Step 2 - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 24
Title: Step 2
1
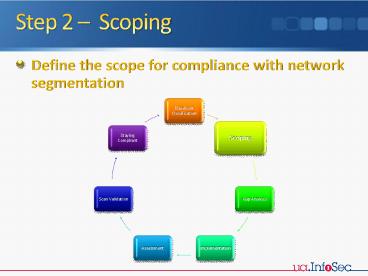
Step 2 Scoping
- Define the scope for compliance with network
segmentation
2
PCI Scope
- Any network component, server or application
included in or connected to the part of the
network that stores, processes or transmits
cardholder or sensitive authentication data
Internet
MERCHANT SITE IT COMPONENTS
Cardholder Data
Web Applications
- Router
- Load balancer
- DNS server
- Mail Server
- OS
- IP Services
Firewall
Database Server
Application Server Web Server
3
Step 3 Gap Analysis
- Understand the technical and operational
requirements and determine your needs
4
Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard
5
3. Protect Stored Cardholder Data
- Ensure that all in-scope systems do not store
full track data, the card validation code or
value, or the PIN or encrypted PIN block. - Mask PAN when displayed the first 6 and last 4
digits are the maximum number of digits you may
display. - Not applicable for those with a legitimate need
to see the full PAN. - Does not supersede stricter requirements in place
for displays of CHD such as on a point-of-sale
receipt.
6
Data Storage Rules of Thumb
- Do not collect and store data you dont need
- Store only cardholder data needed to perform
business functions - Store cardholder data in accordance with the PCI
DSS
7
What's in Your Wallet?
8
UA Resources
- Personal Information Sweep
- Data classification
- Cardholder data inventory
- Common Retention Schedules (http//web.arizona.edu
/records/retention.html) - Receipts 2 years after created
9
4. Encrypt Data Transmission
- Ensure that policies, procedures and practices
are in place to preclude the sending of
unencrypted PANs by end user messaging
technologies (for example, email, instant
messaging, chat).
10
7. Restrict Access to CHD by Need
- Limit access to only those whose job requires it.
Access limitations must include the following - Restriction of access rights to privileged user
IDs to least privileges necessary to perform job
responsibilities - Assignment of privileges is based on individual
personnels job classification and function - Requirement for an authorization form signed by
management that specifies required privileges - Implementation of an automated access control
system
11
9. Restrict Physical Access
- Physically secure all paper and electonic media
that contain CHD. - Maintain strict control over internal and
external distribution of media that contains
CHD. - Classify media so it is clearly identified as
confidential. - Send media via secured courier or other delivery
method that can be accurately tracked. - Require management approval prior to moving any
and all media containing CHD from a secured area. - Maintain strict control over storage and
accessibility of media with CHD. - Destroy media containing CHD when no longer
needed.
12
12. Maintain an Info Security Policy
- Establish and disseminate a security policy
addressing PCI DSS requirements, includes an
annual process for identifying vulnerabilities
and formally assessing risks, and includes a
review at least once a year and when the
environment changes. - Develop daily operational security procedures
consistent with PCI DSS. - Ensure that the security policy and procedures
clearly define information security
responsibilities for all employees and
contractors.
13
Policy Requirements
14
Incident Response
- Notify
- appropriate law enforcement authorities
- FSO-Bursars Department Services, which will
coordinate reporting to Bank of America - Info Sec, which coordinates
- Virtual Security Incident Response Team (VSIRT)
- Breach notification
- Make a note of all actions taken
- Document local procedures
15
UA Resources
- Information Security Standards and Guidelines
- Reviewed/updated annually
- Listed at http//security.arizona.edu/pci
- VISA If Compromised website (http//usa.visa.com
/merchants/risk_management/cisp_if_compromised.htm
l) - Virtual Security Incident Response Team (VSIRT)
- Incident reporting link at http//security.arizona
.edu/pci - Annual awareness program (http//security.arizona.
edu/pci) - Contract provisions for 3rd party vendor
proposals and agreements (http//security.arizona.
edu/files/PCIContractProvision.pdf)
16
Step 4 Implementation
- Implement the requirements to address
non-compliant findings
17
Remediation
- Correct/close identified vulnerabilities or gaps
- Test compensating controls
- Test remediating controls
18
Step 5 Validation by Assessment
- Fill out the Self-Assessment Questionnaire
19
Self Assessment Questionnaires
20
Compensating Controls
- Meet the intent and rigor of requirement
- Rigor provide as much assurance (effectiveness)
as the control in the standard - Intent fulfills the same goal as the control in
the standard - Temporary not intended for long-term use
- Requires QSA concurrence
- Can use compliance with another requirement, if
not required for you - Cant use compliance for another requirement if
its already required - Unless you deploy new/additional controls
21
Sample Worksheet
- Constraints List constraints precluding
compliance with the original requirement.
Company XYZ employs stand-alone Unix Servers
without LDAP. As such, they each require a
root login. It is not possible for Company XYZ
to manage the root login nor is it feasible to
log all root activity by each user.
2. Objective Define the original control
identify the objective met by the compensating
control.
The objective of requiring unique logins is
twofold. First, it is not considered acceptable
from a security perspective to share login
credentials. Secondly, shared logins make it
impossible to state definitively that a person is
responsible for a particular action.
3. Identified Risk Identify any additional
risk posed by the lack of the original control.
Additional risk is introduced to the access
control system by not ensuring all users have a
unique ID and are able to be tracked.
4. Definition of Compensating Controls Define
the compensating controls and explain how they
address the objectives of the original control
and the increased risk, if any..
Company XYZ is going to require all users to log
into the servers from their desktop using the SU
command. SU allows a user to access the root
account and perform actions under the root
account but is able to be logged in the su-log
directory. In this way, each users actions can
be tracked through the SU account..
- Source Appendix C
- Compensating Controls Worksheet
22
Attestation of Compliance
- Accepted by all payment brands
- Complete and sign
- Provide to acquirer
I have read the PCI DSS and I recognize that I
must maintain full PCI DSS compliance at all
times.
23
Step 6 Scan Validation
- Obtain a vulnerability scan, if required
24
Step 7 Stay Compliant