SCOP Sample ppHierarchy PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title: SCOP Sample ppHierarchy
1
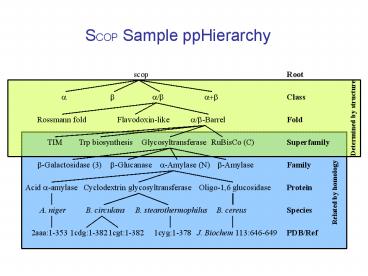
SCOP Sample ppHierarchy
scop
Root
a
b
a/b
ab
Class
Determined by structure
Rossmann fold
Flavodoxin-like
a/b-Barrel
Fold
TIM
Trp biosynthesis
Glycosyltransferase
RuBisCo (C)
Superfamily
b-Glucanase
a-Amylase (N)
b-Amylase
b-Galactosidase (3)
Family
Acid a-amylase
Oligo-1,6 glucosidase
Cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase
Protein
Related by homology
A. niger
B. cereus
B. circulans
B. stearothermophilus
Species
2aaa1-353
J. Biochem 113646-649
1cdg1-382
1cgt1-382
1cyg1-378
PDB/Ref
2
Structural classification of RNAhttp//scor.berke
ley.edu
- 579 PDB entries classified
- Structural, Functional and Tertiary Interactions
- Search by
- PDB or NDB id
- primary sequence
- key word
- Directed Acyclic Graph Architecture
- Glossary
3
Classification principles
- Base pairing
- Watson Crick
- non-canonical
Base stacking
Backbone conformation
Sequence
- Backbone interactions
- backbone-backbone
- backbone-base
4
Organization of structural motifshierarchically
organized queryable attributes
- PDB ID 1dul
- Location
- chain b, res 146-150 chain b, res 161-165
- Sequence
- 146-UCAGG-150
- 165-GACGA-161
- Base pairings
- 146-165 UG cis WC-WC
- 147-164 CA trans WC/Hoogsteen
- 148-163 AC trans WC/sugar edge
- 149-162 GG trans bifurcated/Hoogsteen
- 150-161 GA cis WC-WC
- Base stacking
- Adjacent 145-146, 146-147, 148-149, 149-150
- Non-adjacent 147-162, 148-164 (stack swap)
- Pseudotorsions
- Residue ? ? ?
- 146.B 169.3 195.0 203.9
- 147.B 160.9 144.3 217.6
1dul146-150.b, 161-165.b E. coli SRP/RNA Batey,
et al., Science 2871232 (2000)
5
SCOR 3.0 Attribute-based structural
classification
- Sequence
- Loop length
- Base pairings (RNAVIEW1)
- Backbone torsion angles (e.g., AMIGOS2)
- Hydrogen bonds (HBExplore3)
- Stacking
- adjacent and non-adjacent
- Classification of structural elements by features
- Feature-based searching and characterization of
motifs - 1H. Yang, F. Jossinet, N. Leontis, L. Chen, J.
Westbrook, H.M. Berman, E. Westhof. (2003) Tools
for the automatic identification and
classification of RNA base pairs. Nucleic Acids
Research 31 3450-3460. - 2C.M. Duarte and A.M. Pyle. (1998) Stepping
through RNA structure a novel approach to
conformational analysis. J.Mol. Biol.
2841465-1478. - 3K. Lindauer, C. Bendic, J. Sühnel. (1996)
HBexplore - A New Tool for Identifying and
Analyzing Hydrogen Bonding Patterns in Biological
Macromolecules. Comput. Appl. Biosci. 12281-289.
6
Characteristics of RNA Elements Vs. Motifs
- Elements/Attributes
- Local
- Single feature
- Found in different motifs
- Little sequence specificity
- Loop Motifs (Hairpin Internal)
- May span entire loop
- Multiple features
- May include elements
- Not nested in other loop motifs
- Often have sequence preferences
- Tertiary Interaction Motifs
- Multiple loop or stem interactions
- Evolutionarily conserved
- May include elements or motifs
- Often have sequence preferences
7
Sarcin-Ricin Loop by Elements
PDB ID 483D C.C. Correll, I.G. Wool, and A.
Munishkin J. Mol. Biol 292275 (1999)
8
Sarcin-Ricin Loop by Elements
S-turn
9
Sarcin-Ricin Loop by Elements
S-turn
Base triple
10
Sarcin-Ricin Loop by Elements
S-turn
Base triple
Cross-strand stack
11
Sarcin-Ricin Loop by Elements
U-turn (in a tetraloop)
S-turn
Cross-strand stack
Base triple
12
Sarcin-Ricin Loop by Elements
U-turn (in a tetraloop)
S-turn
Cross-strand stack
Base triple
PLUS Base pairings, backbone-base hydrogen bonds
13
(No Transcript)
14
(No Transcript)