Selling an Idea or a Product - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 43
Title:
Selling an Idea or a Product
Description:
Dorsoventral muscles contracted: wings rise. Dorsolongitudinal muscles contracted: wings lower ... Dorsoventral. muscle. Dorso- longitudinal. muscle. Direct ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:370
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Selling an Idea or a Product
1
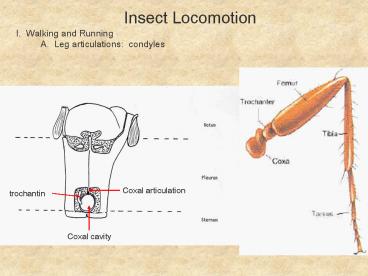
Insect Locomotion I. Walking and Running A.
Leg articulations condyles
Coxal articulation
trochantin
Coxal cavity
2
Insect Locomotion I. Walking and Running A.
Leg articulations condyles 1.
monocondylic 2. dicondylic
3
Insect Locomotion I. Walking and Running B.
Nervous Coordination
Extensor (lower extend leg)
Flexor (raise bend leg)
4
Insect Locomotion I. Walking and Running B.
Nervous Coordination 1. Basic rhythmical
pattern Central Pattern Generator
subpopulation of interneurons and motor neurons
contained entirely within the central nervous
system that can produce a complete motor program
without sensory feedback ex walking in
cockroach flexor burst generator
5
(Command neuron an interneuron that is both
necessary and sufficient to trigger a
complete motor program)
command interneuron
thoracic ganglion
FMN
Flexor muscle
FBG
EMN
Extensor muscle
excitatory synapse
inhibitory synapse
6
- 1. Command interneuron produces continuous
stream of impulses - stimulates EMN leg extends
- simultaneously stimulates FBG
- 2. FBG turns continuous input from command
interneuron into - periodic output FBG fires
- Inhibits EMN
- excites FMN leg flexes
- 3. FBG falls silent
- command interneuron
- stimulates EMN, leg
- extends
- cycle repeats
7
Insect Locomotion I. Walking and Running B.
Nervous Coordination 2. Modification of CPG
by sensory feedback
8
Cuticle stress receptor (campaniform sensillum)
9
Insect Locomotion I. Walking and Running B.
Nervous Coordination 3. CNS control of CPGs
10
Insect Locomotion II. Jumping A. Modified
hindlegs
11
Insect Locomotion II. Jumping B. Furcula of
Collembolans
12
Insect Locomotion II. Jumping C. Cuticular
elasticity
resilin
13
Insect Locomotion III. Aquatic locomotion A.
Surface locomotion
Water strider
Whirligig beetle
14
Gyrinid beeltes
15
Insect Locomotion III. Aquatic locomotion B.
Subsurface locomotion 1. appendages for
swimming dytiscid beetles
16
Insect Locomotion III. Aquatic locomotion B.
Subsurface locomotion 2. jet propulsion
Odonate naiads
17
Insect Locomotion IV. Flight A. Mechanisms for
flight 1. Indirect flight muscles a.
Dorso-longitudinal muscles -- run
between phragma of postnota
-- lower wings b. Dorso-ventral muscles
-- run from notum to sternum
-- raise wings Primary flight muscles
for Diptera, Hymenoptera, Lepidopera,
Coleoptera
18
notum
Dorso- longitudinal muscle
Dorso-ventral muscle
sternum
19
Dorso-ventral muscles
Dorso-longitudinal muscles
20
Dorsoventral muscles contracted
wings rise
Dorsolongitudinal muscles contracted
wings lower
21
Insect Locomotion IV. Flight A. Mechanisms for
flight 1. Indirect flight muscles --
controlled by CPG in thoracic ganglia --
innervated by resonating motor neurons
22
Insect Locomotion IV. Flight A. Mechanisms for
flight 2. Direct flight muscles
23
notum
Dorso- longitudinal muscle
Direct flight muscles
Dorsoventral muscle
sternum
24
Insect Locomotion IV. Flight A. Mechanisms for
flight 2. Direct flight muscles a.
Primary flight muscles for Odonata
Orthoptera
25
26
Insect Locomotion IV. Flight A. Mechanisms for
flight 2. Direct flight muscles b.
steering
27
figure 8 pattern of wing movement
28
hovering
29
Insect Locomotion IV. Flight A. Mechanisms for
flight 3. Cuticular elasticity click
mechanism -- wing hinge has 2 stable
positions full up full down
30
Click Mechanism
wing hinge
Dorso-longitudinal muscles contracted
Dorso-ventral muscles contracted
31
Insect Locomotion IV. Flight B. Sensory
regulation of flight 1. initiation of
flight -- loss of contact with substrate --
touch, sound, visual cues
32
Insect Locomotion IV. Flight B. Sensory
regulation of flight 2. regulation during
flight a. Control of flight speed
1) hairs and bristles (trichoid sensilla)
Example 1 Hair plates of locust
33
Insect Locomotion IV. Flight B. Sensory
regulation of flight 2. regulation during
flight a. Control of flight speed
1) hairs and bristles
Example 2 interommatidial hairs of honey bee
34
Insect Locomotion IV. Flight B. Sensory
regulation of flight 2. regulation during
flight a. Control of flight speed
2) Johnstons organ
controls wing-beat amplitude in honey bees
35
Insect Locomotion IV. Flight B. Sensory
regulation of flight 2. regulation during
flight a. Control of flight speed
3) compound eyes optomotor response
36
Insect Locomotion IV. Flight B. Sensory
regulation of flight 2. regulation during
flight b. adjustments during flight
(steering) -- pitch, roll, yaw
37
Roll side-to-side rocking about
horizontal axis
Pitch up-and-down tilting about vertical axis
Yaw side-to-side drifting about vertical axis
38
Insect Locomotion IV. Flight B. Sensory
regulation of flight 2. regulation during
flight b. adjustments during flight
1) campaniform sensilla
39
Insect Locomotion IV. Flight B. Sensory
regulation of flight 2. regulation during
flight b. adjustments during flight
2) chordonotal organs
40
Insect Locomotion IV. Flight B. Sensory
regulation of flight 2. regulation during
flight b. adjustments during flight
3) halteres of Diptera
41
42
Insect Locomotion IV. Flight B. Sensory
regulation of flight 2. regulation during
flight b. adjustments during flight
4) hair plates of Odonates
43
Insect Locomotion IV. Flight C. Evolutionary
trends in insect flight -- reduction in
functional no. of wings gt reversed wing beat
in Odonates gt wing coupling devices gt
loss of hindwings in Dipterans