Genetics PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 34
Title: Genetics
1
Genetics
2
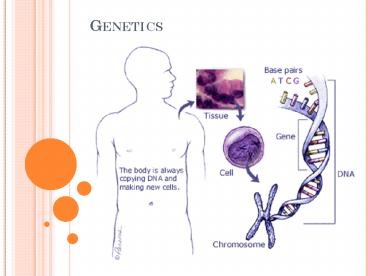
DNA MOLECULE The Code of LIFE
- What is DNA?
- DNA DeoxyriboseNucleic Acid
- Molecule that makes up genes
- Determines traits in all living things
3
What does DNA look like?
- Twisted ladder
- Spiral stair case
- http//learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/tour/
index.html
4
6 Features of DNA
- 1. two main sides (ladder uprights)
- 2. sides are two alternating chemicals
- A sugar
- An acid
- 3. parts connect the uprights (ladder rungs)
- 4. Nitrogen bases form the rungs
- 5. 4 different nitrogen bases
- Adenine (A) -- Thymine (T)
- Guanine (G) -- Cytosine (C)
- 6. Pairing
- A can only pair with T
- C can only pair with G
- These fit together like a puzzle
5
Where is DNA found in the cell?
- Found in the nucleus
- It makes up chromosomes
6
What is a GENE?
- Short piece of a chromosome that determines
traits - Gene has a specific number of DNA base pairs on a
chromosome - http//learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/dna/t
our_gene.html - http//www.fofweb.com/Science/default.asp?ItemIDW
E40
7
chromosome Number
- Human sperm or egg cell has 23 chromosomes
(Meiosis)- not paired - Body cells have 46 chromosomes (23 pairs)
(MITOSIS) - Different organism have different number of
chromosomes - Carrot plant 18 chromosomes 9 pairs
- Corn plant 20 chromosomes 10 pairs
- Rabbit 44 chromosomes 22 pairs
8
What is an Amniocentesis?
- A needle is inserted into a pregnant womans
abdomen - Remove a liquid called amniotic fluid
- Fetal cells are in the liquid
- Happens at 14-16 weeks
- Analyze fetal cells
- Match up chromosome pairs to make a karyotype
- http//www.youtube.com/watch?vfvqJ4lX5I8o
9
Karyotype - A set of photographs of chromosomes
grouped in order of pairs
10
Karyotype
11
Sex- a genetic trait
- Sex chromosomes chromosomes that determine the
sex of a organism (male or female) - XX female
- XY male
- Females can only give an X (only an X in ovary)
- Males can give an X or Y in sperm
- Males determine the sex of the offspring
- ONLY MALES HAVE Y CHROMOSOME
- Autosomes all other chromosomes EXCEPT sex
chromosomes (DONT DETERMINE THE SEX) - http//learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/tour/
index.html
12
Chances of having a boy or girl
- Mother
- X X
- X
- Y
- Father sex
13
Genetic Vocabulary http//learn.genetics.utah.edu
/content/begin/tour/index.html
- Genetics
- The study of how traits are passed through
reproduction/fertilization from parent to
offspring - Trait
- A feature or quality that an animal, plant, or
other organism has or shows - Gene
- Small section of a chromosome that determines a
specific trait - Examples
- Eye color, height, freckles,
- Allele
- Different form of a gene can be dominant or
recessive - Every gene contains 2 alleles
14
- Dominant Allele
- Allele that allows a trait to be expressed while
keeping other alleles from showing - Recessive Allele
- Allele that gets overpowered by or masked by a
dominant allele for the same trait - Present but not expressed
- Each organism receives ONE allele for each trait
from each parent - ½ of the alleles come from the egg (mom)
- ½ of the alleles come from the sperm (dad)
15
- Homozygous Pure both alleles are the SAME
- Homozygous Dominant
- Both alleles are dominant and are written with
capital letter - Ex. TT Tall BB Brown eyes
- Homozygous Recessive
- Both alleles are recessive and are written with
lower case letters - Ex. tt short bb blue eyes
- Heterozygous
- Different two alleles for the same trait are
different - One recessive and one dominant
- The dominant trait gets expressed
- Ex. Tt Tall Bb brown eyes
16
- Genotype
- The combination of alleles or genes
- Represented with letters
- Ex. TT Tt tt
- Phenotype
- Physical appearance or expression of alleles or
genotypes - Ex. Tall Tall Short
17
Punnett Square
- Prediction of what genes can combine when egg and
sperm join (FERTILIZATION) - Review
- F dominant gene FF pure dominant
- f recessive gene Ff heterozygous
- ff
pure recessive
18
5 steps to Punnett Squares
- 1. Draw your punnett square
- 2. Decide which genes will be moms sex cells
and which will be dads. - Ex. Mom and Dad are heterozygous for
Free-earlobes - Ff x Ff Mom
- F f
- F
- Dad
- f
19
5 steps to Punnett Squares
- 3. Copy the letter that appear at the top of the
square into the boxes below each letter - Mom
- F f
- F
- Dad
- f
- 4. Copy the letters that appear at the side of
the square into the boxes next to each letter - Mom
- F f
- F
- Dad
- f
20
5 steps to Punnett Squares
- 5. Calculate the ratio of genotype of the
offspring - of pure dominant of heterozygous of pure
recessive - FF Ff ff
(genotypic ratio) - 1 2 1
21
Example
- What would the offspring look like if the mother
was purely dominant for brown eyes and the father
is heterozygous ? B brown dominant over b
blue - Moms genes ________ Dads genes ________
- Ratio of offspring
22
Incomplete Dominance
- Occurs when NEITHER gene is totally dominant to
the other gene - Results in a NEW trait, which is a BLEND of the
dominant and recessive traits - http//learn.genetics.utah.edu/content/begin/tour/
index.html
23
Incomplete DominanceExamples
- Snap dragon color is incompletely dominant. Red
flowers are dominant to white flowers. Pink
flowers are the result of incomplete dominance - What will the offspring be of a cross between
homozygous red snapdragon and a homozygous white
snapdragon? - What will the results be of a cross between 2
pink snapdragons?
24
Example of Incomplete Dominance
- Blood cell shape
- Normal shape Round (R)
- Recessive shape Sickle (R)
- Person with all round cells RR
- Person with all sickle cells RR
- Person with both types RR
- If a person has RR they have Sickle Cell
Anemia - Genetic disorder that causes serious health
problems - Blood cells cant transport oxygen well
- Blood cells cant move well through the body
25
Example of Incomplete Dominance
- If mom and dad are both heterozygous for blood
cell shape, what are the chances they will
produce a child with sickle cell anemia?
26
Blood Type in Humans
- Humans have 4 different blood types
- A,B,AB,O
- 3 genes control blood typing A,B,O
- Both A and B are DOMINANT to O (Recessive)
- A and B are not dominant to one another they are
incompletely dominant (blend to for AB blood
type) - Most common blood type O
- Rarest blood type AB-
- Universal Donor Type O
- Universal acceptor Type AB
- Rh factor 85 ()/ 15 (-)
27
Blood Type Example
- If mom is homozygous recessive for O type blood
and dad is type AB. What are the possible
genotypes and phenotypes for their offspring?
28
Genetic Disorders
- What causes a genetic disorder?
- Being born with a more or less chromosomes
- Having 47 chromosomes instead of 46
- Sex-linked- genes carried on the sex chromosome
- How can you be born with the wrong chromosome
number? - Chromosomes dont separate correctly when the sex
cells are being made - Chromosomes STICK together instead of separate
- Normal Sex Cell Formation
46
23
23
46
46
23
23
29
- Abnormal Sex Cell Formation
- If the chromosome pair that sticks together are
the sex chromosomes the following will happen
45
23
46
22
47
24
23
XXY
Male
XX
Y
XX
Y
Y
Dies
X
XXY
XY
Male
XY
X
X
Female
30
Genetic Diseases
- Down Syndrome
- Born with an extra chromosome (chromosome 21)
- Slow learner
- Heart problems
- Hemophilia
- Recessive gene on the X chromosome (like
colorblindness) - Blood can not clot (missing Factor VIII)
31
Genetic Diseases
- Dyslexia
- Controlled by a gene on an autosome (non sex
chromosome) - Reverse letter b d, p q
- Reverse numbers 13 31
- Klinefelters Syndrome-
- XXY individual
- Male with abnormal proportions (large breasts,
small testicles)
32
Color blindness- sex linked trait
- Red and Green colors look like shades of gray
- Trait is carried on the X chromosome
- Females (XX) have 2 genes to code for
colorblindness - Males (XY) have only 1 gene to code for
colorblindness - Dominant trait XC can separate red and
green - Recessive trait Xc can NOT separate red
and green - http//www.geocities.com/Heartland/8833/coloreye.h
tml - Males are more likely to be colorblind!
33
Color blindness- sex linked trait
34
Color blindness- sex linked traitExample
- If mom is a carrier for colorblindness and dad is
unaffected.What are the chances of having a
colorblind child?