Inference in a Bayesian Network based on Stochastic Simulation PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Inference in a Bayesian Network based on Stochastic Simulation
1
Inference in a Bayesian Network based on
Stochastic Simulation
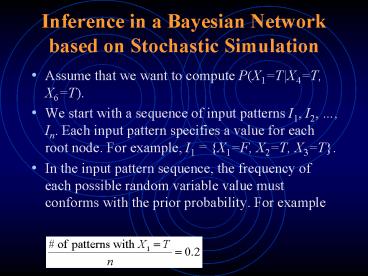
- Assume that we want to compute P(X1TX4T,
X6T). - We start with a sequence of input patterns I1,
I2, , In. Each input pattern specifies a value
for each root node. For example, I1 X1F,
X2T, X3T. - In the input pattern sequence, the frequency of
each possible random variable value must conforms
with the prior probability. For example
2
- Let us use the pattern X1F, X2T, X3T to
illustrate the process. - We start from the root nodes and walk down.
- When the parents of a node are all instantiated,
the node is ready for being instantiated. - Since X2T, X3T, the probability that X5T is
0.1. We can invoke a random number generator to
give us a number between 0 and 1. If the number
generated is less than 0.1, then we set X5T.
Otherwise, we set X5F.
3
- Once all simulation runs have been completed, we
calculate
4
Learning in Bayesian Network
- In general, people employ the cause-and-effect
reasoning to determine the structure of a
Bayesian network. - If the training samples contain observations at
each node, then the learning process is
straightforward.
5
- However, it is common that we do not have
observations of all the nodes.Therefore, we want
to find a setting of the conditional probability
tables so that is maximized, whereis a set of
training samples. - We assume that the training samples are collected
from independent runs of the corresponding
experiment. Therefore,
6
- Since ln(x) is a monotonic increasing function,
is maximized if and only if is
maximized. - For each entry in the conditional probability
tables that is yet to be determined, we compute
k-th column
where wijk is the entry at row j,column k of the
conditionalprobability table of node Xi.
j-th row
7
(No Transcript)
8
- Therefore,
- Furthermore,
9
- The learning process begins wih an initial guess
of all unknown wijk.For each unknown wijk,
computeand set new - Normalize wijk by setting normalized
- If each wijk converges, then terminate.
Otherwise, report the process again.
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.