Chapter 4: Syntax analysis PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Chapter 4: Syntax analysis
1
Chapter 4 Syntax analysis
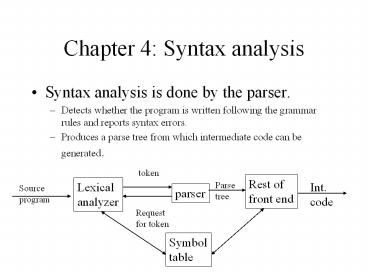
- Syntax analysis is done by the parser.
- Detects whether the program is written following
the grammar rules and reports syntax errors. - Produces a parse tree from which intermediate
code can be generated.
token
Rest of front end
Lexical analyzer
Int. code
Parse tree
Source program
parser
Request for token
Symbol table
2
- The syntax of a programming language is described
by a context-free grammar (Backus-Naur Form
(BNF)). - Similar to the languages specified by regular
expressions, but more general. - A grammar gives a precise syntactic specification
of a language. - From some classes of grammars, tools exist that
can automatically construct an efficient parser.
These tools can also detect syntactic ambiguities
and other problems automatically. - A compiler based on a grammatical description of
a language is more easily maintained and updated.
3
- A grammar G (N, T, P, S)
- N is a finite set of non-terminal symbols
- T is a finite set of terminal symbols
- P is a finite subset of
- An element is written as
- S is a distinguished symbol in N and is called
the start symbol. - Language defined by a grammar
- We say aAb derives awb in one step, denoted as
aAbgtawb, if A-gtw is a production and a and b
are arbitrary strings of terminal or nonterminal
symbols. - We say a1 derives am if a1gta2gtgtam, written as
a1gtam - The languages L(G) defined by G are the set of
strings of the terminals w such that Sgtw.
4
- Example
- A-gtaA
- A-gtbA
- A-gta
- A-gtb
5
- Chomsky Hierarchy (classification of grammars)
- A grammar is said to be
- regular if it is
- right-linear, where each production in P has the
form, or
. Here, A and B are non-terminals and w is a
terminal - or left-linear
- context-free if each production in P is of the
form , where and - context sensitive if each production in P is of
the form where - unrestricted if each production in P is of the
form where
6
- Languages specified by different types of
grammars - Language1 a, aa, aaa, aaaa, .
- Language2 ab, aabb, aaabbb, aaaabbbb,
- Language3 abc, aabbcc, aaabbbccc,
7
- Context-free grammar is sufficient to describe
most programming languages. - Example a grammar for arithmetic expressions.
- ltexprgt -gt ltexprgt ltopgt ltexprgt
- ltexprgt -gt ( ltexprgt )
- ltexprgt -gt - ltexprgt
- ltexprgt -gt id
- ltopgt -gt - /
- derive -(id) from the grammar
- ltexprgt gt -ltexprgt gt - (ltexprgt) gt-(id)
- sentence a strings of terminals that can be
derived from S - sentential form a strings of terminals or none
terminals that can be derived from S.
8
- derive id id id from the grammar
- EgtEEgtEEEgtEEidgtEididgtididid
- leftmost/rightmost derivation -- each step
replaces leftmost/rightmost non-terminal. - EgtEEgtidEgtidEEgtididEgtididid
- Parse tree
- A parse tree pictorially shows how the start
symbol of a grammar derives a specific string in
the language. Given a context-free grammar, a
parse tree has the following properties - The root is labeled by the start symbol
- Each leaf is labeled by a token or the empty
string - Each interior node is labeled by a nonterminal
- If A is a non-terminal labeling some interior
node and abcdefg..z are the labels of the
children of that node from left to right, then
A-gtabcdefg..z is a production of the grammar.
9
- The leaves of the parse tree read from left to
right is called yield of the parse tree. It is
equivalent to the string derived from the
nonterminal at the root of the parse tree. - An ambiguous grammar is one that can generate two
or more parse trees that yield the same string. - E.G
- string -gt string string
- string-gtstring - string
- string -gt0123456789
- stringgtstring string gtstring - string
string gt 9 -5 2 - stringgtstring - stringgtstring - string string
gt9-52