MPS Development PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 51
Title: MPS Development
1
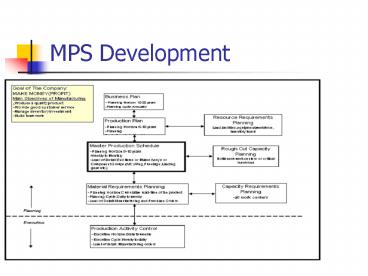
MPS Development
2
MPS Development
- MPS is the statement of Production Plan by end
item,datesquantities that is committed to be
manufactured by the contract. - MPS seeks to plan and control the impact of
independent demand on material and capacity. - A vital link between sales and production.
- Makes possible valid order promises.
- Represents a contract between sales and
production. - It should be realistic and achievable
3
Objectives
- Maintain the desired level of customer service.
- Makes the best use of resources.
- Keep inventories at the desired level.
4
End Item
- A Deliverable unit which might be an A/C or a
component or a subcomponent or a part that is
specifically identified in the contract. - e.gCenter Fuselage, Tailcone,MLG,P-Band Antenna.
5
INPUTS
- End Item Delivery Plan(Production Plan)
- Order changes from customer.
- Capacity constraints.
- Estimated Learning Curve Manhour.
- Bill of Material(BOM)
- Assembly Flow.
- Crew Size Optimization.
- SWBS Schedule Work Breakdown Structure.
- Contract Go-Ahead.
6
STEPS IN MAKING AN MPS
- Make a preliminary MPS.
- Perform Rough-Cut Capacity Analysis.
- Resolve differences.
- Make the official MPS.
7
Rough-Cut Capacity Planning
- Checks whether critical resources are available
to support the Preliminary Master Schedule. - Once the MPSs are made,they must be checked
against the available capacity. - What are the critical resources?
- Manpower
- FixturesCoji,Assembly Fixture,Autoclave etc.
- Available work place,location.
- Etc.
8
Resolving Differences
- If required capacity exceeds the available
capacity - Capacity must be increased, or
- Plan must be altered.
9
MPS Preparation
- Determine SWBSs,
- Determine the line-move rate,
- Determine the optimum crewsizes,
- Span-time calculations,
- Determine fixture quantity,
- Determine the Assembly Flow,
- Determine end-item completion dates,
- Apply setback in order to get the SWBS start
dates,
10
MPS Preparation
- SWBS-Schedule Work Breakdown Structure
- Some examples
- SWBS X111Mating of Fuselage.
- SWBS X116System InstallationCheckout
- SWBS X162Wing Structural Installation.
11
MPS PREPARATION
- Determining the line Move Rate based on end item
delivery/requirement dates. - If the delivery rate is4 end item/month
- Considering 20 working day a month
- Line Move Rate is 5 Days
12
MPS PREPARATION
- Determining the optimum crewsizes.
- -Analysis of work Areas.
- Availability of work places
- Confined spaces
- -Communicate with the shop people
- -Determine the optimum crew
13
MPS PREPARATION
- Calculation of span times for each fixture based
on learning curve manhours optimum crew sizes. - Span TimeLearning Curve Budget
/(CrewsizeWorking Hour Per Day)
14
MPS PREPARATION
- Calculation of fixture Quantity.
- Make iterative calculation to ensure below
equation - Span TimeltFixture QuantityLine Move Rate
- So Fixture QuantitygtSpan Time/Line Move Rate.
- Example Line Move Rate 5 days
- Learning curve hour 160 manhour
- Optimum crewsize2 technician
- Span Time160/(28)10 mdays
- Fixture Quantitygt10/5
- gt2 (Minimum 2 fixtures)
15
MPS Preparation
Item4
Item3
5 Mday
Item2
Item1
8 Mday
16
MPS Preparation
- Determination of end item completion dates based
on line move rate end item delivery dates. - Applying setback based on calculated span times
from end item completion dates to generate start
dates for each SWBS.
17
MPS Preparation
- Assembly Flow
- We need Assembly Flow in order to determine the
SWBS start completion dates.
18
MPS Preparation
- Assembly Flow Examples
- A typical Final Assembly Flow
- A component assembly flow
19
MPS Preparation
- Case StudyOne of the outstanding A/C
Manufacturing Companies in Europe needs to buy 48
Center Wing component in 2008 in order to support
its Final Assembly which delivers 4 A/C per
month.After the negotiations Our Company and the
Customer came to an agreement and signed a
contract.Deliveries should be accomplished in
equal quantities in monthly basis starting from
the beginning of year 2008.
20
MPS Preparation
- WE NEED TO PREPARE AN MPS.
21
- Getting tecnical information from our customer
,we made necessary calculations and analysis - Determine the Production plan
- Line Move Rate analysis
- Determination of delivery dates.
- Learning Curve analysis.
- Determination of assembly flow.
- Crewsize analysis
- Span time analysis
- Determination of fixture quantities.
22
MPS Preparation
- Production Plan
23
MPS Preparation
- MPS Delivery Quantities
24
MPS Preparation
- Line Move Rate Analysis
- 4 centerwing per month
- Line Move Rate 20/4 5 mdays
25
MPS Preparation
- SWBSSchedule Work Breakdown Structure
- Center Box(Coji Operations) X152
- System Operations X151
- AftFront Spar X051
- Trailing Edge X053
- Inboard Flap X056
- Leading Edge X057
26
MPS Preparation
- Assembly Flow
27
MPS Preparation
- Here well take the first 4 units as a case
- Our Estimation section has informed us that first
4 units learning curve hours as follows
28
MPS Preparation
- Optimum Crewsizes
29
MPS Preparation
- Span Time Analysis
- Formula is
- Span TimeManhour/(Crewsize8)
- Based on the assumption that working hour a day
is 8 hours.
30
MPS Preparation
- Calculated span times
31
MPS Preparation
- Fixture Analysis
- Fixture QuantitygtSpan Time/Move Rate
- SWBS X152
- Fix.Qtygt20/54
- SWBS X151
- Fix.Qtygt10/52
- SWBS X051
- Fix Qtygt8/52
- SWBS X053
- Fix Qtygt8/5 2
- SWBS X056
- Fix Qtygt10/52
- SWBS x057
- Fix Qtygt8/52
32
MPS Preparation
- Delivery DatesAccording to Contract deliveries
will be done in one shipment at the end of each
month.(4 items/shipment) - For January 2008 Shipment
33
MPS Preparation
- Determining Completion dates
- First Unit Comp DateDelivery Date Bank Time
- Bank Time is the safety time between delivery
date and completion date. - Move rate is other input in calculating the
remaining units completion dates.
34
MPS Preparation
- Determining SWBS Start Dates
- SWBS start dateCompletion Date-Span Time1
35
MPS Preparation
- Setbacks are done according to the assembly flow
chart by using the span times. - Mdays are converted to Calendar Day by using
VLOOK-UP function of Excel. - MPS can be shown either in Microsoft Excel or
Microsoft Project.
36
MPS Preparation
37
MPS Preparation
- Mps format in microsoft excel/word
38
Royal Jordan Air Force F16 Modification
- SWBS list for F16 Modification
39
Royal Jordan Air Force F16 Modification
40
Royal Jordan Air Force F16 Modification
41
Royal Jordan Air Force F16 Modification
42
Status visibility and Control
- Build Crewload charts
- Crewload charts show detail information of each
task center, - In operation basis,
- Consist operation hours,daily, schedule,actual
and earn hour, - Updated daily/weekly.
43
Status visibility and Control
44
Status visibility and Control
- Schedule hour is the budget hour of each task
that is planned in timely manner. - Earn hour is budget manhour amount of
accomplished tasks . - Earn hour of each task should be equal to its
budget hour when they are done. - Actual hour is the actual manhour that has been
spent in order to perform the each task/operation
,task center or SWBS.
45
Status visibility and Control
- Calculate performance
- PerformanceEarn Hour/Actual Hour
- Performance can be calculated in task center or
SWBS basis.(Even in operation basis). - Issue weekly/monthly performance reports.(In SWBS
/Task Center basis)
46
Status visibility and Control
- In order to provide the status visibility we have
to calculate the completion ratio - The formula is
- CompleteCompleted Task/Total Task.
- It can be calculated in SWBS and/or Task Center
basis.
47
Status visibility and Control
- If we are doing as planned, this means we are on
schedule, - If we have a delay ,this means we are behind of
schedule, - If we are doing better than planned ,this means
we are ahead of schedule.
48
Status visibility and Control
- Provide status visibility to Program Management.
49
Recovery Plans
- Recovery Plans are needed when incomplete work
exceeds shops ability to accomplish it within
its scheduled flow time. - This is usually caused by
- Unavailability of parts
- Unavailability of manpower.
- Prior work being completed.
- Product not meeting the engineering requirements
- Etc.
50
Recovery Plans
- We need to consider
- Overtime
- Second shift
- Additional Manpower
- It might be costly and should be negotiated
either internally or with the customer.
51
We are Done
- THANK YOU !