Chapter 3: Principles of Plant Growth PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 33
Title: Chapter 3: Principles of Plant Growth
1
Chapter 3 Principles of Plant Growth
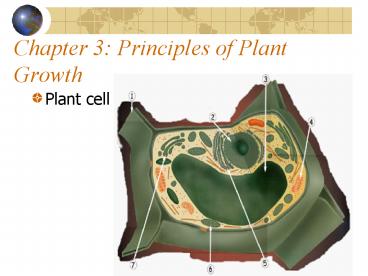
- Plant cell
2
Cell Wall
3
Cell Wall
- A rigid outer layer of the cell composed
primarily of cellulose and lignin. The cell wall
is durable enough to give plants structure and
support, yet porus enough to allow water and
other materials to pass in and out of the cell
4
Cytoplasm
- The fluid surrounded by plasma membrane
- Made up of a complex protein matrix or gel
5
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
6
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
- A complex structure consisting of folded sacs
tunnels. Proteins produced by the ribosomes are
passed through the ER membrane into the ER lumen,
where they are sealed in vesicles for transport
to the cell membrane, golgi apparatus, or other
cell organelles. ER covered with ribosomes if
referred to as rough ER. Whereas ER with few
or no attached ribosomes is termed smooth ER
7
Ribosomes
- The site of protein synthesis. When found
floating freely in the cytoplasm, they produce
protein that will be used in the cell. When
attached to the ER, they produce proteins used
outside the cell.
8
Chlorophyll
9
Chlorophyll
- The site of photosynthesis. Chloroplasts
synthesize the pigment chlorophyll, giving plants
their green color. Chlorophyll, along with other
pigments, allow plants to capture and store
energy from sunlight, which can later be utilized
for photosynthesis.
10
Mitochondria
11
Mitochondria
- The site of respiration within the cell.
Mitochondria utilize oxygen to produce adenosine
triphosphate (ATP). In turn, ATP provides energy
for almost all the cells chemical reactions.
Mitochondria contain DNA and are capable of
manufacturing their own proteins.
12
Nucleus
13
Nucleus
- The control center of the cell. The nucleus
contains chromosomal DNA that regulates the
production and structure of proteins within the
cell. The nucleus is surrounded by the nuclear
membrane, a porous membrane that allows materials
to pass in and out of the nucleus.
14
Golgi Complex
15
Golgi Complex
- A series of flattened sacs and vesicles.
Proteins, as well as other molecules such as
hormones carbohydrates, pass through the
various sacs of the golgi complex where they are
chemically modified. After modification, the
molecules are placed in vesicles for transport
within ad out of the cell
16
Vacuoles
- A fluid filled cavity that stores water, salts,
enzymes, food, and other materials required by
the cell. They can make up 90 of the cell. The
help support the cell.
17
Plant Tissues
- Groups of cells that function as a unit. 4
groups. - Meristematic- a region in which undifferentiated
cells divide. - Fundamental- parenchyma tissue in monocots.
(equivalent of cortex and pith in dicots).
Storage units. - Protective- Epidermal skin protects.
- Vascular- Xylem Phloem is the transport system.
18
Plant Organs
- Groups of tissues form organs.
- Roots
- Stems
- Leaves
19
Root
20
Stem
- Terminal bud
- Axillary bud
- Node
- Internode
- Lenticel
- Terminal bud scar
- Bundle scar
- Leaf scar
21
Leaves
22
Photosynthesis
- 6 CO2 12 H20 Green Plant C6H12O6
6 H20 6 O2 - Light Energy
23
Transpiration
- Loss of water by the plant.
- How does the plant protect itself from losing to
much water?
24
Heredity
- Plant breeding.
25
Growth vs- Time
- S shape growing curve.
- Why is important to know when the plant is going
to start a flush of growth?
26
Temperature
- minimum, maximum, optimal temperatures for a crop
- wheat min40 max90 (when flowering)
- crops generally don't grow in areas where average
24 hour temperature 130
27
Radiant Energy (Amount, quality duration of
sunlight)
- amount of light energy received
- measured in foot candles
- summer day 10,000
- living room 20
- crops need 100-10,000
- if not enough light, grow tall (leggy, weak
stems) - weed control reduces competition for light
- planting rate row spacing
- some plants need shade (tobacco), burlap, lathes,
screens
28
Radiant Energy (Amount, quality duration of
sunlight)
- energy that travels in wavelengths
- short wavelengths high energy (blue)
- long wavelengths low energy (red)
- ultraviolet invisible
29
Radiant Energy (Amount, quality duration of
sunlight)
- amount of light of different colors
- plants absorb red blue, reflect green
- smoke filters blue, sun looks red
- glass plastic filter light
30
Water
- Photsynthesis
- Needed for metabolic functions
- Transpiration
- Evaporation
- Evapotranspiration
31
Atmosphere
- The Primary gases are oxygen and Carbon dioxide
for respiration and photosynthesis. - Excess sulfur dioxide, ethylene, fluorides
others can harm plants
32
Nutrient Requirement
- C HOPKNS CaFe Mg Na Cl Cu Mn Co Zn Mo B
- C Hopkins Café mighty good (but) Not always
Clean. CuMn CoZn MoBy? - Nickel
33
Photoperiodism
- Some plants needs a certain number of hours of
day length to flower - Short day plants (i.e. poinsettias, strawberries,
mums) need long nights uninterrupted to flower - Long Day plants (i.e. spinach sugar beets) need
short nights - Day neutral (i.e. tomatoes)