THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM PASSAGEWAYS PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 29
Title: THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM PASSAGEWAYS
1
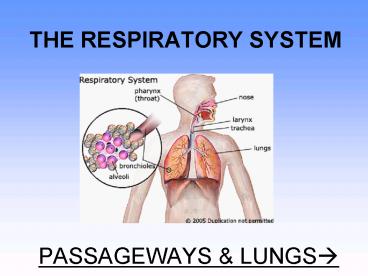
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM PASSAGEWAYS
LUNGS?
2
FUNCTIONS of the respiratory system
- 1 obtaining oxygen removing carbon dioxide
- filtering incoming air
- controlling the temp water content of incoming
air - producing vocal sounds
- plays important roles in the sense of smell
regulation of blood pH
3
the EVENTS of respiration
- breathing / ventilation moving air into or out
of the lungs - external respiration gas exchange between blood
the air in the lungs - gas transport in blood between the lungs body
cells - internal respiration gas exchange between blood
body cells - cell respiration using O2 to break glucose
form ATP
4
PARTS of the respiratory system upper
respiratory tract
- nose w/ 2 nostrils
- nasal cavity / nasal passages
- divided into R L by the nasal septum (may be
deviated) - paranasal sinuses air-filled spaces in the
bones of the skull - pharynx a passageway for air food
5
UPPER respiratory tract
6
PARTS of the respiratory system lower
respiratory tract
- larynx contains the vocal cords
- Trachea windpipe
- bronchial tree branched air passages that lead
from the trachea to the air sacs, or alveoli
7
parts of the respiratory system LOWER
respiratory tract
- 2 lungs the right lung has 3 lobes the left
has 2 lobes - assisted by the diaphragm
- controlled by the medulla
- oblongata pons
- in the brain stem
8
lower respiratory tract
9
(No Transcript)
10
the PATH air takes
- air is taken in through the nose or mouth
inspiration - air flows into the pharynx passes the
epiglottis - it moves through the larynx (voicebox)
- it travels down the trachea which splits into 2
tubes - a bronchial tube leads into each lung
- this pathway is reversed for expiration
11
lung capacity
- tidal volume the amount of air that moves in
during a respiratory cycle (1 inhalation 1
expiration) - residual volume air remaining in lungs after a
maximal exhale - vital capacity the maximum amount of air a
person can exhale after taking in the deepest
breath possible - total lung capacity the vital capacity the
residual volume
12
cleaning dirty air
- theres millions of particles of foreign matter
in air! - air must be filtered before it reaches the lungs
- the nasal cavity, trachea, bronchial tree are
all lined with ciliated cells that secrete mucus
via goblet cells - the cilia beat upward towards the pharynx, where
foreign matter is swallowed or coughed up
13
alveoli the place of gas exchange
- the bronchi branch like a tree (bronchus?
bronchioles? alveoli) - alveoli are the sacs of the lungs where O2 CO2
are exchanged by diffusion between the air and
blood
14
alveoli the place of gas exchange
- grape-like clusters of alveoli are surrounded by
networks of tiny blood vessels / capillaries - the walls of capillaries and of alveoli are only
1 cell thick
15
blood transport of gases
- external respiration the exchange of O2 CO2
between the air in the alveoli and the blood that
circulates through its capillaries - once oxygen diffuses into the bloodstream, it is
pumped by the heart to all cells in the body
16
blood transport of gases
- cellular respiration the process by which cells
use oxygen to break down glucose (via glycolysis)
release energy to form ATP
17
blood transport of gases
- carbon dioxide is a waste product it diffuses
into the blood which carries it back to the
lungs, then it is exhaled - blood going into the alveoli is high in CO2 low
in O2 - blood returning from the alveoli is low in CO2
higher in O2
18
(No Transcript)
19
THE MECHANICS OF BREATHING ?
- breathing is accomplished via the action of the
diaphragm the muscles between the ribs is
assisted by air pressure - inhaling contracts the muscles between the ribs
causes the rib cage to rise - inhaling also contracts the diaphragm, flattening
it, causing it to move lower in the chest cavity
20
THE MECHANICS OF BREATHING ?
- both of these muscular contractions increase the
space in the chest cavity, which creates a slight
vacuum - air rushes to fill the space because the pressure
outside your body is greater than the pressure
inside your lungs
21
(No Transcript)
22
THE MECHANICS OF BREATHING ?
- when you exhale (expiration), the rib muscles
diaphragm relax which lowers the rib cage
diaphragm - this decreases the volume of the chest cavity
forces air out of the alveoli - Check out the animation!
23
THE MECHANICS OF BREATHING ?
- healthy lungs are elastic they stretch as you
inhale go back to their original size when you
exhale - they are never completely empty even after
exhaling (residual volume)
24
CONTROL OF RESPIRATION ?
- usually respiration is involuntary
- the respiratory center is in the brain stem
includes portions of the pons medulla oblongata - it is partially controlled by the medulla
oblongata which maintains the homeostasis of
blood chemistry
25
CONTROL OF RESPIRATION ?
- the medulla oblongata responds to higher levels
of CO2 in blood by sending nerve impulses to the
rib muscles the diaphragm, causing these
muscles to contract you inhale
26
RELEVANT VOCABULARY?
- apnea temporary cessation of breathing
- asphyxia O2 deficiency excess CO2 in blood
tissues - bronchitis inflammation of the bronchial lining
- cystic fibrosis a genetic disorder which causes
the production of extremely thick, sticky mucus
which encourages infection clogs the pancreas
impairs absorption of nutrients leads to salty
sweat - dyspnea difficulty breathing
27
RELEVANT VOCABULARY?
- emphysema a progressive, degenerative disease
that destroys alveolar walls therefore reducing
the volume of gas exchange - eupnea normal breathing
- hypercapnia excess CO2 in the blood
- hyperoxia excess O2 in the blood
- hypoxemia deficiency in blood oxygen
28
RELEVANT VOCABULARY?
- hyperventilation prolonged rapid deep
breathing - pleurisy inflammation of the pleural membranes
- rhinitis inflammation of the nasal cavity
lining - sinusitis inflammation of the sinus cavity
lining
29
RELEVANT VOCABULARY?
- spirometer an instrument that measures
respiratory air volume - tracheotomy incision in the trachea for
exploration or for removal of a foreign object