Quantum Mechanics PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Quantum Mechanics
1
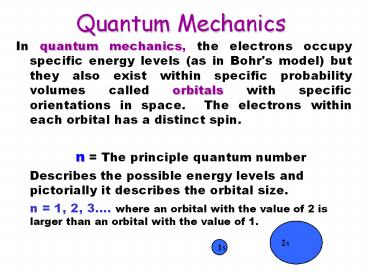
Quantum Mechanics
- In quantum mechanics, the electrons occupy
specific energy levels (as in Bohr's model) but
they also exist within specific probability
volumes called orbitals with specific
orientations in space. The electrons within each
orbital has a distinct spin. - n The principle quantum number
- Describes the possible energy levels and
pictorially it describes the orbital size. - n 1, 2, 3. where an orbital with the value of
2 is larger than an orbital with the value of 1.
2s
1s
2
Quantum Mechanics
- l angular momentum quantum number
- Describes the "shape" of the orbital and can have
values from 0 to n - 1 for each n. - orbital designation s p d f
- shape
- ml magnetic quantum number
- Related to the orientation of an orbital in space
relative to the other orbitals with the same l
quantum numbers. It can have values between l
and - l . - ms spin quantum number
- An electron has either 1/2 or -1/2 spin values
sometimes referred to as spin up and spin down.
Too hard to draw see text
3
Orbital Shapes
4
Electron Configuration
- Electron configuration is a shorthand notation
for describing the arrangement of the electrons
about the nucleus. - General Format using the quantum numbers
- n l e-
- RULES
- 1. Fill the lowest energy levels first.
- 1s 2s 2p 3s 3p 4s 3d 4p
- 2. No more than two electrons per orbital.
n principle quantum number l angular momentum
quantum number e- number of electrons
Lowest
5
Electron Configuration
- Examples
- H 1s1 He 1s2 Li 1s2 2s1
- Co 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d7
- Br 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p5
- The condensed electron configuration
distinguishes the core electrons from the valence
electrons. CORE electrons are tightly held to
the nucleus and resemble a noble gas
configuration. VALENCE electrons are the outer
most electrons and are involved in chemical
reactions. - Examples of the condensed configuration
- LiHe 2s1 CoAr 4s2 3d7
- BrAr 4s2 3d10 4p5
6
Electron ConfigurationPractice Problems
- 1. Give the full electron configuration
- C O Ne Na Si Cl Ar K
- 2. Give the condensed electron configuration
- C O Ne Na Si Cl Ar K
Answers on next slide
7
Electron Configuration
- Answers
- 1 2. Give the full condensed electron
configuration - C 1s2 2s2 2p2 or He 2s2 2p2
- O 1s2 2s2 2p4 or He 2s2 2p2
- Ne 1s2 2s2 2p6 or Ne
- Na 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s1 or Ne 3s1
- Si 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 or Ne 3s2 3p2
- Cl 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p5 or Ne 3s2 3p5
- Ar 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 or Ar
- K 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 or Ar4s1
8
Orbital Diagrams
- Orbital diagrams are written in order of
increasing energy levels starting with the lowest
energy level the 1s orbital. - ___ ___ ___ 4p
- ___ ___ ___ ___ ___ 3d
- ___ 4s
- ___ ___ ___ 3p
- ___ 3s
- ___ ___ ___ 2p
- ___ 2s
- ___ 1s
RULES (1) fill the lowest energy level first (2)
fill each orbital in a subshell with one electron
first before you double up. (3) Completely fill
each subshell before proceeding to the next
energy level.
Remember the order!!
9
Orbital DiagramsPractice Problems
- 1. Fill in the orbital diagrams for
- C O Ne Na Si Cl Ar K
- ___ ___ ___ 4p ___ ___ ___ 4p
- __ __ __ __ __ 3d __ __ __ __ __ 3d
- ___ 4s ___ 4s
- ___ ___ ___ 3p ___ ___ ___ 3p
- ___ 3s ___ 3s
- ___ ___ ___ 2p ___ ___ ___ 2p
- ___ 2s ___ 2s
- ___ 1s ___ 1s
10
Orbital DiagramsPractice Problem Answers
- Fill in the orbital diagrams for
- C O
- ___ ___ ___ 4p ___ ___ ___ 4p
- __ __ __ __ __ 3d __ __ __ __ __ 3d
- ___ 4s ___ 4s
- ___ ___ ___ 3p ___ ___ ___ 3p
- ___ 3s ___ 3s
- ___ ___ ___ 2p ___ ___ ___ 2p
- ___ 2s ___ 2s
- ___ 1s ___ 1s
11
Orbital DiagramsPractice Problem Answers
- Fill in the orbital diagrams for
- Ne Na
- ___ ___ ___ 4p ___ ___ ___ 4p
- __ __ __ __ __ 3d __ __ __ __ __ 3d
- ___ 4s ___ 4s
- ___ ___ ___ 3p ___ ___ ___ 3p
- ___ 3s ___ 3s
- ___ ___ ___ 2p ___ ___ ___ 2p
- ___ 2s ___ 2s
- ___ 1s ___ 1s
12
Orbital DiagramsPractice Problem Answers
- Fill in the orbital diagrams for
- Si Cl
- ___ ___ ___ 4p ___ ___ ___ 4p
- __ __ __ __ __ 3d __ __ __ __ __ 3d
- ___ 4s ___ 4s
- ___ ___ ___ 3p ___ ___ ___ 3p
- ___ 3s ___ 3s
- ___ ___ ___ 2p ___ ___ ___ 2p
- ___ 2s ___ 2s
- ___ 1s ___ 1s
13
Orbital Diagrams Group Study Problems
- Fill in the orbital diagrams and then write the
electron configuration (both full and condensed)
for - B F Ca P S As Zn Pb
- ___ ___ ___ 4p
- __ __ __ __ __ 3d
- ___ 4s
- ___ ___ ___ 3p
- ___ 3s
- ___ ___ ___ 2p
- ___ 2s
- ___ 1s