The B2B Matrix - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 18
Title:
The B2B Matrix
Description:
May host auctions for buyers. Forward Aggregator Model. Small. Resellers. E-hub. Buyers. Large. Suppliers. Ingram. Micro. Direction of Aggregation. Compaq ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:473
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The B2B Matrix
1
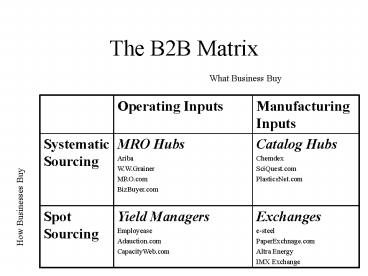
The B2B Matrix
What Business Buy
How Businesses Buy
2
How E-hubs Add Value
What Business Buy
How Businesses Buy
3
Mechanisms Used by E-Hubs
What Business Buy
How Businesses Buy
4
Aggregation
- Brings together large number of buyer and
supplier - Reduces transaction cost by providing one-stop
shopping - Adding another buyer/seller benefits only
sellers/buyers - Works best
- When processing cost is relatively high compared
to product cost - Products are specialized, not commodities
- The number of SKU is very high
- Buyers are not sophisticated to under dynamic
buying mechanism - Purchasing is done through pre-negotiated
contracts - A meta-catalog of products carried by a large
number of suppliers can be created
5
Matching
- Brings together buyers and sellers to negotiate
price on a dynamic and real-time basis
(bids/asks can take the form of auction) - Buyers can be sellers and vice-versa
- Adding new members benefits both buyers and
sellers - Works best in the following scenarios
- Products are commodities and/or near commodities
and can be traded without being seen - Trading volumes are massive relative to
transaction costs - Buyers and sellers are sophisticated enough to
deal with dynamic pricing - Companies are spot purchasing to smooth the peaks
and valleys of supply and demand - Logistics and fulfillment can be conducted by
third parties, often without revealing the
identity of the buyer or seller - Demand and prices are volatile
6
Aggregation vs. Matching
- Matching more powerful than aggregation
- Matching more complex than aggregation
7
Types of E-Hubs
- Neutral E-Hubs
- Biased E-Hubs
8
Neutral E-Hubs
- True market makers equally attractive to both
buyers and sellers - chicken and egg problem
- Sellers channel conflict
- Conflict resolution through partnership
- Can lead to perception of bias
- Likely to succeed in fragmented markets on both
seller and buyer sides
9
Biased E-Hubs
- Biased Sellers forward aggregators
- Biased Buyers reverse aggregators
- Biased e-hubs can exist as aggregators in
systematic markets or as matchers in spot markets - No chicken and egg problem
- Can focus on small buyers/sellers using
aggregation - Not attractive to large buyers
- Higher sales and marketing costs
- Benefits in fragmented demand or supply, not both
10
Forward Aggregation
- Biased toward sellers
- Amass supply and operate downstream in a supply
chain - May host auctions for buyers
11
Forward Aggregator Model
Small Resellers
Large Suppliers
E-hub
Buyers
Compaq
Ingram Micro
IBM
Cisco
Microsoft
Fulfillment Call Center Financing Configurators
Direction of Aggregation
12
Reverse Aggregation
- Biased toward buyers
- E-hubs attract a large number of buyers and then
bargain with suppliers on their behalf
13
The Reverse Aggregator Model
Small Buyers
Large Suppliers
Distributors
E-hub
Dupont
FOB.com
Dow
Ashland
Fulfillment Inspection Receivables Financing
Direction of Aggregation
14
Workflow Redesigner
- Redesigns workflow across businesses in specific
industries - Combine the efficiency of work automation and
effectiveness of process redesign
15
Syndication
- Involves the sale of same good to many customers,
who integrate with other offerings and
redistribute it
16
Three Syndication Roles
- Originators
- Syndicators
- Distributors
17
The Structure of Syndication
18
How Syndication Differs?