RNA secondary structure PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 20
Title: RNA secondary structure
1
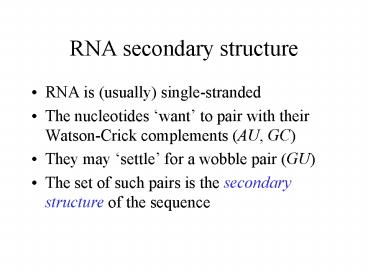
RNA secondary structure
- RNA is (usually) single-stranded
- The nucleotides want to pair with their
Watson-Crick complements (AU, GC) - They may settle for a wobble pair (GU)
- The set of such pairs is the secondary structure
of the sequence
2
The problem
- Input An RNA sequence R
- Output A predicted secondary structure
- S (ri1, rj1), (ri2, rj2) .. (rin, rjn)
3
Faustian bargain for RNA secondary structure
prediction
- Assume an RNA strand folds to lowest energy
- Three types of base pair interactions (G-C, A-U,
G-U) - All structures are nested
- Energies are strictly additive
4
Lowest energy assumption
- There are exponentially many configurations for a
nucleic acid (or protein) sequence - A sequence assumes its stable configuration
quickly (seconds) - How does it find global minimum quickly?
(Levenstein paradox) - Alternative it finds local minimum
5
Base pair interactions
- Atomic interactions too complex to calculate
- Base pair interactions are reasonable compromise
6
Nested structures
- More than 95 of structures are nested, but ..
- Those that arent may well be significant
- Non-nested structures include pseudoknots and
kissing loops
7
Pseudoknot
8
Kissing loops
9
Loops
- Nested structures are loops
- The size of a loop is the number of unpaired
nucleotides it contains - The arity of a loop is the number of interior
pairs it contains - Every loop has exactly one closing pair
10
Hairpin loop
Arity 0 (always), size 4 (variable)
11
Hairpin loop -- size
unpaired nucleotides
12
Hairpin loop - closing pair
Closing pair
13
Bulge
Arity 1 (always), size 1 (variable
14
Interior loop
Arity 1 (always), size 2
15
Multiloop
Arity 2 (variable), size 3 (variable)
16
Composite RNA secondary structure
17
Nearest neighbor formula
- Energy is a function of closing base pair and its
nearest neighbors - Non-symmetric ( E(XYZW) ¹ E(WZYX) )
- Energies of nested loops are additive
- E(R) E(ri1, ri11, rj-11), (ri12, rj-12) ..
(ri1n, rj-1n)
18
Loop recurrence relation
E(Si1,j) E(Si,j1) minE(Si,k) E(Si,k), i lt k
lt j E(Li,j)
E(Si,j)
where ...
19
Li,j recurrence relation
Li,j is a hairpin Li,j is a stacked pair Li,j is
an i-bulge Li,j is a j-bulge Li,j is an interior
loop
E(Li,j)
min
20
Hairpin loop
Nearest neighbors