Evolution of the ER Model - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 19
Title:
Evolution of the ER Model
Description:
Disjointed constraint. Can an entity instance simultaneously be a member of two or more subtypes? Disjoint rule. overlap rule. Subtype discriminators ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:43
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Evolution of the ER Model
1
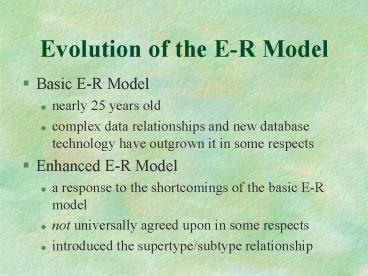
Evolution of the E-R Model
- Basic E-R Model
- nearly 25 years old
- complex data relationships and new database
technology have outgrown it in some respects - Enhanced E-R Model
- a response to the shortcomings of the basic E-R
model - not universally agreed upon in some respects
- introduced the supertype/subtype relationship
2
Supertype/Subtype Relationships
- Supertype (example Employee)
- a generic entity that has a relationship with one
or more subtypes - Subtype (example Manager)
- a subgrouping of a supertype entity that is
meaningful to an organization - shares all attributes of its supertype, but also
has unique attributes of its own and/or - has relationships with other entities distinct
from those of other subtypes
3
Supertype/Subtype Notation
4
The student example
STUDENT
GRAD STUDENT
UNDERGRAD STUDENT
5
Two Rules for When to Use Supertype/Subtypes
- Use this type of relationship when either (or
both) of the following are present - 1. When there are attributes that apply to some
(but not all) of the instances of an entity
type - 2. When the instances of a subtype participate
in a relationship unique to that subtype
6
Attribute Inheritance
- The property by which subtype entities inherit
values of all attributes of the supertype. - This important property makes it unnecessary to
include supertype attributes redundantly with the
subtypes.
7
Supertype/Subtype Example 1
8
Supertype/subtype relationships in a hospital
9
Two Processes to Develop Supertype/Subtypes
- Generalization
- The process of defining a more general entity
type from a set of more specialized entity types - A bottom-up approach
- Specialization
- The process of defining one or more subtypes of a
general entity based on distinguishing
attri-butes or relationships - A top-down approach
Both approaches can be used together
10
Supertype/Subtype Constraints
- Completeness
- Addresses the question of whether an instance of
a supertype must also be a member of at least one
subtype
- Disjointness
- Addresses the question of whether an instance of
a supertype may simultaneously be a member of two
(or more) subtypes
11
Completeness Constraint Two Possible Rules
- Total Specialization Rule (Double-line notation)
- Specifies that each entity instance of the
supertype must be a member of some subtype in the
relationship (Example all STUDENTS are either
UNDERGRADUATE or GRADUATE students) - Partial Specialization Rule (Single-line
notation) - Specifies that an entity instance of the
supertype is allowed to not belong to any subtype
(Example FACULTY and STAFF are not the only
possible members of the entity EMPLOYEE)
12
Completeness constraint
- Can an entity instance be a member of the
supertype but no subtype?
- Total specialization
- partial specialization
13
Disjointed constraint
- Can an entity instance simultaneously be a member
of two or more subtypes?
- Disjoint rule
- overlap rule
14
Subtype discriminators
- Attribute of the supertype whose value determines
to which subtype an instance belongs
15
What does that look like?
16
Yet another example.
17
Supertype/subtype hierarchy
- Arrangement of super- and subtypes where each
subtype has only one supertype.
18
Another example...
19
Lets practice...
- A bank has three types of accounts checking,
savings, and loan. The attributes for each
account are as follows - CHECKING Account_No, Date_Opened, Balance,
Service_Charge - SAVINGS Account_No, Date_Opened, Balance,
Interest_Rate - LOAN Account_No, Date_Opened, Balance,
Interest_Rate, Payment - Assume that each bank account must be a member of
at least one of these subtypes.Develop an EER
model segment to represent this situation.