Strategic Management: Competitiveness and Globalization - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 19
Title:
Strategic Management: Competitiveness and Globalization
Description:
Innovation is a key outcome firms seek through entrepreneurship and is often the ... To innovate through a cooperative relationship, firms must share their knowledge ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:640
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Strategic Management: Competitiveness and Globalization
1
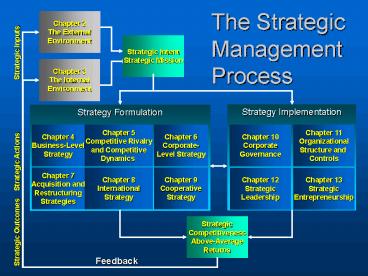
The Strategic Management Process
Chapter 2 The External Environment
Strategic Intent Strategic Mission
Strategic Inputs
Chapter 3 The Internal Environment
Strategy Implementation
Strategy Formulation
Chapter 11 Organizational Structure and Controls
Chapter 10 Corporate Governance
Chapter 6 Corporate- Level Strategy
Chapter 5 Competitive Rivalry and
Competitive Dynamics
Chapter 4 Business-Level Strategy
Strategic Actions
Chapter 12 Strategic Leadership
Chapter 13 Strategic Entrepreneurship
Chapter 9 Cooperative Strategy
Chapter 8 International Strategy
Chapter 7 Acquisition and Restructuring Strategies
Strategic Competitiveness Above-Average Returns
Strategic Outcomes
Feedback
2
Strategic Entrepreneurship
- Strategic entrepreneurship taking
entrepreneurial actions using a strategic
perspective - engaging in simultaneous opportunity seeking and
competitive advantage seeking behaviors - designing and implementing entrepreneurial
strategies to create wealth - These actions can be taken by individuals or by
corporations
3
Innovation
- Innovation is the process of creating a
commercial product from an invention - invention brings something new into being
- innovation brings something new into use
- Innovation is a key outcome firms seek through
entrepreneurship and is often the source of
competitive success - Innovations produced in large established firms
are often referred to as corporate
entrepreneurship
4
Entrepreneurs
- Entrepreneurs are
- individuals acting independently or as part of an
organization - who create a new venture or develop an innovation
and take risks entering them into the marketplace - Entrepreneurs
- can be independent individuals
- can surface in an organization at any level
5
International Entrepreneurship
- Entrepreneurship can
- fuel economic growth
- create employment
- generate prosperity for citizens
- There is a strong positive relationship between
the rate of entrepreneurial activity and economic
development in a nation
6
International Entrepreneurship
- There must be a balance (in the culture)
between - individual initiative and
- the spirit of cooperation and group ownership
of innovation - Successful entrepreneurial firms
- provide appropriate autonomy
- incentives for individual initiative
- promote cooperation and group ownership of an
innovation
7
Innovation Types
Incremental Innovation
- most innovations are incremental
- builds on existing knowledge bases
- provides small improvements in the current
product lines
8
Innovation Types
Radical Innovation
- provides significant technological breakthroughs
- creates new knowledge
- is rare because of difficulty and risk
- requires substantial creativity
- radical innovations are often best developed in
separate units that start internal ventures
9
Internal Corporate Venturing
10
Cross-Functional Product Development Teams
- facilitate efforts to integrate activities
associated with different organizational
functions - design, manufacturing, marketing, etc.
- new product development processes can be
completed more quickly - products can be more easily commercialized when
cross-functional teams work effectively
11
Cross-Functional Product Development Teams
- product development stages are grouped into
parallel or overlapping processes - this approach allows the firm to tailor its
product development efforts - unique core competencies
- needs of the market
12
Barriers to Cross-Functional Team Effectiveness
- Different orientations and perceptions
- individuals from separate functions have
different orientations on issues - perceive product development activities in
different ways - Organizational politics
- aggressive competition for resources among
different organizational functions - must achieve cross-functional integration with
minimal political conflict
13
Creating Value Through Internal Innovation
Processes
14
Cooperative Strategies for Entrepreneurship and
Innovation
- Firms may need to cooperate and integrate
knowledge and resources to successfully
commercialize inventions - entrepreneurial new venture firms may need
investment capital and distribution capabilities - more established companies may need new
technological knowledge possessed by newer
entrepreneurial firms - To innovate through a cooperative relationship,
firms must share their knowledge and skills
15
Acquisitions to Buy Innovation
- Acquisitions
- rapidly extend the product line
- increase the firms revenues
- A key risk of acquisitions is that a firm may
substitute the ability to buy innovations for an
ability to produce innovations internally - firm may lose intensity in RD efforts
- firm may lose ability to produce patents
16
Loss of Innovative Capability Following Large
Acquisitions
Firm Minus Industry RD Intensity
Years Before and After Acquisitions
17
Loss of Innovative Capability Following Large
Acquisitions
Patent Intensity
Years Before and After Acquisitions
18
Capital for Entrepreneurial Ventures
- Venture capital firms
- seek high returns on their investment
- value competence of the entrepreneur or the human
capital in the firm - place weight on the expected scope of competitive
rivalry the firm is likely to experience - evaluate degree of instability in the market
addressed
19
Capital for Entrepreneurial Ventures
- Initial public offerings (IPOs)
- new stock
- firm needs high potential in order to sell new
stock - often quite larger than the amounts obtained from
venture capitalists - investment bankers frequently play major roles in
the development and offering of IPOs - firms that have also received venture capital
backing usually receive greater returns from IPOs