Cosmology Theory PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Cosmology Theory
1
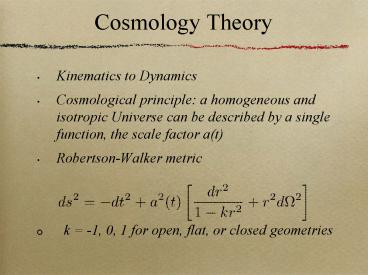
Cosmology Theory
- Kinematics to Dynamics
- Cosmological principle a homogeneous and
isotropic Universe can be described by a single
function, the scale factor a(t) - Robertson-Walker metric
- k -1, 0, 1 for open, flat, or closed
geometries
2
Friedmann Equations
- Combine R-W metric and General Relativity to give
the equations of motion for a(t)
Newtons Law of Gravitation
Conservation of Energy
? - Energy density of the Universes
constituents p - Pressure of the Universes
constituents
Acceleration
3
Normal vs Strange
- Solve Friedmann Equations depending on what the
Universe is made of (k0)
Non-relativistic matter
Radiation
Dark Energy
Cosmological Constant w-1
4
Universe Constituents Dynamics
By measuring a(t), we can determine the
constituents of the Universe, their relative
amounts, and properties of the dark energy.
5
Measuring Universes History and Fatewith
Standard Candles
6
SNAP Telescope
- 2-m primary aperture, 3-mirror anastigmatic
design. - Provides a wide-field flat focal plane.
7
Instrumentation Imager
A large solid-angle camera (0.7 square degrees)
provides multiplexed supernova discovery and
followup. Covers wavelength region of interest,
0.35- 1.7 microns. Fixed filter mosaic on top
of the imager sensors. 3 NIR bandpasses. 6
visible bandpasses. Coalesce all sensors at one
focal plane. 36 2k x 2k HgCdTe NIR sensors
covering 0.9-1.7 µm. 36 3.5k x 3.5k CCDs
covering 0.35-1.0 µm.
CCDs Guider HgCdTe
Spectrograph
Spectr. port
rin6.0 mrad rout13.0 mrad rin129.120 mm
rout283.564 mm
8
Instrumentation Imager
0.7 square degrees 9 passbands 0.35-1.7 microns
REU program, N.A.Sharp/NOAO/AURA/NSF
9
Spectrograph
Slicer Mirror Array
Telescope Focal Plane
Telescope
- Data cube
- Reduces pointing accuracy requirement
- Simultaneous SNe and host galaxy spectra
- Internal beam split to visible and NIR.
?
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.