substitution PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: substitution
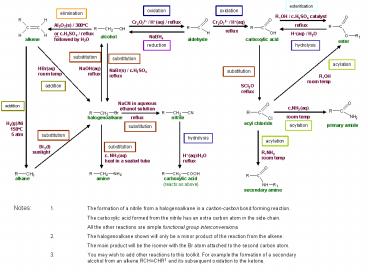
1
esterification
oxidation
oxidation
elimination
Cr2O72- / H(aq) / reflux
H(aq) / H2O
NaBH4
reduction
hydrolysis
substitution
substitution
acylation
HBr(aq) room temp
NaOH(aq) reflux
NaBr(s) / c.H2SO4 reflux
substitution
R1OH room temp
addition
SCl2O reflux
addition
H2(g)/Ni 150?C 5 atm
acylation
substitution
substitution
hydrolysis
acylation
substitution
Br2(l) sunlight
R1NH2 room temp
c. NH3(aq) heat in a sealed tube
H(aq)/H2O reflux
Notes 1. The formation of a nitrile from a
halogenoalkane is a carbon-carbon bond forming
reaction. The carboxylic acid formed from the
nitrile has an extra carbon atom in the
side-chain. All the other reactions are simple
functional group interconversions. 2. The
halogenoalkane shown will only be a minor product
of the reaction from the alkene. The main
product will be the isomer with the Br atom
attached to the second carbon atom. 3. You may
wish to add other reactions to this toolkit. For
example the formation of a secondary alcohol
from an alkene RCHCHR1 and its subsequent
oxidation to the ketone.
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.