From last time PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 16
Title: From last time
1
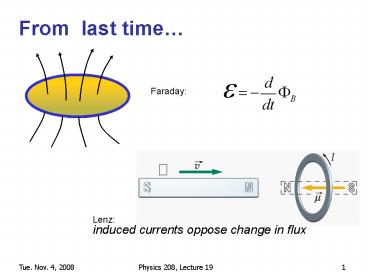
From last time
Faraday
Lenz induced currents oppose change in flux
2
Faradays law
EMF around loop
Magnetic flux through surface bounded by path
EMF no longer zero around closed loop
3
Lenzs law
- Induced current produces a magnetic field.
- Interacts with bar magnet just as another bar
magnet - Lenzs law
- Induced current generates a magnetic field that
tries to cancel the change in the flux. - Here flux through loop due to bar magnet is
increasing. Induced current produces flux to
left. - Force on bar magnet is to left.
4
Question
- Which way is the magnet moving if it is inducing
a current as shown? - A. Up
- B. Down
S N
Current creates flux up. This must be opposing
increase in flux down. So magnet must be falling
down
5
Question
SN
- As current is increasing in the solenoid, what
direction will current be induced in ring?
A. Same as solenoid B. Opposite of solenoid C. No
current
6
Question
- What is the direction of the current induced in
the can?
- Into page
- Out of page
- CW
- CCW
- None of the above
End view
What is the direction of the force on the can?
7
- A copper guillotine blade falls toward a victim.
It enters field from strong magnets on way down.
What is the direction of the current induced in
the loop (blade) as it enters field?
- CW
- CCW
- Depends on field direction
What is the direction of the magnetic force on
the blade?
- Up
- Down
- Depends on field direction.
8
Eddy current braking
Electro-magnets
Steel Rail
- ICE 3 near the Oberhaider Wald Tunnel on the
Cologne-Frankfurt high-speed rail line
Shinkansen
9
Eddy current separation
side view
top view
10
Back to basics solenoid flux
- Uniform field inside
- Change current -gt change flux
11
Magnetic flux in a solenoid
Flux through one turn
?Flux through entire solenoid
inductance
12
Inductance a general result
- Flux (Inductance) X (Current)
- Change in Flux (Inductance) X (Change in
Current)
- Faradays law
13
Changing current in inductor
- Ideal inductor
- Inductance, but zero resistance
- Constant current
- Changing current
- Sign of across ideal inductor
- Opposes change in current.
- Inductor fights to keep a constant current
14
Energy stored in ideal inductor
- Constant current (uniform charge motion)
- No work required to move charge through inductor
- Increasing current
- Work required to
move charge across induced EMF - Total work
Energy stored in inductor
15
Magnetic energy density
- Energy stored in inductor
- Solenoid inductance
- Energy stored in solenoid
Bsolenoid
Energy density
16
Question
- A solenoid is stretched to twice its length while
keeping the same current and same cross-sectional
area. The stored energy
- Increases
- Decreases
- Stays the same
B decreases by 2
Energy density decr by 4
Volume increases by 2