METHODS PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title: METHODS
1
An Impedance Sensor (CLS) is Superior to an
Accelerometer for Chronotropically Incompetent
Patients with Sinus Node Dysfunction Results of
a Pilot Study with a Dual Sensor Pacemaker
Behzad B. Pavri, MD, Sarah Russell, RN
Thomas Jefferson University Hospital, Philadelphia
ENDPOINTS Quality of Life (QoL) scores 0 No
improvement over baseline 1 Modest
improvement 2 Significant improvement 3
Tremendous improvement Holter Data mean,
minimum, and maximum HR Ansar Data HR and
autonomic data during rest isometric handgrip,
deep breathing, Valsalva, and postural change
(standing)
- INTRODUCTION
- Patients (pts) with chronotropic incompetence
(CI) depend on pacemakers (PM) for rate response - Many sensors do not provide physiologic heart
rate (HR) response - The Biotronik Protos PM has 2 independent
sensors - Impedance sensor - DDD-CLS
- Accelerometer - DDDR
- Closed Loop Stimulation (DDD-CLS) monitors local
RV myocardial-blood pool impedance as a surrogate
for contractility
- Accelerometer (DDDR) provides HR increase with
detection of oscillation - The Ansar System? provides a snapshot of
sympathovagal balance during standard maneuvers
- OBJECTIVE AND HYPOTHESIS
- To compare the HR response provided by an
accelerometer (DDDR) to Closed Loop Stimulation
(DDD-CLS) in pts with chronotropic incompetence - DDD-CLS provides more physiologic HR behavior
compared to DDDR
- RESULTS
- 18 pts enrolled over 28 months, 10 male
- Mean age74.8 (60-86) years
- 4/18 rejected due to
- gt50 AF in 2
- No CI in 1 (lt60 atrial pacing at f/u)
- Intercurrent illness and hospitalizations in 1
- 9/14 pts with analyzable data ? completed study
- All pts had normal LV ejection fraction
- 6 randomized to DDDR first, 3 to CLS first
- CLS ? 7/9 pts Significant or Tremendous
improvement - DDDR ? 2/9 pts Significant improvement
- 7/9 blinded pts opted for CLS sensor
- METHODS
- Inclusion Criteria
- Age gt 18 years
- CI defined as average HRlt55 BPM on 24 hour
Holter, AFlt 20 - Single blind, randomized cross-over trial
- Randomized to DDDR or CLS for 4 wks each.
Assessed at the end of each 4 wk period. Pts
served as their own controls - PM programming identical in both modes except for
sensor type - Statistical Methods
- T-test and Wilcoxen Signed-Ranks test for paired
data
- CLS establishes baseline impedance curves (at
rest) - CLS collects impedance curves with each heart
beat, and calculates area deviation from baseline
curve - Pacing rate is based on deviation from baseline
curve
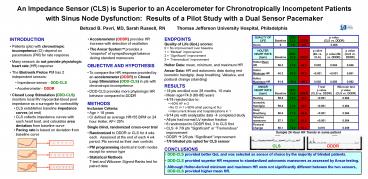
Sample 24 Hour HR Trends in same patient
CLS DDDR
CONCLUSIONS
- DDD-CLS provided better QoL and was selected as
sensor of choice by the majority of blinded
patients. - DDD-CLS provided superior HR response to
standardized autonomic maneuvers as assessed by
Ansar testing. - Although Holter-derived minimum and maximum HR
were not significantly different between the two
sensors, DDD-CLS provided higher mean HR.