Metric spaces - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 43
Title:
Metric spaces
Description:
The functions that we will deal with belong to functional metric spaces ... 'windowing' Relationship. Between cross correlation. Function and. fourier transform ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:2707
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Metric spaces
1
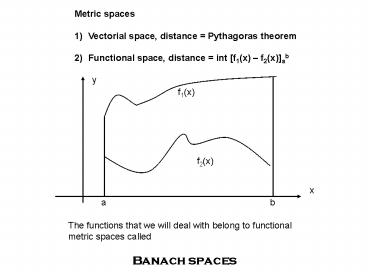
- Metric spaces
- Vectorial space, distance Pythagoras theorem
- Functional space, distance int f1(x) f2(x)ab
y
f1(x)
f2(x)
x
a
b
The functions that we will deal with belong to
functional metric spaces called Banach spaces
2
(No Transcript)
3
(No Transcript)
4
(No Transcript)
5
(No Transcript)
6
(No Transcript)
7
(No Transcript)
8
(No Transcript)
9
Signals can be represented as sums of simple
functions (some times of infinite number of
terms)
10
It is useful to define a series of functions
11
(No Transcript)
12
Binomial distribution
13
(No Transcript)
14
Dirac Delta function (density)
15
A particularly popular methods for representin
signal is FREQUENCY
16
Discrete representations
17
(No Transcript)
18
(No Transcript)
19
(No Transcript)
20
Continuous representation Fourier transform
21
(No Transcript)
22
(No Transcript)
23
(No Transcript)
24
(No Transcript)
25
Time and frequency are scaled In opposite ways
26
(No Transcript)
27
The fourier transform of a gaussian is A nother
gaussian
28
(No Transcript)
29
The importance of windowing
30
(No Transcript)
31
(No Transcript)
32
(No Transcript)
33
Relationship Between cross correlation Function
and fourier transform
34
(No Transcript)
35
(No Transcript)
36
(No Transcript)
37
(No Transcript)
38
(No Transcript)
39
(No Transcript)
40
(No Transcript)
41
(No Transcript)
42
(No Transcript)
43
(No Transcript)