The Digestive System PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 28
Title: The Digestive System
1
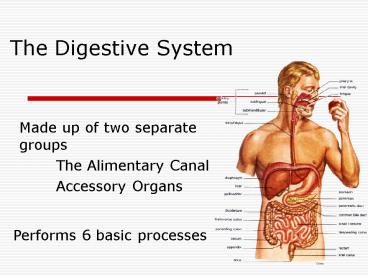
The Digestive System
- Made up of two separate groups
- The Alimentary Canal
- Accessory Organs
Performs 6 basic processes
2
6 Functions of the Digestive System
- Ingestion- taking in food and liquids
- Secretion- water, acid, buffers and enzymes added
to system - Mixing and Propulsion
- Digestion- chemical and physical
- Absorption- nutrients delivered to blood
- Defecation-elimination of waste
3
Digestion
- Mechanical- Teeth, tongue and cheeks cut and
grind food into smaller portions before
swallowing and the stomach and sm intestine churn
the food - Chemical- Digestive enzymes and acids break large
molecules like carbohydrates into simpler sugars
4
Alimentary CanalGI Tract
- Mouth
- Pharynx
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- Small Intestine
- Large Intestine
5
Mouth
- Mechanical and chemical digestion both occur in
the mouth. The teeth and salivary glands combine
to begin the digestive processes. - Swallowing- (deglutition) is the process of
moving food into the pharynx and esophagus.
6
Pharynx
- During swallowing, the epiglottis closes off the
respiratory passage. - The soft palate and uvula close off the
nasopharynx - The food bolus will spend less than 2 seconds in
the pharynx
Sorry, I have a frog in my Throat.
7
Esophagus
- A muscular, collapsible tube about 10 inches
long. - Transports food to the stomach
- No digestion occurs here
- Peristalsis consists of progressive, wavelike
contractions
8
Stomach
- A mixing chamber and holding reservoir.
- Some mechanical digestion as the food is churned
and mixed. - Chemical digestion occurs through the action of
gastric juice - Food is now called Chyme
- Chyme will spend approx. 4 hours in the stomach.
9
Stomach
- Have 2 sphincters
- Lower esophageal
- Pyloric
- 3 layers of muscles
- Longitudinal
- Circular
- Oblilque
- 4 Regions
- Cardia
- Fundus
- Body
- Pylorus
10
Gastric Juice Contains
- Pepsin- which breaks down proteins
- Gastric lipase- acts on fats
- Hydrochloric acid- kills microbes and assists in
other chemical digestion - Mucus- protects stomach wall
11
Small Intestine
- Most digestion and absorption occurs in the small
intestine - Its length of 10 feet allows time for nutrients
to be properly absorbed - Diameter of about 1 inch
- Internally, the intestine is lined with folds,
villi and microvilli to further support
absorption.
12
Small Intestine
- Divided into 3 regions
- Duodenum (10 inches)
- Receives chemicals from pancreas, liver and
gallbladder - Jejunum (3 feet)
- Ileum (6 feet)
13
Villi in the Small Intestine
- Work to increase the surface area of so more
substances can be absorbed.
14
Villi in the Small Intestine
Contain Blood vessels and Lymphatic vessels to
absorb nutrients.
15
Large Intestine
- 5 Feet long, and 2.5 inches in diameter
- Functions
- Completion of absorption
- Production of certain vitamins
- Formation of feces
- Expulsion of feces from body
16
Regions of the Large Intestine
- Cecum
- Colon
- Rectum
- Anal canal
17
Cecum
- The Cecum is a large pouch-like sac.
- A sphincter acts as a doorway between the small
intestine and cecum. - The appendix hangs off the cecum, it is about 3
inches long and its function is a mystery.
18
The Colon
- The walls of the colon are much more muscular
than those of the small intestine. - The Colon is divided into the following regions
- Ascending
- Transverse
- Descending
- Sigmoid
19
Accessory Organs
These organs assist in the process of digestion,
but do not come in direct contact with food.
20
Accessory Organs Include
- Salivary Glands-
- 3 major pairs Parotid, Submandibular and
Sublingual - Water helps to lubricate dry foods
- Salivary amylase begins working on starches
21
Accessory Organs Include
- Teeth- cut tear and pulverize food
- Adults have 32
- Classified as
- Molars
- Incisors
- Canine
- Tongue- swallowing, maneuvers food
- Contains taste buds
22
Pancreas
- Found just under the stomach
- Delivers pancreatic juice thru a duct into the
duodenum - Pancreatic juice buffers the acid in gastric juice
Enzymes work on proteins, fats and nucleic acids.
23
Liver
- The second largest organ in the body.
- In addition to many complex functions, the liver
creates bile. - Bile breaks down fats thru emulsification.
The liver also removes toxic substances from the
blood and stores nutrients for a more even
release into the blood stream.
24
Gallbladder
- The gallbladder stores the bile made by the
liver. - It senses when fats are present in the duodenum
and then squirts bile when needed thru ducts.
25
Common Disorders of the Digestive System
- Ulcers- created when acid production overwhelms
mucus in the stomach and the stomach lining is
damaged - Gallstones- occur when bile stored in gallbladder
crystallizes to form stones. - Appendicitis- occurs when the appendix gets
twisted, cutting off its blood supply. Infection
and sepsis can result. - Heartburn- occurs when stomach acid leaks back up
into the esophagus
26
Food- 6 types
- Carbohydrates- (starches) broken into simple
sugars - Proteins-broken down into amino acids
- Fats- triglycerides and lipids
- Water-directly absorbed
- Vitamins-directly absorbed
- Nucleotides-broken into components
27
Chemical Digestion
- Mouth- Saliva
- Salivary amylase- starch
- Lingual lipase- triglycerides
- Stomach-Gastric Juice
- Pepsin-proteins
- HCL-bacteria
- Gastric lipase- triglycerides
28
Chemical Digestion
- Pancreas
- Pancreatic amylase- starches
- Trypsin-proteins
- Pancreatic lipase- triglycerides
- Liver/Gallbladder
- Bile- emulsification of lipids
- Small Intestine
- Sugars to simple sugars
- Dipeptides to amino acids
- Nucleotides to simpler components