collagen ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
KEY CONCEPT Muscles are tissues that can contract, enabling movement. Humans have three types of muscle. The muscular system moves substances throughout the body ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Muscle Teamwork Agonist (prime mover): - the muscle or group of muscles producing a desired effect Antagonist: - the muscle or group of muscles opposing the action
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Chapter 17 Musculature System The Musculature System The Musculature System Includes 3 types of Muscle: Striated, Smooth & Cardiac Function of the Muscles: Provide ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Muscle Physiology Anatomy & Physiology/Tissues, Bones and Muscles Muscle Functions Muscles have four major roles in our bodies: Produce movement Maintain posture ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
The Muscular System and Methods of Movement Functions Movement Protection Body Form Heat production Muscle Cells Cardiac Heart Muscle Involuntary Smooth Intestinal ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Muscle Physiology Lecture Outline Muscle Function Muscle Characteristics Muscle Tissue Types Skeletal Muscle General Functions of Skeletal Muscle Functional Anatomy ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Muscle Structure and Function Chapter 9 Part 3 Muscle Movements and Contractions Structures of a skeletal muscle fiber Neuromuscular Junction Connects the nervous ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Muscle Anatomy Outer part of skeletal muscle: Tendon: At the end of muscle fibers. Attach the muscle to the bone. Fascia: Dense connective tissue covering entire muscle.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
The Muscular System ANS 215 Anatomy & Physiology of Domesticated Animals
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Muscle Physiology ... Chapter 6
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: Chapter 9 MUSCLE TISSUE Author: FBinstruct Last modified by: asus Created Date: 10/13/2003 9:25:35 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show (4:3)
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Your grade: in class and homework, experiment, 3 X exams... Final Plus up to 3 points for discussions Exam 3 in-class Th 5/5 take-home will be due Th 4/28 Final exam ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
According to contraction speed and resistance to fatigue during ... acidosis. Slow-twitch fibers. Fatigue slowly. Oxidative phosphorylation for ATP production ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
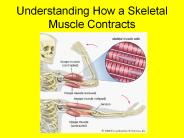
Understanding How a Skeletal Muscle Contracts A skeletal muscles contraction begins at the neuromuscular junction. What do you think the definition of ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: MUSCULAR SYSTEM (muscles, tendons) Author: CICH22 Last modified by: CARCICH, MICHELE Created Date: 12/4/2005 6:38:38 PM Document presentation format
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
MUSCLE DR. AYISHA QURESHI ASSISTANT PROFESSOR MBBS, MPhil Sarcotubular System The sarcoplasm of the myofibril is filled with a system of membranes, vesicles and ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
KEY CONCEPT The skeletal system includes bones and tissues that are important for supporting, protecting, and moving your body.
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
What is the function of: Cone cells? Rod cells? The perceived pitch of a sound is dependent on ? What is the difference between perception and sensation?
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Muscle Tissue Myology The scientific study of muscles Orthopedics Branch of medicine concerned with the prevention or correction of disorders of the musculoskeletal ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Title: Chpt. 49 Author: OCSD Last modified by: OCSD Created Date: 4/19/2006 11:00:38 PM Document presentation format: On-screen Show Company: Mobile Lab
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Chapter 10: Muscle Tissue
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Title: Bio211 Lecture 16 Subject: Muscle Struct & Physio Author: Greg Erianne Last modified by: Gregs Desktop Created Date: 1/14/2003 8:16:27 PM Document presentation ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Muscle Physiology Chapter 11
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Action and Support: The Muscles and Skeleton Chapter 34: Muscular and Skeletal System Muscle Tissue (Muscle = little mouse ): Composed of single cell type ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
CLIL SCIENCE Muscle tissue and muscle contraction Rosalie Crawford - Veronica Revel Fondazione Liceo Linguistico Courmayeur How does it happen?? How do our muscles work??
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
a1 In the thin filaments actin proteins are strung together like a bead of pearls In the thick filaments myosin proteins look like golf clubs bound together Muscle ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
of nuclei- multinucleate; formed by fusion of embryonic cells ... Ageing can increase flavor and tenderness for up to 1 month. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
SKELETAL MUSCLE NOTES Anterior forearm Anterior thigh Lateral thigh Posterior thigh Terms epi = upon peri = around endo = within or inner mys = muscle sarco = flesh ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
Both demonstrate 'striations' or stripes when seen with a microscope ... Functional contractile unit of striated muscle. 2-3 mm in length. Striations ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Standard 9 h. Students know the cellular and molecular basis of muscle ... 4- Binding of new ATP releases myosin head. Creatine phosphate~ supplier of phosphate to ADP ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Muscle Exam Review. Exam February 1st. Muscle Groups ... Know their names and do not rely on a word bank you won't have one for the test. ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Ninth Edition Marieb w Hoehn Chapter 9 Muscles and Muscle Tissue Lecture 16 *
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to download
In order to move all animals require muscle activity in response to nervous system input. ... Myosin cross-bridges attach and detach, powered by ATP pulling the actin ...
| PowerPoint PPT presentation | free to view