Coding region PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Coding region
1
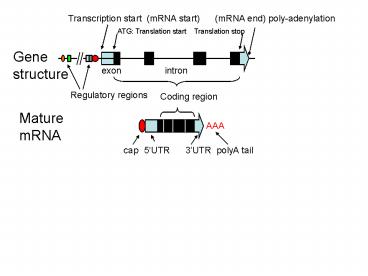
Transcription start (mRNA start) (mRNA end)
poly-adenylation
ATG Translation start Translation stop
Gene structure
exon intron
Regulatory regions
Coding region
Mature mRNA
AAA
cap
5UTR 3UTR polyA tail
2
Transgenic gain-of-function (transgene injection
in fertilized eggs)
Gene of interest
Heterologous regulatory region
cDNA from gene of interest
Heterologous regulatory region
3
BAC transgenics
GFP
recombineering
200 kb
Regulatory elements can many kb away from gene
4
Gene inactivation (constitutive) by gene
targeting in ES cells
Simple targeting construct
NEO
Replace critical exon with Neomycin resistance
gene
NEO
Heterozygote /-
NEO
Homozygote -/-
NEO
5
Targeted gene knock-in (knock-out) in ES cells
CRE
Targeting construct
NEO
NEO
Cre (or a reporter gene) is now driven by
regulatory elements of gene of interest.
Critical parts of gene of interest are removed so
it is also a null allele.
CRE
NEO
NEO
6
Conditional gene inactivation
Neo may disrupt function KO
Targeted allele
Frt-NEO
loxP sites
Remove Frt-NEO With FLIP recombinase
Breed to homozygosity and introduce Cre gene
CRE
Cell-specific expression of Cre recombinase
(transgene or knock-in)
7
Cre-mediated recombination wherever Cre expressed
(loss of critical exon)
CRE
Cre-mediated recombination wherever whenever
Cre is expressed (loss of critical exon)
CRE ERt
Cell-specific control temporal control
with tamoxifen
8
Conditional gene activation
Inactive allele
loxP sites
CRE
Cell-specific promoter
Active allele
loxP site
9
Conditional gene activation
Inactive allele
loxP sites
CRE
Cell-specific promoter
Active allele
loxP site
- Reporter gene
- Ion channel
- GPCR
- Toxin
10
Targeted introduction of a mutation
mutation
Targeting construct
Inactive allele
loxP sites
CRE
mutation
Active allele with mutation
loxP site
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.