Research process IV - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 24
Title:
Research process IV
Description:
Factors influencing communication during an interview. The ... Sherlock Holmes. Business Research Methods - Nina R hr Tunstall. 16. Scientific observation ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:97
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Research process IV
1
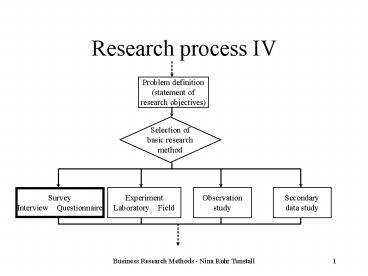
Research process IV
Problem definition (statement of research
objectives)
Selection of basic research method
Experiment Laboratory Field
Observation study
Secondary data study
Survey Interview Questionnaire
2
Survey methods
Types of survey
No direct contact to respondent
Direct contact to respondent
Telephone interviews
Personal interviews
Questionnaire
Structured interview (interview guide)
Focus interview Focus group
Non-structured interview (in-depth)
3
Survey Methods
- Personal interviews
- Telephone interviews
- Door-to-door
- Postal - mail interviews
- Mall intercept
- Combination of methods
- Questionnaire always needed
4
Factors influencing communication during an
interview
The interview situation Time Place Third
persons Norms
The interviewer Social characteristics Ability
to interview Motivation
The respondent Social characteristics Ability to
respond Willingness to respond
The researched topic Sensitive Difficult Interest
s Fear
5
Personal interviews
6
Telephone interviews
- mouth-to-ear - visualisation issues
- feedback - probing - willingness
- anonymity (sensitive topics) - more impersonal
- central based interviewer - cost
- callback issues - (see sampling errors - next)
- speed - duration
- simplicity - sampling (random digit calling)
- cultural differences
- questionnaire needed
7
Sampling errors in telephone interviews
Population
Sample
Telephone
No direct access to telephone
No telephone at home
Just moved etc.
Number available
Secret number
Not at home Interruption
Refuse
Accept interview
8
Self-administrated questionnaires
- hard copy questionnaires
- no interviewer
- different ways of distribution
- different structures/lay outs
- cultural differences or literacy
9
Self-administrated questionnaires - Distribution
- mailed
- distributed by hand
- enclosure
- available in room
- internet
10
Mail questionnaires - Pros and Cons
- Cost effective
- Convenience/time - easy/fast
- Standardisation/no feedback possible
- Length - limited
- Response rate - low
11
Factors influencing response rate
- Pre-notification
- Incentives/arguments - prepaid return envelope
- Covering letter or instruction
- Topic
- Type, wording and order of questions
- On line help or personlisation
- Lay out - print on both pages or colour
- Reminder/follow up
12
Surveys
- Questionnaire
- cheap - fast - anonymous
- low respons - questions are critical
- Personnal interviews
- high respons, explanations kan be given/obtained
- expensive and time consuming
- Telephone interviews
- relatively fast and cheap - good respons
- only a few (closed) questions - non respondents
13
Pretest considerations
- Should it be
- by experts ?
- by a pilot sample ?
14
Research process IV
Problem definition (statement of research
objectives)
Selection of basic research method
Survey Interview Questionnaire
Experiment Laboratory Field
Secondary data study
Observation study
15
SCIENTIFIC OBSERVATION IS SYSTHEMATIC
YOU SEE, BUT YOU DO NOT OBSERVE.
Sherlock Holmes
16
Scientific observation
Science Fact of knowing (as opposed to
intuition) Observation The act of noting and
recording facts and events Scientific
observation Systematic process of recording
(without communicating)
17
TYPES OF OBSERVATION
- HUMAN versus MECHANICAL
- VISIBLE versus HIDDEN
- Passive or active observer
18
Observations
- Not observable
- attitudes
- intentions
- motivations
- expectations
- preferences
- Advantages
- often more exact information compared to
questioning due to - memory
- perception
- desirability
19
Direct observations - Potential Errors
- Observers objectivity
- Recording vs. interpretation
- Response latency
- Knowing you are being observed
- Planned observation
- Monday morning syndrome
20
Observation
- the participants (characteristics/relationship)
- the setting
- the purpose (arranged/by chance)
- frequency and duration
21
Ethics
- Hidden observation vs. privacy
- Contrived observation vs. deception
- A question of balance
- need of information vs. unpleasant situation
22
Scientifically collected observations
- Creation of artificial surroundings is necessary
for making the test - Showrooms
- Displays in shop
- Etc.
23
Mechanical Observation
- Trafic counting
- Data from mobile phones
- Data from scanners
- Counting machines
- Psychological measurements (see next)
24
Psychological measurements
- Eye tracking - Measure unconscious eye movements
- Pupilometer - changes in the size of pupils
- Psychogalvanometer -
- Measure changes in the skin (unconscious
electrical resistance in the skin) - Assumption - physical changes are related to
emotional reactions - Voice analysis
- Register emotional changes in the voice