FIXED EXCHANGE RATES - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title:
FIXED EXCHANGE RATES
Description:
CB intervention in the foreign exchange market. Result: Base Money is endogenous ... money supply is totally endogenous. A Simple Model (Krugman 1979) fixed ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:58
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: FIXED EXCHANGE RATES
1
FIXED EXCHANGE RATES and Foreign Exchange
Intervention
1
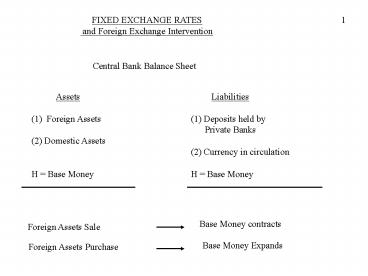
Central Bank Balance Sheet
Assets (1) Foreign Assets (2)
Domestic Assets H Base Money
Liabilities (1) Deposits held by
Private Banks (2) Currency in circulation H
Base Money
Base Money contracts
Foreign Assets Sale
Base Money Expands
Foreign Assets Purchase
2
2
Fixed Exchange Rate
S
fixed exchange rate
1,2
return
1
output shock
2
Automatic increase in M following CB
intervention in the foreign exchange market.
Result Base Money is endogenous
3
3
The Sustainability of Fixed Exchange Rate Regime
demand for money
(1)
interest parity
(2)
4
Purchasing Power Parity
4
(3)
Substitute (2) (3) into (1)
(4)
5
Fixed Exchange Rate
5
money supply is totally endogenous
A Simple Model (Krugman 1979)
fixed exchange rate
flexible exchange rate
6
6
International Reserves
7
7
Central Bank Balance Sheet
Domestic Credit Expands Indefinitely
rate of expansion
Shadow Exchange Rate
8
8
Logarithmic Approximation
f(x0)
9
9
The Shadow exchange rate is a market-based
exchange rate when the central bank has no
international reserves
10
10
Implications (1) Instantaneous Collapse
s
time
0
(2) Calculations
11
11
s
time
T
T
T
time
T
time
T
i
time
T
12
12
Sustainability of Fixed Exchange Rate
fixed shadow
(1)
time
no budget deficit (?0)
(2) imperfect asset substitutability (a)
regulating capital inflows (b) risk premium
? is a function of external debt
13
13
if ? is a function of external debt (B) minus
domestic assets (A) a sterilized intervention
which keeps M constant switches
reserves (negative external debt) for domestic
assets would change the risk premium, and change
domestic interest rate. Sales of reserves
accompanied by purchase of domestic bonds will
raise ? and i.