Query Processing - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 36
Title:
Query Processing
Description:
Values are instances of type classes ... 4 bytes of flag: is null, little indian/big indian, ... Value. Padding: ... on cardinality of intermediate relations. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:84
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Query Processing
1
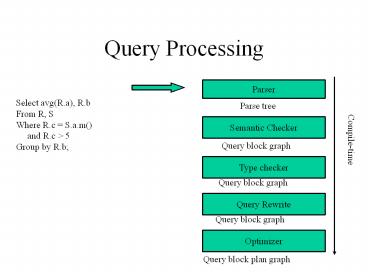
Query Processing
Parser
Select avg(R.a), R.b From R, S Where R.c
S.a.m() and R.c gt 5 Group by R.b
Parse tree
Semantic Checker
Query block graph
Compile-time
Type checker
Query block graph
Query Rewrite
Query block graph
Optimizer
Query block plan graph
2
Query Processing
Select avg(R.a), R.b From R, View Where R.c
View.a.m() and R.c gt 5 Group by R.b
Execution plan
Execution Engine
Run-time
45, t1 76, t2 10, t3
3
Parse Tree
RelViewClassfromselection projectiongroup
byhavingorder by
4
Query Block Graph
Before Type Checking
Proj Avg(R.a), R.b
GBY
Agg Avg(R.a)
Gby R.b
SPJ
Proj R.a, R.b
Sel R.c View.a.m() and R.c gt 5
SPJ
Access to R
Proj S.a
Access to S
5
Query Block Graph
After type checking
Proj Avg(0(1)), 0(2)
GBY
Agg Avg(0(1))
Gby 0(2)
SPJ
Proj 0(1), 0(2)
Sel 0(3) 1(1).m() and 0(3) gt 5
Access to R
SPJ
Proj 0(1)
Access to S
6
Query Block Graph
After query rewrite
Proj Avg(0(1)), 0(2)
GBY
Agg Avg(0(1))
Gby 0(2)
SPJ
Proj 0(1), 0(2)
Sel 0(3) 1(1).m() and 0(3) gt 5
Access to R
Access to S
7
Execution Plan
Executor
Proj Avg(0(1)), 0(2)
GbyPlanOp
Agg Avg(0(1))
Gby 0(2)
Proj 0(1), 0(2)
SMJoinPlanOp
Sel 0(3) 1(1).m() and 0(3) gt 5
Access to S(sequential)
Access to R(indexed)
Stored Relation S
Stored Relation R
8
Query Processing modules
- Types - values - records schema
- Expressions
- Relation
- Storage manager
- Catalog Manager
- Indexes
- Parser
- Optimizer
- Execution Engine
Independent of relational query processing
9
Types and Records
Date (Type)
Specific Date Type
M/D/Cye (Meta-Info)
Date Value
ValuesArray, Date Value,
Record
offset
ADT array
RecordSchema , Att i,
10
Abstract Data Types (fields)
- Identifier index in ADT array
- Type Name
- MethArray array of scalar methods
- AggrMethod array of aggregate methods
- MaintainsCatalog is there meta-information to be
stored in the catalog? - StoreInField is the value stored in place in a
record?
11
Abstract Data Types (some methods)
- MaxObjectSize()
- TypeCopy()
- Equals()
- ReadText(), WriteText()
- GetMetaInfo()
- CreateStatsInfo()
- FuncTypeCheck()
- FuncOptimize()
- FuncReorganize()
- GetMethByIndex()
- CastCheck()
- CreateEnv()
12
ADT Values
- Data Behavior
- Using programming language objects
- Values are instances of type classes
- Need for serialization mechanism to translate
from in-memory to on-disk data representation - Using a specific mechanism (Predator approach)
- Predator ADT Values are not instances of ADT
classes - Data representation is similar in-memory and
on-disk - Type information is more than behavior and
storage management - Optimization
- Catalog Management
13
ADT Values
- Header
- 4 bytes of flag is null, little indian/big
indian, - Value
- Padding
- For aligment purpose (value length must be a
multiple of 8 bytes)
padding
header
value
14
Methods
- To register a function with an ADT
- XxxFuncMethodInfo
- Fields ArgInfo, ArgTypes
- Methods Constructor, Matches
- XxxAggrMethodInfo
- To represent a function in the parse tree
- XxxFuncParseInfo
- To represent a function in the execution plan
- XxxFuncPlanInfo
- Evaluate(XxxValueEnv Env, XxxFuncMethodInfoThisM
ethInfo, XxxADTValue ReturnValue)
15
Record and Record Schema
- Record
- GetField(int position, RecordSchema Schema,
char Field) - Record Schema
- GetAttribute
- Name
- Type
- Meta-information
- GetOffset
- In record structure
16
Expressions
17
Unknown Value (fields)
- Name of the attribute
- Index
- Source child block
- Attribute Index position in child block
- Correlation Height
18
Unknown Value (some methods)
- Resolve Variables / Update Unknowns
- Manipulate index for source and attribute
- Get Dependencies / Redirect Dependencies
- Initialize dependency bitmap structure
- Match
- Checks whether function expression matches a
given expression -- matching information is
returned - Evaluate
- Extracts the ADT Value from position
AttributeIndex in SourceIndex child record
19
Expression Plan
- Function Expression
- FuncParseInfo
- Owner, Arg
- Update Unknowns, GetDependencies, Match
- Optimize
- Function Plan
- FuncPlanInfo
- OwnerPlan, ArgPlan
- evalOwner, evalArgs
- Evaluate
20
Relational Query Processing
- Relational ADT
- No ADT methods defined
- Data Engine
- Relation
- Storage Manager
- Catalog Manager
- Query Processing Engine
- Parse
- Optimize
- Execute
21
Relation
- Relation Type
- Stored Shore File Relation
- matchIndex (Expression, MatchedInfo)
- chooseAccessPath
- Add to / delete from index
- Derived
- Access
- Indexed access
- Sequential access
- Init cursor, next item, close cursor
- Delete record, insert record, update record
22
Relation
- Relation subclassed as ShoreFileRelation,
DerivedRelation, - RelImplInfo
- IndexImplInfo
- IndexList
- Stored / derived
- RelStatsInfo
- Cardinality, average tuple size
- RelCatalogInfo
- Relation name
- Record schema
23
Storage Manager
- Storage Structures
- Create, mount, delete device
- Create, delete file
- Insert, update, delete object
- Iterator, get, pin object
- Transaction support
- Begin, commit, abort
- Indexes
- Btree, Rtree
- Clustered / Unclustered
- Sorting
- Sort File
- Problem how to pass expression used for sorting
- Threads
- Thread model
- Preemptive scheduling
- Non preemptive scheduling
- Synchronization primitives
24
Catalog Manager
- Catalog relations
- _STABLES(tablename, arity)
- _SATTRS(tablename, attname, attindex, atttype,
key?, attmetainfo) - _SINDXS(tablename, indexname, indexexpression)
- _SSTATS
- _SATSTATS
- One catalog per storage device
- GetCatalogRel Bootstrapping problem
25
Indexes
- Index Class (superclass of ShoreBTree and
ShoreRTree) - Type Id
- Index range get range(given an Expression),
merge ranges - Create / delete index
- Insert, delete, get entry
- Match (specific to Index class)
- IndexImplInfo associated to a relation
- Index Type
- Index expression
- Match
26
SQL Parser
- Flex (tokenizer)/ Bison (grammar)
- Interaction with
- Expressions
- Types
- Data Engine
- Insert, Update, Delete Record into Relation
- Create, Delete Index
- Create, Delete Relation
- Query Engine
- Store View
- Exec Query
- Generates Parse Tree
27
Semantic Checker
- Creates Query Graph
- SPJ block
- One block per relation in the From clause
- Views are developed
- Aggregate block is added
- If needed a SPJ block is added at the root
- Verifies conditions on SQL input
- Targets with similar names, aggregates in where
clause, grouping without aggregates, same
expression in aggregate and to group on,
28
Type Checker
- Traverses the Query Block graph
- Bottom-up then top down
- Relies on
- Query graph structure
- Methods defined for Unknown Variables
- Resolve Variables
29
Query Rewrite Rules
- Rule Engine
- Vector list of rules
- Execute rules on one downward and one upward pass
- Rules
- Manipulation across query blocks
- Pushing projections, selections
- Merging query blocks
- Eliminating distinct clauses
- Each rule is a class that implements the
following method - ApplyRule(RelQueryNode In, XxxBool Success,
RelQueryNode Out)
30
Optimizer
- Predicates
- Array of predicate plans, predicate dependencies
and predicate selectivities - Init, Selection, Join, Residual bitmaps
- Query Block Plan
- Redirect dependencies
31
Optimizers
- Simple
- Naive
- Join order fixed by order in the from clause.
Generates a single N-way SPJ node. - Greedy
- Join order based on cardinality of intermediate
relations. Generates a left-deep pipeline of
two-way joins.
- Cost based
- Simplified KBZ
- Tries each relation as outer most relation and
compares cost. Generates a left-deep pipeline of
two-way joins. - Dynamic Programming
- System R like enumeration of join space and
pruning. Generates a left-deep pipeline of
two-way joins.
32
SPJ Naive Optimization phases
- Step1
- Generate plan for children blocks
- Step2
- Create the predicate bitmap for the selections
and joins - Step3
- Construct a remapping of unknown variables
depending on schema of children - Step4
- Modify all expressions based on remapping
- Step5
- Generate plan operator for SPJ
33
Relational Operators
- Iterator interface
- Shared data structure (handles) for passing
arguments - State information e.g., end-of-stream
- Operator specific information cursor position
(nested loop) - Single records flowing across operators
- Access Method is chosen dynamically for each
accesses
34
Execution
- Executor wrapper on top of execution plan
- creates a derived relation
- Initializes derived relation (recursively
initializes execution plan) - Iterates over records
- Process resulting records
- Write to client
- Close iterator
- Clean-up
35
Server Architecture
Console
Server Thread
Monitor Thread
Client
Init Thread
Request Thread Client interaction Relies on
Protocol - text - binary
Request Thread
Request Thread
Request Thread
Request Thread
36
Summary
- Predator achieves extensibility by isolating
these modules which are independent from the rest
of the system - Types and Expressions are used throughout the
system and are prone to changes - Predator reuses the clean internal data
structures defined in Starbust