Physical Characteristics of Streams PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Physical Characteristics of Streams
1
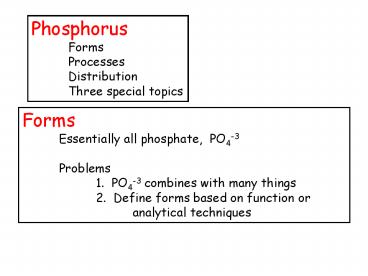
Phosphorus Forms Processes Distribution Three
special topics
Forms Essentially all phosphate,
PO4-3 Problems 1. PO4-3 combines with many
things 2. Define forms based on function or
analytical techniques
2
Functional forms -- what we think is in the
water I. Dissolved a. dissolved inorganic
PO4-3 b. dissolved polyphosphates c.
Dissolved organic PO4
II. Particulate a. Organic b. PO4 adsorbed
to organic particles c. PO4 adsorbed to
inorganic particles d. Particles of insoluble
P compounds III. Gaseous -- phosphene PH3
3
- Light spectrophotometry
- Combine target chemical with another chemical
that produces a color - Measure the intensity of the color
4
Analytical forms
SRP -- soluable reactive phosphorus
Filterable
TDP -- total dissolved phosphorus
Dissolved organic phosphorus -- DOPTDP-SRP
Sample
Non-filterable
Particulate phosphorus -- PP
Total phosphorus -- TP
PPTP-TDP
5
Major questions SRP PO4? TP all
phosphorus?
6
Phosphorus reactions I. Reactions with cations
(A) a. Calcium b. Redox metals Fe, Mn, Al
O2 present O2
absent High redox potential (Eh) Low
redox potential Ferric iron Fe3
Ferrous iron Fe2 Fe(OH)3
Fe2 Precipitates
In solution Complexes with PO4 PO4
PO4 in solution
7
Phosphorus reactions (cont.) II. Adsorption to
particles (A, B)
III. Autotrophic immobilization (C)
IV. Heterotrophic immobilization (B)
V. Mineralization of P (D)
8
Precipitation (P) Adsorption and Heterotrophic
Immobilization (H) Autotrophic Immobilization
(A) Mineralization (M) Excretion (E) Death and
Feeding (F) Leaching (L)
Runoff
N
-
M
L
A
L
L
I
L
E
F
Death
H
A
F
F
F
M
M
P
Sedimentation
Sediments
9
Phosphorus distribution Thermally
stratified Oligotrophic Orthograde O2 curve
Phosphorus distribution Thermally
stratified Eutrophic Clinograde O2 curve
10
Phosphorus in sediment Sediment concentrations
may be much higher than concentrations in the
overlying water
11
The role of animals on the phosphorus cycle 1. A
source of P 2. Form of P 3. Bioturbation 4.
Diel migration
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.