Functional Responses PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 10
Title: Functional Responses
1
Functional Responses
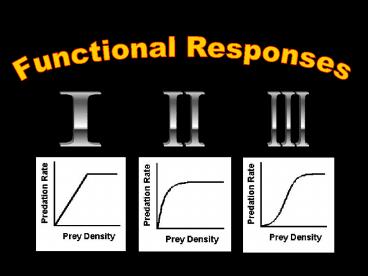
I
II
III
2
Lecture Goals
- Distinguish between a functional and a numerical
response - Define the 3 classic functional responses
- Explain how functional responses can influence
relationships between populations
3
Definitions
NumericalResponse
- a change in the abundance (numbers) of predators
due to consumption of prey - population growth
FunctionalResponse
- the variation in the consumption rate of
predators as a result of changes in the abundance
of prey
4
Type I
- Lotka-Volterra assumption
- initially consumption conversion proportional
to N - some saturation point (discontinuous rate change)
- example Daphnia consuming yeast (Fig. 9.8)
5
- consumption rate declines with increasing prey
density until saturation level - possible result of 'handling time' (Holling)
- opening shells (oystercatchers)
- oviposition (parasitoids)
- mastication
- i.e. a FIXED time per prey item
Type II
6
Type III
- saturation similar to Type II
- early acceleration in predation rate due to
- increasing capture efficiency
- decline in handling time
- learning? switching?
- still saturates at high densities
- sigmoid curve
7
Dynamics and Type II Functional Responses
- creates a 'hump' in the prey isocline
- intermediate prey saturates predation but
competition among prey is not intense - hump also could be due to 'Allee effect'
- stability varies with crossing of the predator
isocline
8
Dynamics and Type III Functional Responses
- less predation (lower rate) at low prey
densities Stabilizing - predator learning, refuges from predation, etc.
- Switching?
- generalist predators stabilizing?
- Scandinavian Rodents...
9
Scandinavian Rodents
- Cycles in the North
- few predators
- minmax densities of 1100
Gradient in Dynamics
- No regular cyclic dynamics in the south
- many predators(owls, foxes, cats, etc.)
10
The Role of Models
- Ideas, Concepts models Math makes models more
explicit - testable, refutable
- can communicate and build
- Simple predator prey models inadequate
- logical results unlikely in light of observations
- then examined predation RATE
- predictions more reasonable
- Developing and testing models requires
quantitative skills - analytical (mathematics computers)
- empirical (experimental design in lab and field)
- statistical (testing of hypotheses from above)