Instrumentation for PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 15
Title: Instrumentation for
1
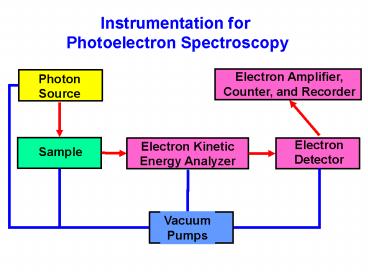
Instrumentation for Photoelectron Spectroscopy
2
Overall Experimental Resolution
1 eV 8066 cm-1 23.06 kcal/mol 96.48 kJ/mol
0.037 au
3
Samples
- Gas-Phase Photoelectron Spectroscopy
- Atoms, Neutral Molecules, Anions, Clusters,
etc. - Molecular beam allows cooling of sample by
super-sonic jet expansion - For neutral molecules, need a vapor pressure of
10-4 torr in high vacuum at temperatures lt 500
C - Condensed-Phase Photoelectron Spectroscopy
- Film on conductive surface
- For valence spectroscopy, need uniform film
- (vapor deposition, SAMs, spin coating)
4
Photon Sources
Laboratory gas discharge sources, 0.005 eV
resolution (40 cm-1) He I - 21.2 eV energy
covers important valence structure most common
for UPS He II 40.8 eV energy covers deeper
valence region valuable in comparison to He I
for changing probabilities (cross sections) of
ionizations. Ne I 16.7 eV energy good for low
valence region Laboratory X-ray sources, 1 eV
resolution Mg K? 1253.6 eV energy allows
ionization of core electrons Al K? 1486.6 eV
monochromator increases resolution other
sources from 100 8000 eV available Laser
sources, 8 eV max energy, very high resolution
and intensity photoelectron spectroscopy of
negative ions multiphoton ionization
5
Synchrotron Photon Sources
range of resolutions with monochromators continuou
s range of photon energies additional cross
section, resonance, polarization information
The Advanced Photon Source, Argonne National Lab
6
Electron Kinetic Energy Analyzers
Throughput What of photoelectrons produced are
detected Resolution How close in kinetic
energy can two electrons be, and still be
separated by the analyzer Resolving Power
E/?E higher kinetic energy, lower
resolution Time of Flight Analyzers Resolving
power 100 Deflection Analyzers Resolving
power gt1,000
7
Deflection Analyzer with Electron Optics
Rather than scanning through electron kinetic
energies with a deflection analyzer Use an
electron-optics lens to slow electrons to a pass
energy
8
Analyzer Throughput
Analyzer Entrance
steradian solid angle subtended by a circular
surface A sphere subtends 4? steradians
9
TOF Magnetic Bottle Spectrometer
Magnetic field in ionization region allows a
large solid angle of photoelectrons to be
collected, increasing spectrometer
sensitivity. In principle, 2? steradians of
photoelectrons can be collected.
10
Electron Detectors
Channel Electron Multiplier
Microchannel Plate
CCD detectors can also be used, typically with a
phosphor screen to convert electrons to photons
11
Vacuum Pumps
- Low pressure is required for operation of
electron detectors - Pressure must be low enough to allow
mean-free-path of electrons through the analyzer - Pressure must be low enough that gas-phase
samples are volatile - Ultra-high vacuum is required to lower surface
contamination for condensed-phase spectroscopy
12
How Low Must Pressure be for a Surface to be
Clean?
If sticking coefficient S 1 And pressure
2.5 x 10-6 Torr A monolayer will form in 1 second
Lower pressure to 10-9 Torr A monolayer forms
in 1,000 seconds S is usually ltlt1
13
Gas-Phase Photoelectron Instrument
h?
Sample Chamber
Photon Source
Photon Induces the Photoelectric Effect.
Electrons are separated according to kinetic
energy
Output is plot of Ionization Energy vs. Counts
14
Surface Photoelectron Instrument
Sample Prep and Storage
Fast Entry
Main Analysis
15
Mass-Selected Gas-Phase Photoelectron Instrument
MCP (mass detector)
Time-of-flight mass spectrometer
magnet
2.5 m
5x10-11 Torr
Time-of-flight magnetic botter photoelectron spect
rometer
4.0 m
Electrospray Ionization source
Z-stack MCP (photoelectron detector)