Process Capability PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 6
Title: Process Capability
1
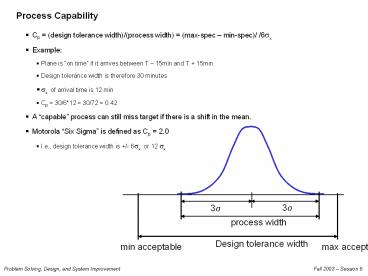
Process Capability
- Cp (design tolerance width)/(process width)
(max-spec min-spec)/ /6?x - Example
- Plane is on time if it arrives between T
15min and T 15min. - Design tolerance width is therefore 30 minutes
- ?x of arrival time is 12 min
- Cp 30/612 30/72 0.42
- A capable process can still miss target if
there is a shift in the mean. - Motorola Six Sigma is defined as Cp 2.0
- I.e., design tolerance width is /- 6?x or 12 ?x
3?
3?
process width
Design tolerance width
min acceptable
max acceptable
2
There are multiple solutions to most parametric
design problems
Analytical Expression for Brownie Mix
Chewiness Chewiness FactorA FactorB Where
FactorA 600(1-exp(-7T/600)) T/10 And FactorB
10Time
HYPOTHETICAL
FactorA
FactorB
Temperature
Time
200F
400F
20 min
26 min
Option 1
Option 2
Options 1 and 2 deliver the same value of
chewiness. Why might you prefer one option over
the other?
3
Parametric Tuning
- Existing system that basically works.
- Adjustments involve setting values of parameters.
- In ideal case, have a nice analytical model and
can optimize mathematically. This is rare in
practice. - Examples
- Physical Processes
- Almost any continuous manufacturing process, e.g.
chemical processing, food processing - Products
- Windshield wiper spray parameters
- Catapult settings
- Engine control settings
- Services
- Direct mail parameters (drop locations, mailing
dates, placement of graphics) - Boarding process at airline gate
- Call center procedures
- Automated check-in process at hotel
- Ad placement on Yahoo
4
Taguchi Methods
- Any deviation from the target value is quality
lost. - Use of statistical experimentation to find robust
combinations of parameters. - Field is called Design of Experiments or DOE.
- Systematically explore space of possible
parameter values. - Based on analysis of relative influence of
parameters on mean and variance of performance
variable, select robust design.
Quality
Quality Loss
Loss C(x-T)2
Good
Performance Metric
Performance Metric, x
Bad
Maximum acceptable value
Minimum acceptable value
Target value
Target value
5
Methodology for Achieving Robust Design
- Identify key variables and metrics
- Articulation of performance metrics, goals
- Causal diagram
- Hypothesized sources of variability
- Analytical models where available
- Conduct exploratory experiments
- Reduce variability
- Design changes
- Instructions/aids for user
- Use logic, analysis, and rough experiments to
focus further experimentation - Avoid wasting experiments on clearly infeasible
regions of design space. - Perform focused experimentation within narrow
ranges of variables - Use Design of Experiments techniques if
combinatorically intractable - See Ulrich and Eppinger Robust Design chapter
for details. - Control variability in laboratory setting
- Focus on identifying combination of settings that
minimize variability in performance. - Select final values for design variables.
6
Take Aways
- Products and processes are causal systems
- Typically have lots of variables
- Internal variables are set by the
manufacturer/provider - Target settings and associated variance
- External variables are set by the environment or
the user - Target settings and associated variance (variance
often much harder to control than with internal
variables) - Impossible to eliminate all variability
- GOAL find target settings for variables such
that variability in other values of these
variables has minimal effect on
output/performance.a robust design. - Methodology for achieving robust design
- Causal model, even if not explicitly analytical
- Early exploratory experimentation
- Control of variability and increased robustness
through design changes - Focused experimentation to refine settings