PN12 Workshop PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 23
Title: PN12 Workshop
1
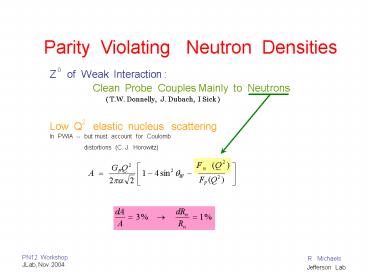
Parity Violating Neutron Densities
0
Z of Weak Interaction
Clean Probe Couples Mainly to Neutrons
( T.W. Donnelly, J. Dubach, I Sick )
2
Low Q elastic nucleus scattering
In PWIA -- but must account for Coulomb
distortions (C. J. Horowitz)
2
- Parity Violating Asymmetry
2
Applications
- Nucleon Structure (strangeness)
- Nuclear Structure (neutron density)
- Standard Model tests ( )
3
Z sees the neutrons
0
4
PREX in Hall A at JLab
Lead Foil Target
5
Measured Asymmetry
Physics Impact of
Correct for Coulomb
Lead Parity
Distortions
2
Weak Density at one Q
Mean Field
Small Corrections for
s
n
Other
G
G
MEC
Atomic Parity Violation
E
E
Models
2
Neutron Density at one Q
Assume Surface Thickness Good to 25 (MFT)
Neutron Stars
R
n
6
Lead Parity
pins down the symmetry energy (1 parameter)
energy cost for unequal protons
neutrons
( R.J. Furnstahl )
7
Pb Parity Neutron Stars
( C.J. Horowitz, J. Piekarweicz )
R calibrates EOS of Neutron Rich Matter
n
Crust Thickness
Explain Obs. Glitches in Pulsar Frequency ?
Combine R with Neutron Star Radius
n
Exotic Core ? (strange matter, quark star)
Some Neutron Stars too Cold
Cooling by neutrino emission (URCA)
Crab Pulsar
0.2 fm URCA probable, else not
( from hubblesite.org )
8
Optimum Kinematics for Lead Parity E
850 MeV,
0.5 ppm. Accuracy in Asy 3
1 month run 1 in R
n
9
High Resolution Spectrometers
Spectrometer Concept Resolve Elastic
Elastic
detector
Inelastic
Quad
target
Dipole
Q Q
10
Septum Magnets (INFN)
- Superconducting magnets
- Commissioned 2003-4
Electrons scattered at 6 deg sent to the HRS at
12.5 deg.
11
Integrating Detection
- Integrate in 30 msec helicity period.
- Deadtime free.
- 18 bit ADC with
- But must separate backgrounds inelastics
( HRS).
- 4
Integrator
Calorimeter (for lead, fits in palm of hand)
ADC
PMT
electrons
12
Lead Target
208
Pb
Liquid Helium Coolant
12
beam
C
Diamond Backing
- High Thermal Conductivity
- Negligible Systematics
Beam, rastered 4 x 4 mm
13
Polarized Electron Source
Laser
GaAs Crystal
Halfwave plate (retractable, reverses
helicity)
Pockel Cell flips helicity
Gun
-
e beam
- Rapid, random helicity reversal
- Electrical isolation from rest of lab
- Feedback on Intensity Asymmetry
14
Beam Asymmetries
Araw Adet - AQ ??E ??i?xi
- natural beam jitter (regression)
- beam modulation (dithering)
Slopes from
15
Helicity Correlated Differences Position,
Angle, Energy
Energy BPM
Scale /- 100 nm
BPM Y2
Position Diffs avg 10 nm Negligible
Systematic Error
BPM Y1
BPM X1
BPM X2
16
Polarimetry
Møller dPe/Pe 3 (foil polarization) ?Compton
2 syst. At present
2 analyses based on either electron or photon
detection
Superlattice Pe86 !
17
Upgrade of Compton Polarimeter (Nanda,
Lhuillier)
To reach 1 accuracy
- Green Laser
- Integrating Method
18
Summary -- Neutron Skin
- R is Fundamental to Nuclear Physics
- HAPPEX program to demonstrate most technical
aspects - Polarimetry Upgrade needed
- Planned 2-day test run in 2005
n
19
- extra slides --
20
Moller Polarimetry with Atomic
Hydrogen Target
( E. Chudakov, V. Luppov)
H atoms
Ultra Cold Traps
- Polarization 100
- Density
- Lifetime 10 min
Solenoid 8T
Trap
beam
Polarimetry
- 1 stat. err. in 30 min at 30 A
- Low background
- High beam currents allowed (100 A)
- Goal 0.5 systematic error
21
Polarized Source
High Pe High Q.E. Low Apower
- Optical pumping of solid-state photocathode
- High Polarization
- Pockels cell allows rapid helicity flip
- Careful configuration to reduce beam asymmetries.
- Slow helicity reversal to further cancel beam
asymmetries
controls effective analyzing power
Tune residual linear pol.
Slow helicity reversal
Intensity Attenuator
22
Beam Modulation to Calibrate Sensitivity to
Beam Systematics
23
P I T A Effect
Polarization Induced Transport Asymmetry
Intensity Asymmetry
Laser at Pol. Source
where
Transport Asymmetry
drifts, but slope is stable.
Feedback on