Basics: PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title: Basics:
1
Basics
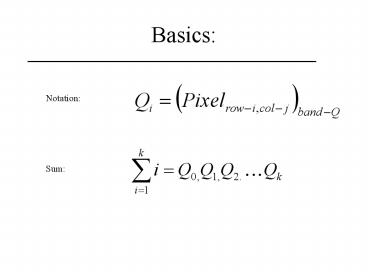
Notation
Sum
2
PARAMETERS
the statistical average the central
tendency the spread of the values about the
mean
MEAN Sample Variance Standard Deviation
3
Covariance
measures the tendencies of data file values for
the same pixel, but in different bands, to vary
with each other in relation to the means of their
respective bands.
4
Dimensionality
N the number of bands dimensions . an (n)
dimensional data (feature) space
Measurement Vector
Mean Vector
Feature Space - 2dimensions
190 85
Band B
Band A
5
Spectral Distance
a number that allows two measurement vectors to
be compared
6
terms
- Parametric based upon statistical parameters
(mean standard deviation) - Non-Parametric based upon objects (polygons) in
feature space - Decision Rules rules for sorting pixels into
classes
7
ClusteringMinimum Spectral Distance -
unsupervised
Band B
Band A
Band B
Band A
1st iteration cluster mean
2nd iteration cluster mean
8
Classification Decision Rules
- Non-Parametric
- parallelepiped
- feature space
- Unclassified Options
- parametric rule
- unclassified
- Overlap Options
- parametric rule
- by order
- unclassified
- Parametric
- minimum distance
- Mahalanobis distance
- maximum likelihood
- If the non-parametric test results in one unique
class, the pixel will be assigned to that class. - if the non-parametric test results in zero
classes (outside the decision boundaries) the the
unclassified rule applies either left
unclassified or classified by the parametric rule - if the pixel falls into more than one class the
overlap rule applies left unclassified, use the
parametric rule, or processing order
9
Parallelepiped
- Maximum likelihood
- (bayesian)
- probability
- Bayesian, a prior (weights)
Band B
Band A
Minimum Distance
Band B
Band A
10
GeoStatistics
- Univariate
- Bivariate
- Spatial Description
11
Univariate
- One Variable
- Frequency (table)
- Histogram (graph)
- Do the same thing (i.e count of observations in
intervals or classes - Cumulative Frequency (total below cutoffs)
12
Summary of a histogram
- Measurements of location (center of distribution
- mean (m µ x )
- median
- mode
- Measurements of spread (variability)
- variance
- standard deviation
- interquartile range
- Measurements of shape (symmetry length
- coefficient of skewness
- coefficient of variation
13
Bivariate
Scatterplots
Correlation
Linear Regression
slope constant
14
Spatial Description
- Data Postings symbol maps (if only 2 classes
indicator map - Contour Maps - Moving Windows
gt heteroscedasticity (values in some region
are more variable than in others) - Spatial
Continuity (h-scatterplots
Spatial lag h (0,1) same x, y1
h(0,0) h(0,3) h(0,5)
correlation coefficient (i.e the correlogram,
relationship of p with h
15
- Correlogram p(h) the relationship of the
correlation coefficient of an h-scatterplot and h
(the spatial lag) - Covariance C(h) the relationship of
thecoefficient of variation of an h-scatterplot
and h - Semivariogram variogram moment of
inertia
OR half the average sum difference between the x
and y pair of the h-scatterplot OR for a h(0,0)
all points fall on a line xy OR as h
points drift away from xy