Sound Localization PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title: Sound Localization
1
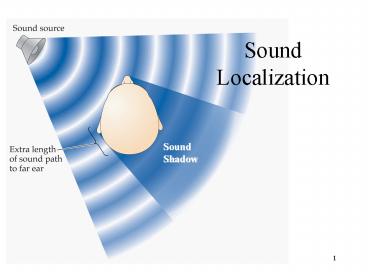
Sound Localization
2
Sound Localization (cont.)
- Binaural Neurons (A1) compare information
differences from the two ears - Interaural Time - Slight delay in the arrival of
a signal to the further ear (0 - 7/10,000 sec.)
3
Sound Localization (cont.)
- Interaural Intensity - Slight differences in
loudness to each ear - the head occludes some
sound - Phase Disparity - The peaks (compressions) and
valleys of the sound waves arrive at different
times for the two ears - good for continuous
sound sources - Barn owls use this to catch
running mice in total darkness
4
Sound Localization (cont.)
5
Cone of Confusion
- Using normal cues, all you can detect is the time
difference between your two ears. This specifies
an azimuth not a position.
6
Cone of Confusion
Solution - tilt your head, like the RCA dog
7
Auditory Scene Analysis
8
Auditory Scene Analysis
- Separation of sounds into distinct streams -
how is it that complex sounds are grouped
appropriately? - Common Time Course or Sequential Integration -
sounds are grouped together according to which
ones vary together over time - eventually
distinct sources of sound will produce distinct
sounds - Sound Location or Simultaneous Integration -
sounds which emanate from the same source
9
Auditory Scene Analysis (cont.)
- Spectral Harmonics - Harmonic frequencies are
multiples of the fundamental frequency - Familiar sounds - groups of sound which have
been perceived as together in the past are more
easily grouped together in the present - Visual (or other perceptual) input can help to
sort out which sounds belong with which source
10
Auditory Scene Analysis (cont.)
- How do listeners know how far a sound is?
- Simplest cue Relative intensity of sound
- Inverse-square law As distance from a source
increases, intensity decreases faster such that
decrease in intensity is distance squared - Spectral composition of sounds Higher
frequencies decrease in energy more than lower
frequencies as sound waves travel from source to
one ear - Relative amounts of direct vs. reverberant energy
11
Auditory Scene Analysis (cont.)
12
Auditory Event Perception
- Quantity
- Length
- Volume
- Energy
- Velocity
- Time Course
13
Attention
- Once target sounds are determined and segmented,
the brain amplifies those and diminishes others -
The Cocktail Party Effect