BCHOBI 812 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 18
Title:
BCHOBI 812
Description:
Rhodopsin: A specialized 7TM receptor mediating the visual cycle: ... Lysine-296 of rhodopsin forms a protonated Schiff base with 11-cis-retinal in the dark: ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:107
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: BCHOBI 812
1
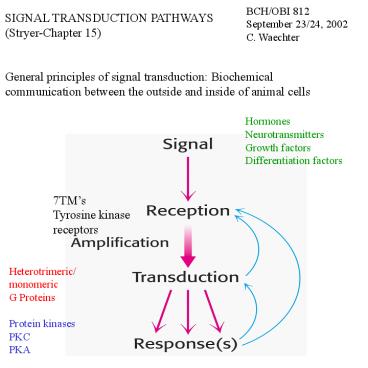
BCH/OBI 812 September 23/24, 2002 C. Waechter
SIGNAL TRANSDUCTION PATHWAYS (Stryer-Chapter
15) General principles of signal transduction
Biochemical communication between the outside and
inside of animal cells
Hormones Neurotransmitters Growth
factors Differentiation factors
7TMs Tyrosine kinase receptors
Heterotrimeric/ monomeric G Proteins Protein
kinases PKC PKA
2
Common second messengers mediating
intracellular communication
3
Protein phosphorylation Mechanism for
information transfer
3. Protein phosphorylation is a common means of
information transfer. Many second messengers
elicit responses by activation protein kinases.
These enzymes transfer phosphoryl groups from ATP
to specific serine, threonine, and tyrosine
residues in proteins.
4
- Seven-transmembrane (7TM) -helix
receptors change conformation in response to
binding external ligands and activate G-proteins - Some hormones using cAMP as a second messenger
- 1. Epinephrine
- 2. Glucagon
- 3. Follicle-stimulating hormone
- 4. Calcitonin
- 5. Parathyroid hormone
- General structure of 7TM receptors
5
Role of heterotrimeric G-protein in the
activation of adenyl cyclase Stimulation of
glycogen breakdown by epinephrine (Stryer-p. 587)
(64 kDa)
Hydrolysis by GTPase acctivity
Phosphorylates Ser/Thr residues in Target
proteins
6
ACTIVATION OF PKA BY cAMP
7
Signal termination by phosphorylation and
arrestin-binding
8
Cleavage of phosphatidylinositol bisphosphate
(PIP2) by phospholipase Cb produces two second
messengers, IP3 and diacylglycerol (DAG)
(ER)
Activated by C Ca DAG PS
9
Modular structures of phospholipase Cs
10
Modular structures of protein kinase Cs (PKC)
Activation by DAG/PS/Ca
DAG
PS/Ca
Ala replaces Ser/Thr
Phosphorylates Ser/Thr residues in Target proteins
PS
11
Binding of EGF to its receptor leads to
activation of Ras, a monomeric G-protein, via
interactions with SH2 domains.
Ras 20-25 kDa small monomeric G protein
Grb-2
12
Rhodopsin A specialized 7TM receptor mediating
the visual cycle Anatomy of a rod cell
(Stryer-p. 908)
13
Lysine-296 of rhodopsin forms a protonated Schiff
base with 11-cis-retinal in the dark
Isomerization of 11-cis-retinal to
11-trans-retinal is triggered by photons
14
Conversion of rhodopsin to metarhodopsin II (R)
activates heterotrimeric G-protein called
transducin which stimulates phosphodiesterase
Plasma membrane Of outer segment
Disc membrane
15
Hydrolysis of cGMP closes cGMP-gated channel,
resulting in lower cytosolic Ca levels
hyperpolarization of retinal rod cell membrane
triggers neuronal signalling
16
Mechanism for re-setting visual cycle
- Hydrolysis of GTP on a-subunit.
- Phosphorylation of cytoplasmic loop
- of rhodopsin (opsin) allowing b-arrestin
- to bind.
- Re-synthesis of cGMP by guanyl cyclase
- is stimulated by lower Ca levels.
17
Recovery mechanism Lower Ca increases guanyl
cyclase activity restoring cGMP levels and
re-opening of cGMP-gated channel
18
THE END